Summary
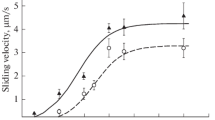
Brevin is a protein which regulates the actin gel-sol transformation: it severs F-actin filaments into shorter ones. This action is Ca-dependent and is prevented by tropomyosin. We tested the effect of brevin on isometric contractions of skinned smooth muscle (taenia coli) and noted a dramatic loss of tension that possibly reflects some F-actin fragmentation. This effect is tentatively attributed to a partial loss of tropomyosin in the skinning procedure. We also studied the effect of brevin on unloaded shortenings of skinned preparations: thin bundles and enzymatically dissociated cells. We observed a marked increase of the velocity of shortening in the presence of brevin. This effect cannot be attributed to an increased ATPase activity as the latter is slightly reduced in the presence of brevin. We interpret this result as reflecting a decrease in internal resistance to movement, possibly by solation of an actin-filamin domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond, M., &Somlyo, A. V. (1982) Dense bodies and actin polarity in vertebrate smooth muscle.J. Cell Biol. 95, 403–13.
Chaponnier, C., Yin, H. L. &Stossel, T. P. (1987) Reversibility of gelsolin/actin interaction in macrophages.J. Exp. Med. 165, 97–106.
Cooper, J.A., Bryan, J., Schwab III, B., Frieden, C., Loftus, D. J. &Elson, E. L. (1987). Microinjection of Gelsolin into living cells.J. Cell Biol. 104, 491–501.
Cooper, J. A., Loftus, D. J., Frieden, C., Bryan, J. &Elson, E. L. (1988). Localization and mobility of gelsolin in cells.J. Cell Biol. 106, 1229–40.
Endo, M., Kitazawa, T., Yagi, S., Iino, M. &Kakuta, Y. (1977) Some properties of chemically skinned smooth muscle fibers. InExcitation-Contraction Coupling in Smooth Muscle (edited by Casteels, R., Godfraind, T. & Rüegg, J. C.) pp. 199–209. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Fattoum, A., Hartwig, J. H. &Stossel, T. P. (1983) Isolation and some structural and functional properties of macrophage tropomyosin.Biochem. 22, 1187–93.
Filo, R. S., Bohr, D. F. & rRüegg, J. C. (1965) Glycerinated skeletal and smooth muscle: calcium and magnesium dependence.Science 147, 1581–3.
Gaertner, A., Ruhnau, K., Schröer, E., Selve, N., Wanger, M. &Wegner, A. (1989) Probing nucleation, cutting and capping of actin filaments.J. Muse. Res. Cell Mot. 10, 1–9.
Gailly, P. (1989) The effect of brevin on unloaded shortening of isolated smooth muscle cell.Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. 98, 22.
Gailly, P., Lejeune, T., Capony, J. P. &Gillis, J. M. (1989) Action of brevin on the contraction of skinned fibres from smooth and striated muscles.Arch. int. Physiol. Biochim. 97, P. 58.
Gordon, A. R. (1978) Contraction of detergent-treated smooth muscle.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 75, 3527–30.
Güth, K. &Junge, J. (1982) Low Ca2+ impedes cross-bridge detachment in chemically skinned Taenia coli.Nature. 300, 775–6.
Higuchi, H. &Funatsu, T. (1989) Structure and function of connectin (titin) filaments revealed by selective removal with gelsolin of thin filaments in skeletal muscle.Proc. Internat. Union of Physiol. Sciences,XVII, P. 1449.
Hinssen, H., Small, J. V. &Sobieszek, A. (1984) A Ca2+-dependent actin modulator from vertebrate smooth muscle.FEBS Letters 166, 90–5.
Kilhoffer, M-C., Mely, Y. &Gerard, D. (1985) The effect of plasma gelsolin on actin filaments. Ca2+-dependency of the capping and the severing activities.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 131, 1132–8.
Koffer, A. &Sleep, J. (1987) Activation of myosin ATPase by actin isolated from cultured BHK cells and the effect of gelsolin.J. Musc. Res. Cell Mot. 8, 541–7.
Kossmann, T., Fürst, D. &Small, J. V. (1987) Structural and biochemical analysis of skinned smooth muscle preparations.J. Muse. Res. Cell Mot. 8, 135–44.
Kwiatkowski, D. J., Stossel, T. P., Orkin, S. H., Mole, J. E., Colten, H. R. &Yin, H. L. (1986) Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain.Nature.323, 455–8.
