Abstract
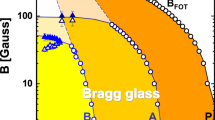
A metastable supercooled homogeneous vortex liquid state exists down to zero fluctuation temperature in systems of mutually repelling objects. The zero temperature liquid state therefore serves as a (pseudo) ‘fixed point’ controlling the properties of vortex liquid below and even around the melting point. Based on this picture, a quantitative theory of vortex melting and glass transition in Type II superconductors in the framework of Ginzburg-Landau approach is presented. The melting line location is determined and magnetization and specific heat jumps are calculated. The point-like disorder shifts the line downwards and joins the order-disorder transition line. On the other hand, the disorder induces irreversible effects via replica symmetry breaking. The irreversibility line can be calculated within the Gaussian variational method. Therefore, the generic phase diagram contains four phases divided by the irreversibility line and melting line: liquid, solid, vortex glass and Bragg glass. We compare various experimental results with the theoretical formula.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
For a review on the vortex phase diagram, see P Gammel, D A Huse and D J Bishop, inSpin glasses and random fields edited by A P Young (World Scientific, 1998) and references therein
D R Nelson,Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 1973 (1988)
F Bouquet, C Marcenat, E Steep, R Calemczuk, W K Kwok, U Welp, G W Crabtree, R A Fisher, N E Phillips and A Schilling,Nature 411, 448 (2001)
T Giamarchi and P Le Doussal,Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3372 (1994);Phys. Rev. B52, 1242 (1995)
D Ertas and D R Nelson,Physica C272, 79 (1996)
Y Nonomura and X Hu,Phys. Rev. Lett. 28, 5140 (2001)
E Zeldov, D Majer, M Konczykowski, V B Geshkenbein, V M Vinokur and H Shtrikman,Nature (tLondon) 375, 373 (1995)
R Liang, D A Bonn and W N Hardy,Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 835 (1996)
A Schilling, R A Fisher, N E Phillips, U Welp, D Dasgupta, W K Kwok and G W Crabtree,Nature (London) 382, 791 (1996)
M Roulin, A Junod and E Walker,Science 273, 1210 (1996)
H Pastoriza, M F Goffman, A Arribêre and F de la Cruz,Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 2951 (1994)
X Liang, D A Bonn and W N Hardy,Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 835 (1996)
B Khaykovich, E Zeldov, D Majer, T W Li, P H Kes and M Konczykowski,Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 2555 (1996)
Y Radzyner, A Shaulov and Y Yeshurun,Phys. Rev. B65, 100513 (R) (2002)
Y Radzyner, A Shaulov, Y Yeshurun, I Felner, K Kishio and J Shimoyama,Phys. Rev. B65, 100503 (R) (2002)
N Avraham, B Khaykovich, Y Myasoedov, M Rappaport, H Shtrikman, D E Feldman, T Tamegai, P H Kes, M Li, M Konczykowski, K van der Beek and E Zeldov,Nature (London) 411, 451 (2001)
N Kobayashi, T Nishizaki, K Shibata, T Sato, M Maki and T Sasaki,Physica C362, 121 (2001)
K Shibata, T Nishizaki, T Sasaki and N Kobayashi,Phys. Rev. B66, 214518 (2002)
D Li and B Rosenstein,Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 167004 (2003)
D Pal, S Ramakrishnan, A K Grover, D Dasgupta and Bimal K Sarma,Phys. Rev. B63, 132505 (2001)
D Pal, S Ramakrishnan and A K Grover,Phys. Rev. B65, 096502 (2002)
K Deligiannis, M Charalambous, J Chaussy, R Liang, D Bonn and W N Hardy,Physica C341, 1329 (2000)
B J Taylor, Shi Li, M B Maple and M P Maley,Phys. Rev. B68, 054523 (2003)
D T Fuchs, E Zeldov, T Tamegai, S Ooi, M Rappaport and H Shtrikman,Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4971 (1998)
E Zeldov, private communication
U Divakar, A J Drew, S L Lee, R Gilardi, J Mesot, F Y Ogrin, D Charalambous, E M Forgan, G I Menon, N Momono, M Oda, C D Dewhurst and C Baines,Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 237004 (2004)
V Dotseko,An introduction to the theory of spin glasses and neural networks (Cambridge University Press, 2001)
M P A Fisher,Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 1415 (1989)
D S Fisher, M P A Fisher and D A Huse,Phys. Rev. B43, 130 (1991)
T Natterman,Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 2454 (1990)
T Natterman and S Scheindl,Adv. Phys. 49, 607 (2000)
P Olsson and S Teitel,Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 1370001 (2001)
T Giamarchi and S Bhattacharya, inHigh magnetic fields: Applications in condensed matter physics and spectroscopy edited by C Berthieret al (Springer-Verlag, 2002) p. 314
