Abstract
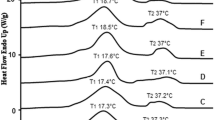
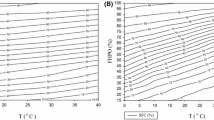
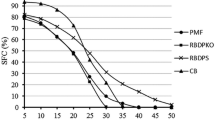
Manufacture of soaps from distilled fatty acids of palm oil (PO) and palm kernel oil (PK) is a well-established technology in Malaysia. Data on quality and characteristics of various blends of PO/PK fatty acid-based (palm-based) soaps made in Malaysia are not available, however. In view of this, the study described in this paper was undertaken. Eleven blends of palm-based bar soaps were made, and their properties were evaluated. There was an increase in the acid value of blended raw materials with increasing amounts of PK fatty acids. The iodine value and titer (°C) of blended raw materials, however, bear an inverse relationship with the amount of PK fatty acids. As expected, the hardness of the soap bars from the various blends increased with increasing PK fatty acid. Total fatty matter ranged from 76–85%, free caustic content was 0.1%, and sodium chloride content was 0.3–0.4%. Characteristics of soap blends made for this study were comparable with those from other countries. Quality of the soap obtained was comparable to those produced commercially.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta, S.,Soap Technology for the 1990s, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, 1990, p. 48.
Technology of Laundry and Toilet Soaps, SBP Chemical Engineering Series No. 44 Small Business Publications, Delhi, pp. 10, 32.
Kifli, H., and S. Krishnan, Palm Oil Products in Soap Making Including Measurement of Properties of the Soap Developed, inProceedings of the 1987 International Oil Palm/Palm Oil Conference-Progress and Prospects, Conference II: Technology, Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia (PORIM), Selangor, 1988, pp. 304–315.
Ainie, K., and K. Hamirin,Palm-Based Soap in Selected Readings on Palm Oil and Its Uses, Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia, Selangor, 1994, pp. 183–196.
Ahmad, I.,Significance of Palm Oil and Palm Stearin as Fatty Raw Materials for Soap, PORIM Occasional Paper No. 13, Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia, Selangor, 1984.
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 4th edn., edited by D. Firestone, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, 1989.
PORIM Test Methods, compiled and edited by W.-L. Siew, Palm Oil Research Institute of Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, 1988.
Kenya Bureau of Standards, KS 03-45: 1977, UDC 668. 1:543.05.
Kuntom, A., H. Kifli, and K.H. Chen, Gas Chromatographic Analysis of Fragrances in Palm-Based White Soaps,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 69:614–620 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kuntom, A., Kifli, H. & Lim, PK. Chemical and physical characteristics of soap made from distilled fatty acids of palm oil and palm kernel oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 73, 105–108 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523455
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523455