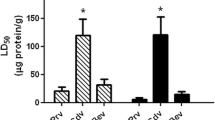
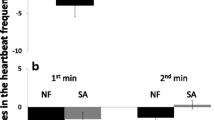
Abstract
Mexico is a rich country in biological diversity; among them, the mygalomorph (also called the orthognatha) spider species of the genus Brachypelma contain in their poisonous glands a great variety of biomolecules that can have benefits in agriculture and medicine. Species of this genus have been studied at the Institute of Biotechnology (IBt-UNAM) and the Biotechnology Research Center (CeiB-UAEM) in Cuernavaca, Morelos, in order to detect venom components with biotechnological applications. This chapter addresses the advances of research on the venom components from species of the genus Brachypelma – B. smithi, B. albiceps, B. verdezi and B. vagans – which were chromatographically separated and biochemically analyzed, searching for antimicrobial, insecticidal, analgesic, and enzymatic activities. Although Brachypelma venoms contain similar types of molecules, their minor differences could be important for a gain in stability and function. The primary structures of the most relevant molecules found in those four species of Brachypelma are described and reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardisson-Araujo DM, Morgado Fda S, Schwartz EF, Corzo G, Ribeiro BM. A new theraphosid spider toxin causes early insect cell death by necrosis when expressed in vitro during recombinant baculovirus infection. PLoS One. 2013;8:e84404.
Cevallos MA, Navarro-Duque C, Varela-Julia M, Alagon AC. Molecular mass determination and assay of venom hyaluronidases by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Toxicon. 1992;30:925–30.
Chan TK, Geren CR, Howell DE, Odell GV. Adenosine triphosphate in tarantula spider venoms and its synergistic effect with the venom toxin. Toxicon. 1975;13:61–6.
Chen JQ, Zhang YQ, Dai J, Luo ZM, Liang SP. Antinociceptive effects of intrathecally administered huwentoxin-I, a selective N-type calcium channel blocker, in the formalin test in conscious rats. Toxicon. 2005;45:15–20.
Clement H. Purificación y caracterización de hialuronidasa del veneno de Brachypelma vagans, una tarántula mexicana, y comparación con otras posibles actividades enzimáticas del veneno de algunas Scolopendra sp. Centro de Investigaciones en Biotecnología. Cuernavaca, Morelos: Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos; 2003
Clement H, Olvera A, Rodriguez M, Zamudio F, Palomares LA, Possani LD, Odell GV, Alagon A, Sanchez-Lopez R. Identification, cDNA cloning and heterologous expression of a hyaluronidase from the tarantula Brachypelma vagans venom. Toxicon. 2012;60:1223–7.
Corzo G, Villegas E, Gomez-Lagunas F, Possani LD, Belokoneva OS, Nakajima T. Oxyopinins, large amphipathic peptides isolated from the venom of the wolf spider Oxyopes kitabensis with cytolytic properties and positive insecticidal cooperativity with spider neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:23627–37.
Corzo G, Diego-Garcia E, Clement H, Peigneur S, Odell G, Tytgat J, Possani LD, Alagon A. An insecticidal peptide from the theraphosid Brachypelma smithi spider venom reveals common molecular features among spider species from different genera. Peptides. 2008;29:1901–8.
Corzo G, Bernard C, Clement H, Villegas E, Bosmans F, Tytgat J, Possani LD, Darbon H, Alagon A. Insecticidal peptides from the theraphosid spider Brachypelma albiceps: an NMR-based model of Ba. BBA Proteins Proteomics. 2009;1794:1190–6.
Criscuolo F, Font-Sala C, Bouillaud F, Poulin N, Trabalon M. Increased ROS production: a component of the longevity equation in the male mygalomorph, Brachypelma albopilosa. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13104. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013104.
Escoubas P, Rash L. Tarantulas: eight-legged pharmacists and combinatorial chemists. Toxicon. 2004;43:555–74.
Escoubas P, Diochot S, Corzo G. Structure and pharmacology of spider venom neurotoxins. Biochimie. 2000;82:893–907.
Estrada G, Villegas E, Corzo G. Spider venoms: a rich source of acylpolyamines and peptides as new leads for CNS drugs. Nat Prod Rep. 2007;24:145–61.
García F. Caracterización química de moléculas antimicrobianas provenientes del veneno de arácnidos y su efecto microbicida en presencia antibióticos, Instituto de Biotecnología. Cuernavaca, Morelos: Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico; 2010.
Garcia F, Villegas E, Espino-Solis GP, Rodriguez A, Paniagua-Solis JF, Sandoval-Lopez G, Possani LD, Corzo G. Antimicrobial peptides from arachnid venoms and their microbicidal activity in the presence of commercial antibiotics. J Antibiot. 2013;66:3–10.
