Abstract
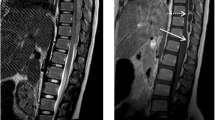
We report the case of a patient with tuberculous L1-L2 spondylo-discitis complicated by a spinal epidural abscess which extended anteriorly to the cord up to the low cervical level. Mild signs and symptoms of spinal cord involvement improved with antituberculous therapy; however, after seven months of therapy, the MRI appearance of the abscess findings was unchanged. An attempt at surgical decompression and drainage of the abscess was unsuccessful because of the presence of dense scar tissue.
Sommario
Riportiamo un caso di spondilodiscite tubercolare L1-L2 complicato da un ascesso epidurale sviluppatosi in sede anteriore al midollo ed esteso in senso craniale fino al livello cervicale inferiore. Il trattamento antitubercolare ha comportato un miglioramento dei lievi segni clinici di sofferenza midollare; tuttavia, dopo sette mesi di terapia, i reperti di risonanza magnetica erano sostanzialmente invariati. Un tentativo di decompressione e drenaggio chirurgico dell'ascesso è risultato infruttuoso a causa della presenza di tessuto fibroso cicatriziale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bharucha N.E., Bharucha E.P.:Regional neurology: F. Neurology in India. In: Neurology in clinical practice. Bradley W.G., Daroff R.B., Fenichel G.M., Marsden C.D., eds. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 1925–1941, 1991.
Culotta E., Koshland D.E.:Tackling tuberculosis. Science 262: 196, 1993.
Govender S.:Extradural extraosseous spinal tuberculosis. Neuro-Orthopedics 12: 35–41, 1991.
Griffiths D.Ll.:Tuberculosis of the spine: a review. Adv. Tuberc. Res. 20: 92–110, 1980.
Hamada J., Sato K., Seto H., Ushio Y.:Epidural tuberculoma of the spine: case report. Neurosurgery 28: 161–163, 1991.
Hoffman E.B., Crosier J.H., Cremin B.J.:Imaging in children with spinal tuberculosis. A comparison of radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 75-B: 233–239, 1993.
Latronico N., Tansini A., Gualandi G.F. et al.:Successful nonoperative treatment of tuberculous spinal epidural abscess with cord compression: the role of magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Neurol. 33: 177–180, 1993.
Leong J.C.Y.:Tuberculosis of the spine. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 75-B: 173–175, 1993.
Massey E.W.:Disorders of bones, joints, ligaments, cartilage, and meninges. In: Neurology in clinical practice. Bradley W.G., Daroff R.B., Fenichel G.M., Marsden C.D., eds. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 1625–1660, 1991.
Sharif H.S., Aideyan O.A., Clark D.C. et al.:Brucellar and tuberculous spondylitis: comparative imaging features. Radiology 171: 419–425, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pareyson, D., Savoiardo, M., D'Incerti, L. et al. Spinal epidural abscess complicating tuberculous spondylitis. Ital J Neuro Sci 16, 321–325 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02249108
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02249108