Abstract
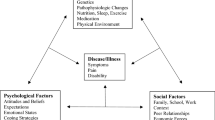
Commentators have repeatedly attacked the traditional view that alcoholism is a disease. Their arguments that alcoholism is a central aspect of life, a deviant life style, or a form of learned behavior are examined in the light of the history and philosophy of medicine as well as current bio-behavioral research. Our conclusion is that alcoholism, as a lawful pattern of observable signs and symptoms that deviate significantly from a norm of health, is a bio-psychosocial disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ader, R. (Ed.). (1981)Psychoneuroimmunology. New York: Academic Press.
Armor, D.J., Polich, J.M., & Stambul, H.B. (1976).Alcoholism and treatment. Report R-1739-NIAAA. Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corporation.
Berg, G., Laberg, J.C., Skutle, A., & Ohman, A. (1981). Instructed versus pharmacological effects of alcohol in alcoholics and social drinkers.Behaviour Research & Therapy, 19, 55–66.
Berman, K.F., Illowsky, B.P., & Weinberger, D.R. (1988). Physiological dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. IV. Further evidence for regional and behavioral specificity.Archives of General Psychiatry, 45, 616–622.
Blakiston’s Gould Medical Dictionary. (1979). (Fourth Edition). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Cala, L.A. (1987). Is CT scan a valid indicator of brain atrophy in alcoholism?Acta Medica Scandinavica, 717, 27–32.
Cohen, H. (1961). The evolution of the concept of disease. In B. Lush (Ed.).Concepts of Medicine. (pp. 159–169). New York: Pergamon Press.
Davies, D.L. (1962). Normal drinking in recovered alcohol addicts.Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 23, 94–104.
Dubos, R. (1968).Man, medicine, and environment. London: Pall Mall Press.
Edwards, G. (1985). A later follow-up of a classic case series: D.L. Davies’s 1962 report and its significance for the present.Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 46, 181–190.
Engel, G.L. (1977). The need for a new medical model: A Challenge for biomedicine.Science, 196, 129–136.
Fingarette, H. (1988).Heavy Drinking. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Foy, D.W., Nunn, L.B., & Rychtarik, F.G. (1984). Broad-spectrum behavioral treatment for chronic alcoholics: Effects of training controlled drinking skills.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 52, 218–230.
Graber, R.A., & Miller, W.R. (1988). Abstinence or controlled drinking goals for problem drinkers: A randomized clinical trial.Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 2, 20–33.
Harper, C., Kril, J., & Daly, J. (1987). Are we drinking our neurones away?British Medical Journal, 294, 534–536.
Heather, N., & Robertson, I. (1983).Controlled Drinking. (Revised Edition). London: Methuen.
Hodgson, R., Rankin, H., & Stockwell, T. (1979). Alcohol dependence and the priming effect.Behaviour Research and Therapy, 17, 379–387.
Jellinek, E.M. (1952). Phases of alcohol addiction.Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alchol, 13, 673–684.
Jellinek, E.M. (1960).The disease concept of alcoholism. New Brunswick, N.J.: Hillhouse Press.
King, L.S. (1954). What is disease?Philosophy of Science, 21, 193–203.
Knight, L.J., Barbaree, H.E., & Boland, F.J. (1986). Alcohol and the balanced-placebo design: The role of experimenter demands in expectancy.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 95, 335–340.
Korytnyk, N.X. & Perkins, D.V. (1983). Effects of alcohol versus expectancy for alcohol on the incidence of graffiti following an experimental task.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 92, 382–385.
Lemere, F. (1956). The nature and significance of brain damage from alcoholism.The American Journal of Psychiatry, 113, 361–362.
Lhermitte, F. (1986). Human autonomy and the frontal lobes. Part II: Patient behavior in complex and social situations: The “environmental dependency syndrome.”Annals of Neurology, 19, 335–343.
Luria, A.R. (1980).Higher cortical functions in man. (Second Edition) New York: Basic Books.
Lyvers, M.F. & Maltzman, I. (1991). Selective effects of alcohol on Wisconsin Card Sorting Test Performance.British Journal of Addiction, 86, 399–407.
Maltzman, I. (1987). Controlled drinking and the treatment of alcoholism.Journal of the American Medical Association.257, 927, 3229.
Margolis, J. (1976). The concept of disease.The Journal of Medicine and Philosophy, 1, 238–255.
