Abstract
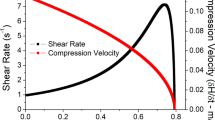
A study on the deformation rate response of an important Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy prepared from rapidly solidified powder is undertaken, through hot extrusion and tensile tests which cover a wide variation of strain rate. The individual effects of ram speed in extrusion and crosshead speed in tensile tests on the flow behavior of the material are analyzed. It is derived that the pressure requirement for extrusion is a combined function of ram speed (or strain rate) and temperature rise. The balance of the two factors gives an increase in extrusion pressure with rising ram speed—a result being different from that found in the extrusion of some other aluminum alloys. The tensile results obtained from the extruded material, using constant and incremental strain rate methods, prove that the flow stress of the alloy under study is more sensitive to strain rate than that of other aluminum alloys. Finally, a direct comparison between the two deformation processes is made in terms of the flow stress dependence of strain rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Akechi, Y. Odani, and N. Kuroishi:Sumitomo Electric Technical Review, 1985, No. 24, pp. 191–198.
J. Zhou and J. Duszczyk,J. of Materials Shaping Technology, 1989, vol. 6, pp. 241–250.
T. Sheppard: in Extrusion—Scientificand Technical Developments, G. Lang, A.F. Castle, M. Bauser and G. Scharf (eds.), Deutshe Gesellschaft für Metallkunde E. V., 1981, pp. 17–43.
T. Sheppard and P.J.M. Chare:Powder Metallurgy, 1972, vol. 15, pp. 17–41.
N.C. Parson and T. Sheppard:Materials Science and Technology, 1988, vol. 4, pp. 816–823.
K. Ashcroft and G.S. Lawson:J. of the Institute of Metals, 1960–61, vol. 89, pp. 369–375.
R.D. Parkinson and T. Sheppard:Powder Metallurgy, 1986, vol. 29, pp. 135–141.
A.F. Castle and T. Sheppard:Metal Technology, 1979, vol. 3, pp. 465–475.
T. Sheppard, H.B. McShane, M.A. Zaidi, and G.H. Tan:J. of Mechanical Working Technology, 1983, vol. 8, pp. 43–70.
Song Yuquan and Lian Shujun:Materials Science and Technology, 1989, vol. 5, pp. 443–449.
A.R.E. Singer and J.W. Coakham:J. of the Institute of Metals, 1960-61, vol. 89, pp. 177–182.
H.L. Yiu and T. Sheppard:Materials Science and Technology, 1985, vol. 1, pp. 209–219.
J. Zhou and J. Duszczyk: inProc. of the European Conf. on Advanced Materials and Processes, Aachen, FRG, Nov. 22–24, 1989, in press.
C.E. Pearson and R.N. Parkins:The Extrusion of Metals, Chapman & Hall, London, 1960, pp. 189–205.
P. Feltham:Metal Treatment, 1956, vol. 23, pp. 440–444.
D. Raybould, inProc. of the Symposium on Dispersion Strenthened Aluminum Alloys, Y-W Kim and W.M. Griffith (eds.), Phoenix, Arizona, Jan. 1988, TMS, pp. 199–215.
J. Zhou and J. Duszczyk:J. of Materials Science, in press.
P.P. Gillis and T.S. Gross: inMetal Handbook, 9th Edition, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1988, vol. 8, pp. 38–46.
D.W. Chung and J.R. Cahoon:Metal Science, 1979, vol. 13, pp. 635–640.
M.D.C. Moles and G.J. Davies:Scripta Metallurgica, 1976, vol. 10, pp. 455–458.
W.A. Backofen, I.R. Turner, and D.H. Avery:Trans. ASM, 1964, vol. 57, pp. 981–990.
G.S. Murty and M.J. Koczak: inProc. of a Symp. on Processing and Properties for Powder Metallurgy Composites, Denver, Colorado, Feb. 1987, P. Kumar, K. Vedula and A. Ritter (eds.), AIME, 1987, pp. 139–153.
A. Aran:Scripta Metallurgica, 1979, vol. 13, pp. 843–846.
T. Altan, S. Oh, and H. Gegel:Metal Forming: Fundamentals and Applications, ASM, Metals Park, Ohio, 1983, pp. 65–66.
T. Chandra and J.J. Jonas:Metallurgical Trans. A, 1970, vol. 1, pp. 2079–2082.
W.A. Wong and J.J. Jonas:Trans. AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 2271–2280.
E.G. Thomsen et al:Mechanics of Plastic Deformation in Metal Processing, The Macmillan Company, New York, 1965, pp. 279–317.
G.W. Rowe:An Introduction to the Principles of Metalworking, Edward Arnold, London, 1965, pp. 163–193.
J.J. Jonas, H.J. McQueen, and W.A. Wang: inDeformation under Hot Working Conditions, Iron and Steel Institute, London, 1968, pp. 49–59.
J. Zhou, J. Duszczyk, and B.M. Korevaar: inProc. of the 3rd Int. Conf. on Technology of Plasticity, Kyoto, Japan, July 2–6, 1990, in press.
T. Sheppard and D. Raybould:J. of the Institute of Metals, 1973, vol. 101, pp. 73–78.
J.J. Jonas:Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp. 300–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Duszczyk, J. & Korevaar, B.M. Deformation rate response of an Al-Si alloy prepared from rapidly solidified powder. J. Materials Shaping Technology 8, 91–100 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833620