Abstract
To analyze the inhibitory effect of thyroxine (T4) on thyroid growth, freshly obtained biopsies of human nontoxic multinodular goiter tissue from 9 patients were transplanted to nude mice. After the implantation period, thyroid growth was stimulated by either hemithyroidectomy (HT) or by administration of the goitrogen propylthiouracil (PTU), with or without simultaneous administration of T4. During the latter period,3H-thymidine was continuously administered by osmotic minipumps to label replicating cells. After processing of the tissue for autoradiography, the fraction of labeled cells (LI) was calculated.
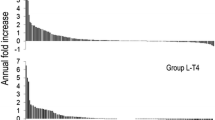
Following HT, the fraction of labeled cells in nontoxic multinodular goiter tissue was 4.8%. T4 significantly reduced the LI to 1.0%. The goitrogen induced transplant growth, the LI varying between 28% and 61% in the different specimens. Administration of T4 resulted in lower LI in all transplants: in 5 specimens the LI was similar to control transplants. In transplants from 3 goiter specimens, however, significantly higher LI were found.
The present results show that administration of T4 significantly inhibits growth of human thyroid tissue. The effect seems, however, to vary in different specimens of nontoxic goiter, indicating a varying degree of autonomous replicating activity.
Résumé
Pour analyser l'effet inhibiteur de la thyroxine (T4) sur la croissance thyroidienne des fragments de goitre multinodulaire atoxique prélevés par biopsie ont été transplantés chez des souris nues. Après la période de transplantation la croissance thyroidienne fut stimulée soit par hémi-thyroidectomie (HT) soit par l'administration de propylthiouracile goitrigène (PTU) associée ou non à l'administration simultanée de T4. Pendant la dernière période de la3H-Thymidine fut administrée en continu par des mini-pompes pour marquer les cellules reproduites. Après avoir soumis le tissu à l'auto-radiographie la fraction de cellules marquées fut calculée.
Après hémithyroidectomie cette fraction fut de 4.8%. La thyroxine réduisit ce taux à 1%. L'agent goitrigène provoqua une croissance du transplant, le taux des cellules marquées variant de 28% à 61% en fonction des différents specimens. L'administration de thyroxine entraÎna une diminution des cellules marquées au niveau de tous les greffons. Dans 5 cas le taux de ces cellules fut identique à celui des cellules des transplants. Dans 3 cas de transplants un taux significativement plus élevé de cellules marquées fut constaté.
Ces résultats montrent que l'administration de T4 inhibe la croissance du tissu thyroidien. Cependant l'effet de la thyroxine varie en fonction des différents spécimens de goitre atoxique, ce qui indique un degré variable de l'activité autonome de la reproduction cellulaire.
Resumen
Con el propósito de analizar el efecto inhibitorio de la tiroxina (T4) sobre el crecimiento tiroideo, se trasplantaron biopsias frescas de tejido tiroideo de 9 pacientes con bocio multinodular no tóxico en ratones atímicos. Transcurrido el período de implantación se estimuló el crecimiento del trasplante por medio de la hemitiroidectomía (HT) o de la administración del agente goitrogénico propiltiouracilo (PTU) con o sin la administración simultánea de T4. En esta ultima fase del estudio se administró3H-timidina en forma continua mediante minibombas osmóticas para marcar las células en proceso de replicación. Después de procesar el tejido para auradiografía se procedió a calcular la fracción de células marcadas (LI).
Después de HT la fracción de células marcadas en el tejido multinodular no tóxico fue 4.8%. La T4 redujo en forma significativa la LI a 1.0%. En el grupo de crecimiento del trasplante inducido por el agente goitrogénico, la LI osciló entre 28% y 61% en los diversos especímenes. La administración de T4 resultó en una menor LI en todos los trasplantes: en 5 especimenes la LI fue similar a la de los trasplantes control. Sin embargo en trasplantes de 3 especímenes de bocio se hallaron valores de LI significativamente mayores.
