Abstract
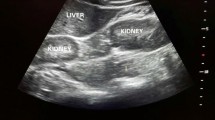
Medullary sponge kidney is a benign asymptomatic developmental anomaly of the kidney mostly seen in adult females. Presentation in childhood is uncommon. Urinary tract infection, nephrolithiasis, hematuria and hypercalciuria are the common complications. We report a eleven-year-old female child who presented with recurrent urinary tract infection and nephrolithiasis and was found to have bilateral medullary sponge kidney.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watkins SL, McDonald RA, Avner ED. Renal dysplasia, hypoplasia and miscellaneous cystic disorders. In Barratt TM, Avner ED, Harmon WE, eds.Pediatr Nephrology. Baltimore; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, 1999; 420–421.
Patriquin HB, O’Regan S. Medullary sponge kidney in childhood.Am J Roentgenol 1985; 145(2): 315–319.
Beetz R, Schofer O, Riedmiller H, Schumacher R, Gutjahr P. Medullary sponge kidney and unilateral Wilm’s tumor in a child with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.Eur J Pediatr 1991; 150(7): 489–492.
Proesmann W, Van Molhem S, Lateur L. A 16-year-old boy with medullary sponge kidneys, osteoporosis, and premature loss of all teeth.Pediatr Nephrology 2000; 14: 259–262.
Osther PJ, Mathiasen H, Hansen AB, Nissen HM. Urinary acidification and urinary excretion of calcium and citrate in women with bilateral medullary sponge kidney.Urol lnt 1994; 52:126–30.
Levine E, Hartman DS, Meilstrup JW, Van Slyke MA, Edgar KA, Barth JC. Current concepts and controversies in imaging of renal cystic diseases.Urol Clin North Am 1997; 24(3): 523–543.
Holmes SA, Eardley I, Corry DA, Nockler I, Whitfield HN. The use of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy for medullary sponge kidney.Br J Urol 1992; 70(4): 352–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Shanbag, P. & Vaidya, M. Medullary sponge kidney. Indian J Pediatr 69, 1091–1092 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724396
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724396