Marlatt, G.A. (1979). Alcohol use and problem drinking & cognitive-behavioral analysis. In P.C. Kendall, and S.D. Hollon (Eds.).Cognitive-behavioral interventions: Theory, research, and procedures. (pp. 319–355). New York: Academic Press.
Marlatt, G.A. (1983). The controlled-drinking controversy: A Commentary.American Psychologist, 38, 1097–1110.
Marlett, G.A., Demming, B., & Reid, J.B. (1973). Loss of control drinking in alcoholics: An experimental analogue.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 81, 233–241.
McQueen, D.V., & Siegrist, J. (1982). Social factors in the etiology of chronic disease: An overview.Social Science and Medicine, 16, 353–367.
Miller, W.R., Leckman, A.L., & Tinkcom, M. (1987). Controlled drinking and the treatment of alcoholism.Journal of the American Medical Association, 257, 3228–3229.
Orne, M.T. (1962). On the social psychology of the psychological experiment: With particular reference to demand characteristics and their implications.American Psychologist, 17, 776–783.
Peele, S. (1988). Can alcoholism and other drug addiction problems be treated away or is the current treatment binge doing more harm than good?Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 20, 375–383.
Pendery, M.L., Maltzman, I.M., & West, L.J. (1982). Controlled drinking by alcoholics? New findings and a reevaluation of a major affirmative study.Science, 217, 169–175.
Piazza, N.J. & Wise, S.L. (1988). An order-theoretic analysis of Jellinek’s disease model of alcoholism.The International Journal of the Addictions, 23, 387–397.
Pokorny, A.D., & Kanas, T.E. (1980). Stages in the development of alcoholism. In W.E. Fann, I. Karacan, A.D. Pokorny, and R.L. Williams, (Eds.).Phenomenology and treatment of alcoholism. (pp. 45–68). New York: Spectrum Publications.
Polich, J.M., Armor, D.J., & Braiker, H.B. (1980).The course of alcoholism: Four years after treatment. Report R-2433-NIAAA. Santa Monica, CA.: Rand Corporation.
Rychtarik, R.G., Foy, D.W., Scott, T., Lokey, L., & Prue, D.D. (1987). Five-six-year follow-up of broad-spectrum behavioral treatment for alcoholism: Effects of training controlled drinking skills.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55, 106–108.
Selye, H. (1956).The stress of life. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Smith, J.W. & Frawley, P.J. (1990). Long-term abstinence from alcohol in patients receiving aversion therapy as part of a multimodal inpatient program.Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 7, 77–82.
Sobell, M.B. & Sobell, L.C. (1978).Behavioral treatment of alcohol problems: Individualized therapy and controlled drinking. New York: Plenum Press.
Sobell, M.B. & Sobell, L.C. (1987a). Conceptual issues regarding goals in the treatment of alcohol problems. In M.B. Sobell and L.C. Sobell (Eds.),Moderation as a goal or outcome of treatment for alcohol problems: A Dialogue. (pp. 1–37). New York: The Haworth Press.
Sobell, M.B. & Sobell, L.C. (1987b). Stalking white elephants.British Journal of Addiction, 82, 245–247.
Stockwell, T.R., Hodgson, R.J., Rankin, H.J., & Taylor, C. (1982). Alcohol dependence, beliefs and the priming effect.Behaviour Research and Therapy, 20, 513–522.
Stuss, D.T. & Benson, D.F. (1984). Neuropsychological studies of the frontal lobes.Psychological Bulletin, 95, 3–28.
Taylor, J.R., Helzer, J.E., & Robins, L.N. (1986). Moderate drinking in ex-alcoholics: Recent studies.Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 47, 116–121.
Walker, N.D. (1987). Long term outcome for alcoholic patients treated in a hospital based unit.New Zealand Medical Journal, 100, 554–556.
Wallace, J. (1989). Can Stanton Peele’s opinions be taken seriously? A reply to Peele.Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 21, 259–271.
Wallace, J. (1990). Controlled drinking, treatment effectiveness, and the disease model of addiction: A commentary on the ideological wishes of Stanton Peele.Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 22, 261–284.
Wallace, J., McNeill, D., Gilfillan, D., MacLean, K., & Fanella, F. (1988). I. Six-month treatment outcomes in socially stable alcoholics: Abstinence rates.Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 5, 247–252.
Weinberger, D.R., Berman, K.F., & Zec, R.F. (1986). Physiologic dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia.Archives of General Psychiatry, 43, 114–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maltzman, I. Is alcoholism a disease?. Integr. psych. behav. 26, 200–210 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912511
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912511