Abstract
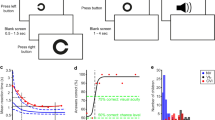
Visual acuity was measured in 140 3–9-year-old children using Landolt’s rins with a gap in one of four orientations. The influence of surrounding additional contours on the detection of orientation of rings of a minimal visible size was studied in the same children, depending on the distance between the rings and the surrounding. The latter consisted of four bands, located symmetrically with reference to the ring. Visual acuity increased with age, reaching the adult level by approximately seven years. A deterioration of the orientation recognition was detected in all children when the surrounding was close to a ring. The distance that caused a perception deterioration decreased with age, reaching the adult level by nine years. The obtained data are discussed from the viewpoint of a possible influence of individual visual areas formed during ontogeny on task performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehlers, H., Clinical Testing of Visual Acuity,A.M.A. Arch. Ophthalmol., 1953, vol. 49, p. 431.
Flom, M.C., Contour Interaction and the Crowding Effect, inProblems of Optometry, Rutstein, R.P., Ed., 1991, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 237.
Flom, M.C., Weymouth, F.W., and Kahneman, D., Visual Resolution and Contour Interaction,J. Opt. Soc. Am., 1963, vol. 53, p. 1026.
Atkinson, J., Review of Human Visual Development: Crowding and Dyslexia, inVision and Visual Dysfunction, Cronly-Dillon, J.R., Ed., 1991, vol. 13; Vision and Visual Dyslexia, Stein, J.F., Ed., p. 44.
Woodrow, H., The Effect of Pattern upon Simultaneous Letter Span,Am. J. Psychol., 1938, vol. 51, p. 83.
Nevskaya, A.A., Leushina, L.I., and Bondarko, V.M., The Formation of Visual-Image Thinking in Infants with Vision Defects in the First Year of Their Life.Fiziol. Chel., 1998, vol, 24, no. 3, p. 20.
Khyuvyarinen, L.,Zrenie u detei: normal’noe i s narusheniyami (Children’s Vision: Normal and Disordered), St. Petersburg: XXI Vek, 1996.
Vaschenko, D.I., and Rozhkova, G.I., Dynamics of Visual Acuity in Schoolchildren,Perception, 1998, vol. 27, suppl., p. 203.
Riggs, L.A., Visual Acuity, inVision and Visual Perception, Graham, C.H.,et al., Eds., New York: Wiley, 1965, p. 321.
Bondarko, V.M. and Danilova, M.V., What Spatial Frequency Do We Use to Detect the Orientation of a Landolt’s C?,Vision Res., 1997, vol. 37, p. 2153.
Bondarko, V.M. and Danilova, M.V., Influence of Surrounding Stimuli on the Detection of the Orientation of Rectangular Gratings at the Threshold of Resolving Capacity of the Human Visual System,Fiziol. Chel., vol. 24, no. 5, p. 65.
Bondarko, V.M. and Danilova, M.V., Crowding Effect with Various Surroundings and Distances between Stimuli,Sens. Sist. (Moscow), 1996, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 132.
Farber, D.A., Semenova, L.K., Alferova, V.V.,et al., Strukturno-funktsional’naya organizatsiya razvivayushchegosya mozga (The Structural-Functional Organization of the Developing Brain), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semenov, L.A., Chernova, N.D. & Bondarko, V.M. Measurement of visual acuity and crowding effect in 3–9-year-old children. Hum Physiol 26, 16–20 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760711
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760711