Nuestros resultados muestran que la administración de T4 inhibe en forma significativa el crecimiento del tejido tiroideo humano. Sin embargo, el efecto parece ser variable en los diferentes especimenes de bocio no tóxico, lo cual es indicativo de grados variables de autonomía en la actividad de la replicación celular.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astwood, E.B., Cassidy, C.E., Auerbach, G.D.: Treatment of goitre and thyroid nodules with thyroid. J.A.M.A.5:459, 1960
Badillo, J., Shimaoka, K., Lessman, E.M., Marchetta, F.C., Sokal, J.E.: Treatment of nontoxic goitre with sodium liothyronine. J.A.M.A.1:151, 1963
Hanen MØholm, J., Kampmann, J., Madsen, S.: L-thyroxine treatment of diffuse non-toxic goitre evaluated by ultrasonic determination of thyroid volume. Clin. Endocrinol.10:1, 1979
Perrild, H., Hansen, J.M., Hegedus, L.: Triiodothyronine and thyroxine treatment of diffuse non-toxic goitre evaluated by ultrasonic scanning. Acta Endocrinol.6:391, 1982
Linder, M.M., Voight, H.G.: Die Wirkung einer Rezidivprophylaxe nach Strumaresektion. Med. Klin.70:847, 1975
Bergfeit, G., Risholm, L.: Postoperative thyroid hormone therapy in nontoxic goitre. Acta Chir. Scand.126:531, 1963
Geerdsen, J.P., Hee, P.: Nontoxic goitre. Surgical complications and long-term prognosis. Acta Chir. Scand.148:221, 1982
Smeds, S., Wollman, S.H.:3H-thymidine labelling of endothelial cells in thyroid arteries, veins and lymphaties during thyroid stimulation. Lab. Invest.48:285, 1983
Smeds, S., Wollman, S.H.: Epithelial, endothelial and capsule cell multiplication during development of thyroid hyperplasia. Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris)43:14A, 1982
Smeds, S., Anderberg, A., Boeryd, B., Ericsson, L.E., Gillquist, J., Persliden, J.: The nude mouse. A possible experimental model for investigation of human thyroid tissue. J. Endocrinol. Invest.4:11, 1981
Smeds, S., Jörtsö, E., Anderberg, B., Boeryd, B., Ericsson, L.E., Mölne, J., Persliden, J., Tegler, L.: Ultrastructural morphology and evidence of iodine uptake and protein synthesis in normal human thyroid transplants in nude mice. J. Endocrinol. Invest.7:569, 1984
Clark, O.H., Lambert, W.R., Cavalieri, R.R., Rapoport, B., Hammond, M.E., Ingbar, S.H.: Compensatory thyroid hypertrophy after hemithyroidectomy in rats. Endocrinology99:988, 1976
Sharard, A., Purves, H.D., Cague, W.S.: Effect of pretreatment of mice with varying doses of thyroxine in the assay for LATS and TSH. Proc. Univ. of Otago Med. Schl.48:77, 1970
Westermark, K., Karlsson, F.A., Westermark, B.: Thyrotropin modulates EGF receptor function in porcine thyroid follicle cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.40:17, 1985
Westermark, K., Karlsson, F.A., Westermark, B.: Epidermal growth factor modulates thyroid growth and function in culture. Endocrinology112:1680, 1983
Westermark, K., Westermark, B., Karlsson, F.A., Ericsson, L.E.: Location of EGF receptors on porcine thyroid follicle cells and receptor regulation by TSH. Endocrinology118:1040, 1986
Peter, H.J., Gerber, H., Studer, H., Smeds, S.: Pathogenesis of heterogeneity in human multinodular goitre. A study on growth and function of thyroid tissue transplanted onto nude mice. J. Clin. Invest.76:1992, 1985
Geerdsen, J.P., Frölund, L.: Recurrence of nontoxic goitre with and without postoperative thyroxine medication. Clin. Endocrinol.21:529, 1984
Westermark, K., Persson, P.A., Johansson, H., Karlsson, F.A.: Nodular goiter: Effects of surgery and thyroxine medication. World J. Surg.10:481, 1986
Bürgi, U., Gebel, F., Gerber, H.: Die diagnostische Bedeutung der Thyreoglobulinbestimmung im Blut. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr.114:365, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grant no. 4482 of the Swedish Medical Research Council and grant no. 3.987-0.84 of the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeds, S., Peter, H.J., Gerber, H. et al. Effects of thyroxine on cell proliferation in human multinodular goiter: A study on growth of thyroid tissue transplanted to nude mice. World J. Surg. 12, 241–244 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01658065
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01658065