H K Bokil and A P Young,Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3021 (1995)
A van Otterlo, R T Scalettar and G T Zimanyi,Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1497 (1998)
C Reichhardt, A van Otterlo and G T Zimanyi,Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 1994 (2000)
S E Korshunov,Phys. Rev. B48, 3969 (1993)
G I Menon,Phys. Rev. B65, 104527 (2002)
E H Brandt,Rep. Prog. Phys. 58, 1465 (1995)
G P Mikitik and E H Brandt,Phys. Rev. B64, 184514 (2001);Phys. Rev. B68, 054509 (2003)
J Kierfeld and V Vinokur,Phys. Rev. B61, R 14928 (2000)
D J Thouless,Phys. Rev. Lett. 34, 946 (1975)
E Brezin, D R Nelson and A Thiaville,Phys. Rev. B31, 7124 (1985)
A T Dorsey, M Huang and M P A Fisher,Phys. Rev. B45, 523 (1992)
H Sompolinsky and A Zippelius,Phys. Rev. B25, 6860 (1982)
Z Tesanovic and I F Herbut,Phys. Rev. B50, 10389 (1994)
G Eilenberger,Phys. Rev. 164, 628 (1967)
K Maki and H Takayama,Prog. Theor. Phys. 46, 1651 (1971)
B Rosenstein,Phys. Rev. B60, 4268 (1999)
H C Kao, B Rosenstein and J C Lee,Phys. Rev. B61, 12352 (2000)
G J Ruggeri and D J Thouless,J. Phys. F6, 2063 (1976)
D Li, B Rosenstein,Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3618 (2001);Phys. Rev. B65, R220504, (2002)
D Li and B Rosenstein,Phys. Rev. B65, 024514 (2002)
Z L Xiao, O Dogru, E Y Andrei, P Shuk and M Greenblatt,Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 227004 (2004)
Y Paltiel, E Zeldov, Y N Myasoedov, H Shtrikman, S Bhattacharya, M J Higgins, Z L Xiao, E Y Andrei, P L Gammel and D J Bishop,Nature (London) 403, 398 (2000)
Y Paltiel, E Zeldov, Y Myasoedov, M L Rappaport, G Jung, S Bhattacharya, M J Higgins, Z L Xiao, E Y Andrei, P L Gammel and D J Bishop,Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3712 (2000)
X S Ling, S R Park, B A McClain, S M Choi, D C Dender and J W Lynn,Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 712 (2001)
Z L Xiao, E Y Andrei and M J Higgins,Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1664 (1999)
Dingping Li and B Rosenstein,Phys. Rev. B70, 144521 (2004)
D J Amit,Field theory, the renormalization group, and critical phenomena (World Scientific, Singapore, 1984)
G A Baker,Quantitative theory of critical phenomena (Academic Press, Boston, 1990)
S Hikami, A Fujita and A I Larkin,Phys. Rev. B44, R10400 (1991)
E Brezin, A Fujita and S Hikami,Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 1949 (1990);65, 2921(E) (1990)
R Sasik and D Stroud,Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2582 (1975)
J Hu and A H MacDonald,Phys. Rev. B56, 2788 (1997)
Y Kato and N Nagaosa,Phys. Rev. B48, 7383 (1993)
J Hu and A H MacDonald,Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 432 (1993)
A E Koshelev,Phys. Rev. B56, 11201 (1997)
I F Herbut and Z Tesanovic,Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 484 (1994)
I Affleck and E Brezin,Nucl. Phys. B257, 451 (1985)
M A Moore, T J Newman, A J Bray and S-K Chin,Phys. Rev. B58, 9677 (1998)
A Lopatin and G Kotliar,Phys. Rev. B59, 3879 (1999)
T Maniv, V Zhuravlev, I Vagner and P Wyder,Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 867 (2001)
V Zhuravlev and T Maniv,Phys. Rev. B69, 024522 (2004)
Z Tesanovic, L Xing, L Bulaevskii, Q Li and M Suenaga,Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 3563 (1992)
Z Tesanovic and A V Andreev,Phys. Rev. B49, 4064 (1994)
G Parisi,J. Phy. A13, 1101 (1980)
Dingping Li and B Rosenstein, cond-mat/0411096
M Mezard and G Parisi,J. Phys. (France) I 1, 809 (1991)
A V Lopatin,Europhys. Lett. 51, 635 (2000)
G I Menon and C Dasgupta,Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1023 (1994)
G I Menon, C Dasgupta and T V Ramakrishnan,Phys. Rev. B60, 7607 (1999)
A Schilling, U Welp, W K Kwok and G W Crabtree,Phys. Rev. B65, 054505 (2002)
M Roulin, A Junod and E Walker,Science 273, 1210 (1996)
M Roulin, A Junod, A Erb and E Walker,J. Low Temp. Phys. 105, 1099 (1996)
B Revaz, A Junod and A Erb,Phys. Rev. B58, 11153 (1998)
T Shibauchi, M Sato, S Ooi and T Tamegai,Phys. Rev. B57, 5622 (1998)
S Ooi, T Shibauchi and T Tamegai,Physica C302, 339 (1998)
T Sasagawa, Y Togawa, J Shimoyama, A Kapitulnik, K Kitazawa and K Kishio,Phys. Rev. B61, 1610 (2000)
B J Taylor, S Li, M B Maple and M P Maley,Phys. Rev. B68, 054523 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Rosenstein, B. & Lin, P. Quantitative theory of thermal fluctuations and disorder in the vortex matter. Pramana - J Phys 66, 99–111 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704940
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704940