Gentz MC, Jones A, Clement H, King GF. Comparison of the peptidome and insecticidal activity of venom from a taxonomically diverse group of theraphosid spiders. Toxicon. 2009;53:496–502.
Kaiser II, Griffin PR, Aird SD, Hudiburg S, Shabanowitz J, Francis B, John TR, Hunt DF, Odell GV. Primary structures of two proteins from the venom of the Mexican red knee tarantula (Brachypelma smithi). Toxicon. 1994;32:1083–93.
Kreil G. Hyaluronidases-A group of neglected enzymes. Protein Sci. 1995;4:1666–9.
Locht A, Yáñex I, Vázquez M. Distribution and natural history of Mexican species of Brachypelma and Brachypelmides (Theraphosidae, Theraphosinae) with morphological evidence for their synonymy. J Arach. 1999;27:196–200.
Locht A, Medina F, Rojo R, Vázquez I. Una nueva especie de Tarántula del género Aphonopelma Pocock 1901 (Araneae, Theraphosidae, Theraphosinae) de México con notas sobre el Género Brachypelma Simon 1891. Bol Soc Entomol Aragon. 2005;37:105–8.
Machkour-M’Rabet S, Henaut Y, Winterton P, Rojo R. A case of zootherapy with the tarantula Brachypelma vagans Ausserer, 1875 in traditional medicine of the Chol Mayan ethnic group in Mexico. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2011;7:12.
Mazzuca M, Heurteaux C, Alloui A, Diochot S, Baron A, Voilley N, Blondeau N, Escoubas P, Gelot A, Cupo A, Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Eschalier A, Lazdunski M. A tarantula peptide against pain via ASIC1a channels and opioid mechanisms. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:943–5.
Menzel E, Farr C. Hyaluronidases and its substrate hyaluronan: biochemistry, biological activities and therapeutic uses. Cancer Lett. 1998;131:3–11.
Odell GV, Fenton AW, Ownby CL, Doss MP, Schmidt JO. The role of venom citrate. Toxicon. 1999;37:407–9.
Park SP, Kim BM, Koo JY, Cho H, Lee CH, Kim M, Na HS, Oh U. A tarantula spider toxin, GsMTx4, reduces mechanical and neuropathic pain. Pain. 2008;137:208–17.
Platnick, NI. The world spider catalog, version 14.5. American Museum of Natural History, online at http://research.amnh.org/entomology/spiders/catalog/index.html doi:10.5531/db.iz.0001. Available from: http://research.amnh.org/entomology/spiders/catalog/index.html (2014).
Schanbacher FL, Lee CK, Hall JE, Wilson IB, Howell DE, Odell GV. Composition and properties of tarantula Dugesiella hentzi (Girard) venom. Toxicon. 1973;11:21–9.
Schmalhofer WA, Calhoun J, Burrows R, Bailey T, Kohler MG, Weinglass AB, Kaczorowski GJ, Garcia ML, Koltzenburg M, Priest BT. ProTx-II, a selective inhibitor of NaV1.7 sodium channels, blocks action potential propagation in nociceptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:1476–84.
Shu Q, Huang R, Liang S. Assignment of the disulfide bonds of huwentoxin-II by Edman degradation sequencing and stepwise thiol modification. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2301–7.
Souza AH, Ferreira J, Cordeiro Mdo N, Vieira LB, De Castro CJ, Trevisan G, Reis H, Souza IA, Richardson M, Prado MA, Prado VF, Gomez MV. Analgesic effect in rodents of native and recombinant Ph alpha 1beta toxin, a high-voltage-activated calcium channel blocker isolated from armed spider venom. Pain. 2008;140:115–26.
Villegas E, Corzo G. Pore-forming peptides from spiders. Toxin Rev. 2005;24:345–57.
Wang X, Connor M, Smith R, Maciejewski MW, Howden ME, Nicholson GM, Christie MJ, King GF. Discovery and characterization of a family of insecticidal neurotoxins with a rare vicinal disulfide bridge. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:505–13.
Zhu S, Darbon H, Dyason K, Verdonck F, Tytgat J. Evolutionary origin of inhibitor cystine knot peptides. FASEB J. 2003;17:1765–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this entry
Cite this entry
Clement, H. et al. (2015). Antimicrobial, Insecticides, Analgesics, and Hyaluronidases from the Venom Glands of Brachypelma Spiders. In: Gopalakrishnakone, P., Corzo, G., Diego-Garcia, E., de Lima, M. (eds) Spider Venoms. Toxinology. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6646-4_20-1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6646-4_20-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-6646-4
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences