Abstract
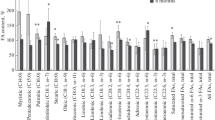
The myocardial uptake of fatty acids labeled with radioactive iodine and injected i.v. can only be evaluated with SPECT if their oxidation kinetics is slow enough. For this reason, we evaluated different iodomethylated fatty acids in mice and dogs to determine which of them shows the highest myocardial uptake and the slowest oxidation. The most suitable was found to be 16-iodo-3-methyl hexadecanoic acid (mono β) since its myocardial fixation was the same as that of the reference, i.e. 16-iodo-9-hexadecenoic acid (IHA), whereas it was degraded more slowly. Thirty min after injection of mono β into dogs, the decrease in myocardial activity with respect to the maximum was two fold less than after IHA injection. The myocardial uptake of the two dimethylated fatty acids studied, i.e. 16-iodo-2,2-methyl hexadecanoic acid and 16-iodo-3,3-methyl hexadecanoic acid, was less than that of IHA in mice and dogs. In the latter, the myocardial uptake was so small that we were unable to study the time course of its activity. Consequently, these dimethylated fatty acids are not suitable for the study of the myocardial uptake of fatty acids in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avigan J, Steinberg D, Gutman A, Mize CE, Milne JWA (1966) alpha-decarboxylation, an important pathway for degradation of phytanic acid in animals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 24:838–844
Bergström S, Borgström B, Tryding N, Westö G (1954) Intestinal absorption and metabolism of 2:2-dimethylstearic acid in the rat. Biochem J 58:604–608
Comet M, Wolf JE, Pilichowski P, Dubois F, Busquet G, Mathieu JP, Pernin C, Riché F, Vidal M (1983) Scintigraphie myocardique après injection. I.V. d'acide 123 I hexadécène-9-oïque. J Biophys Med Nucl 7:139–145
Comet M (1987) Experimental studies on myocardial metabolism of iodinated fatty acids: a proposal for a new curve analysis technique. In: Van der Wall E.E. (ed) Non-invasive imaging of cardiac metabolism. Nijhoff Dardrecht, pp 109–127
Cuchet P, Demaison L, Bontemps L, Keriel C, Mathieu JP, Pernin C, Marti-Batlle D, Riche F, Vidal M, Comet M (1985) Do iodinated fatty acids undergo a non specific deiodination in the myocardium? Eur J Nucl Med 10:505–511
Demaison L, Dubois F, Apparu M, Mathieu JP, Vidal M, Comet M, Cuchet P (1988) Myocardial metabolism of radioiodinated methyl-branched fatty acids. J Nucl Med 29:1230–1236
Den H (1965) The biological oxidation of 2,2 dimethyloctanoic acid. Biochem Biophys Acta 98:462–469
Elmaleh DR, Livni E, Levy S, Varnum D, Strauss HW, Brownell GL (1983) Comparison of 11C and 14C labeled fatty acids and their β-methyl analogs. Int J Nucl Med Biol 10:181–187
Fagret D, Bontemps L, Apparu M, Keriel C, Mathieu JP, Pernin C, Vidal M, Comet M, Cuchet P (1985) Kinetics of iodomethylated hexadecanoic acid metabolism in rat myocardium: influence of the number and the position of methyl radicals. Int J Nucl Med Biol 12:363–367
Goodman MM, Ambrose KR, Neff KH, Knapp FF (1986) Synthesis and biological evaluation of (E)-19-iodo-3,3-dimethyl-18-nonadecenoic acid, a new dimethyl-branched long-chain fatty acid to evaluate regional myocardial fatty acid uptake. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 23:1252–1254
Knapp FF, Ambrose KR, Goodman MM (1986) New radioiodinated methyl-branched fatty acids for cardiac studies. Eur J Nucl Med 12:539–544
Livni E, Elmaleh DR, Levy S Brownell GL, Strauss WH (1982) β-methyl [1–11C] heptadecanoic acid: A new myocardial metabolic tracer for positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med 23:169–175
Otto CA, Brown LE, Scott AM (1984) Radioiodinated branchedchain fatty acids: substrates for β oxidation? Concise communication. J Nucl Med 25:75–80
Poe ND, Robinson GD, Zielinski FW, Cabeen WR, Smith JW, Gomez AS (1977) Myocardial imaging with 123I hexadecenoic acid. Radiology 124:419–424
Reske SN, Biersack HJ, Lackner K, Machulla HJ, Knopp R, Hahn N, Winkler C (1982) Assessment of regional myocardial uptake and metabolism of ω-(p-123I-phenyl) pentadecanoic acid with serial single-photon emission tomography. Nucl Med 21:249–253
Schmitz B, Reske SN, Machulla HJ, Egge H, Winkler C (1984) Cardiac metabolism of omega-(p-iodo-phenyl)-pentadecanoic acid: a gas-liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis. J Lipid Res 25:1102–1108
Spector AA, Steinberg D, Tanaka A (1965) Uptake of free fatty acids by Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem 240:1032–1041
Stokke O, Try K, Eldjarn L (1967) α oxidation as an alternative pathway for the degradation of branched-chain fatty acids in man, and its failure in patients with Refsum's disease. Biochem Biophys Acta 144:271–284
Tryding N, Westö G (1956) Synthesis and metabolism of 2,2-dimethylnonadecanoic acid. Acta Chem Scand 10:1234–1242
Tryding N, Westö G (1957) Metabolism of 2-methylstearic acid in the rat. Acta Chem Scand 11:427–438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagret, D., Wolf, JE., Pilichowski, P. et al. Iodomethylated fatty acid metabolism in mice and dogs. Eur J Nucl Med 14, 624–627 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251787
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251787