Abstract
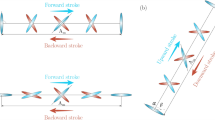
The lift response of houseflies Musca domestica in fixed flight to periodic gratings movins in 12 different orientations has been measured. Two projectors were arranged symmetrically to the flies stimulating successively 18 circular patches of 50° (25°) diameter (9 for each eye) in their visual field. The shapes of the lift responses measured as a function of the orientation of the moving grating varied when different patches in the visual field were stimulated. A qualitative comparison of these response curves leads to the conclusion that the orientation of the movement detecting substrate acting on the flight lift response varies as a function of the stimulated area in the visual field. A straightforward correlation between the geometry of the ommatidial pattern and the orientation of the movement detecting substrate valid for all stimulated areas of the compound eyes does not seem very likely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, L.G., Keehn, D.G.: Neural correlates of the optomotor response in the fly. Kybernetik 3, 288–295 (1967)
Braitenberg, V.: Priodic structure and structural gradients in the visual ganglia of the fly. In: Information processing in the visual system of Arthropods. Wehner, R. (ed.) pp. 3–15. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer (1972)
Buchner, E.: Elementary movement detectors in an insect visual system. Biol. Cybernetics 24, 85–101 (1976)
Buchner, E., Götz, K.G., Straub, C.: Elementary detectors for vertical movement detection in Drosophila (1978, in preparation)
Dvorak, D.R., Bishop, L.G., Eckert, H.E.: On the identification of movement detectors in the fly optic lobe. J. comp. Physiol. 100, 5–23 (1975)
Eckert, H.: Optomotorische Untersuchungen am visuellen System der Stubenfliege Musca domestica L. Kybernetik 14, 1–23 (1973)
Fermi, G., Reichardt, W.: Optomotorische Reaktionen der Fliege Musca domestica. Kybernetik 2, 15–28 (1963)
Götz, K.G.: Optomotorische Untersuchungen des visuellen Systems einiger Augenmutanten der Fruchtfliege Drosophila. Kybernetik 2, 77–92 (1964)
Götz, K.G.: Die optischen Übertragungseigenschaften der Komplexaugen von Drosophila. Kybernetik 2, 215–221 (1965)
Götz, K.G.: Flight control in Drosophila by visual perception of motion. Kybernetik 4, 199–208 (1968)
Götz, K.G.: Movement discrimination in insects. In: Processins of optical data by organisms and by machines. Rendiconti S.J.F. XLIII, Reichardt, W., ed., pp. 494–509. London-New York: Academic Press 1969
Götz, K.G.: The optomotor equilibrium of the Drosophila navigation system. J. comp. Physiol. 99, 187–210 (1975)
Hassenstein, B., Reichardt, W.: Funktionsanalyse der Bewegungsrezeption eines Käfers. Naturwissenschaften 21, 507–508 (1951)
Hassenstein, B., Reichardt, W.: Functional structure of a mechanism of perception of optical movement. In: Proceedings of the First International Congress on Cybernetics, pp. 797–801. Namur, 1956
Hausen, K.: Functional characterization and anatomical identification of motion sensitive neurons in the lobula plate of the blowfly Calliphora erythrocephala. Z. Naturforsch. 31c, 629–633 (1976a)
Hausen, K.: Struktur, Funktion und Konnektivität bewegungsempfindlicher Interneurone im dritten optischen Neuropil der Schmeißfliege Calliphora erythrocephala. Dissertation Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen (1976b)
Hausen, K.: Signal processins in the insect eye. In: Function and formation of neural systems, Stent, G.S., ed., pp. 81–110. Berlin: Dahlem Konferenzen (1977)
Heisenberg, M., Wonneberger, R., Wolf, R.: Optomotor blind H A Drosophila mutant of the lobula giant neurons. J. comp. Physiol. 124, 287–296 (1978)
Hengstenberg, R.: The effect of pattern movement on the impulse activity of the cervical connective of Drosophila melanogaster. Z. Naturforsch. 28c, 593–597 (1973)
Hengstenberg, R.: Spike responses of “non-spiking” visual interneurones. Nature 270, 338–340 (1973)
Kirschfeld, K.: The visual system of Musca: studies on optics, structure and function. In: Information processing in the visual system of Arthropods. Wehner, R. (ed.), pp. 61–74. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer (1972)
McCann, G.D., Arnett, D.W.: Spectral and polarization sensitivity of the dipteran visual system. J. Gen. Physiol. 59, 534–558 (1972)
McCann, G.D., Dill, J.C.: Fundamental properties of intensity form and motion perception in the visual nervous systems of Calliphora and Musca. J. gen. Physiol. 53, 385–413 (1969)
McCann, G.D., Foster, S.F.: Binocular interactions of motion detection fibers in the optic lobes of flies. Kybernetik 8, 193–203 (1971)
Mimura, K.: Integration and analysis of movement information by the visual system of the fly. Nature 266, 964–966 (1970)
Pierantoni, R.: A look into the cock-pit of the fly. The architecture of the lobular plate. Cell Tiss. Res. 171, 101–122 (1976)
Poggio, T., Reichardt, W.: Considerations on models of movement detection. Kybernetik 13, 223–227 (1973a)
Poggio, T., Reichardt, R.: A theory of the pattern induced flight orientation of the fly Musca domestica. Kybernetik 12, 185–203 (1973b)
Rowell, C.H.F.: The Orthopteran descending movement detector [DMD] neuron: a characterisation and review. Z. vgl. Physiol. 73, 167–194 (1971)
Strausfeld, N.J.: Atlas of an insect brain. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Wehrhahn, C.: Flight torque and lift responses of the housefly (Musca domestica) to a single stripe moving in different parts of the visual field. Biol. Cybernetics 29, 237–247 (1978)
Wehrhahn, C., Reichardt, W.: Visually induced height orientation of the fly Musca domestica. Biol. Cybernetics 20, 37–50 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wehrhahn, C. The angular orientation of the movement detectors acting on the flight lift response in flies. Biol. Cybernetics 31, 169–173 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337003
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337003