Kwiatkowski, D. J., Mehl, R. &Yin, H. L. (1988) Genomic organization and biosynthesis of secreted and cytoplasmic forms of gelsolin.J. Cell Biol. 106, 375–84.
Lind, S. E., Smith, D. B., Janmey, P. A. &Stossel, T. P. (1986) Role of plasma gelsolin and vitamin D-binding protein in clearing actin from the circulation.J. Clin. Invest. 78, 736–42.
Mooseker, M. S., Graves, T. A., Wharton, K. A., Falco, N. &Howe, C. L. (1980) Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells.J. Cell Biol. 87, 809–22.
Murakami, U. &Uchida, K. (1985) Contents of myofibrillar proteins in cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscles.J. Biochem. 98, 187–97.
Nodes, B. R., Shackelford, J. E. &Lebherz, H. G. (1987) Synthesis and secretion of serum gelsolin by smooth muscle tissue.J. Biol. Chem. 262, 5422–7.
Pollard, T. D. &Cooper, J. A. (1986) Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55, 987–1035.
Porte, F. &Harricane, M-C. (1986) Interactions of plasma gelsolin with actin. Isolation and characterization of binary and ternary plasma-gelsolin-actin complexes.Eur. J. Biochem. 154, 87–93.
Potter, J. D. (1974) The content of troponin, tropomyosin, actin, and myosin in rabbit skeletal muscle myofibrils.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 162, 436–41.
Rome, E. (1972) Structural studies by X-ray diffraction of striated muscles permeated with certain ions and proteins.Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology,37, 331–9.
Small, J. V. (1974) Contractile units in vertebrate smooth muscle cells.Nature. 249, 324–7.
Small, J. V. (1977) Studies on isolated smooth muscle cells: the contractile apparatus.J. Cell Sci. 24, 327–49.
Small, J. V., Fürst, D. O. &De Mey, J. (1986) Localization of filamin in smooth muscle.J. Cell Biol. 102, 210–20.
Smith, D. B., Janmey, P. A. &Lind, S. E. (1988) Circulating actin-gelsolin complexes following oleic acid-induced lung injury.Am. J. Path. 130, 261–7.
Soua, Z., Porte, F., Harricane, M-C., Feinberg, J. &Capony, J-P. (1985) Bovine serum brevin. Purification by hydrophobic chromatography and properties.Eur. J. Biochem. 153, 275–87.
Sparrow, M. P., Mrwa, U., Hofmann, F. &Rüegg, J. C. (1981) Calmodulin is essential for smooth muscle contraction.FEBS Letters. 125, 141–5.
Stendahl, O. I. &Stossel, T. P. (1980) Actin-binding protein amplifies actomyosin contraction, and gelsolin confers calcium control on the direction of contraction.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 92, 675–81.
Strzelecka-Golaszewska, H., Hinssen, H. &Sobieszek, A. (1984) Influence of an actin-modulating protein from smooth muscle on actin-myosin interaction.FEBS Letters. 177, 209–16.
Sugino, H. &Matsumura, F. (1983) Fragmin induces tension reduction of actomyosin threads in the presence of micromolar levels of Ca2+.J. Cell Biol. 96, 199–203.
Weeds, A. G., Gooch, J., Pope, B. &Harris, H. E. (1986) Preparation and characterization of pig plasma and platelet gelsolins.Eur. J. Biochem. 161, 69–76.
Yin, H. L. &Stossel, T. P. (1979) Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein.Nature. 281, 583–6.
Yin, H. L., Zaner, K. S. &Stossel, T. P. (1980) Ca2+ control of actin gelation. Interaction of gelsolin with actin filaments and regulation of actin gelation.J. Biol. Chem. 255, 9494–9500.
Yin, H. L., Albrecht, J. H. &Fattoum, A. (1981) Identification of gelsolin, a Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein of actin gel-sol transformation, and its intracellular distribution in a variety of cells and tissues.J. Cell Biol. 91, 901–6.
Yin, H. L., Kwiatkowski, D. J., Mole, J. E. &Cole, F. S. (1984) Structure and biosynthesis of cytoplasmic and secreted variants of gelsolin.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 5271–6.
Zeece, M. G., Robson, R. M. &Bechtel, P. J. (1979) Interaction of α-actinin, filamin and tropomyosin with F-actin.Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 581, 365–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gailly, P., Lejeune, T., Capony, J.P. et al. The action of brevin, an F-actin severing protein, on the mechanical properties and ATPase activity of skinned smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 11, 293–301 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01766667
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01766667