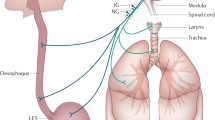
Abstract
The frequent association of gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and respiratory disorders, in particular asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic dry cough, cystic fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, is well known [1–4]. In this short review, the terms COPD and chronic bronchitis will be used indifferently to indicate a clinical picture characterized by chronic productive cough (for at least two months a year in the past two years) and possible bronchial obstruction with a significant irreversible component. The incidence of GER in asthma ranges from 40% to 80% according to the series; the figures for chronic bronchitis are about 50%–60% [1, 5]. In the study of Ducoloné et al. [5], about 50% of patients with GER had no clinical complaint of GER (although half of these had cough and nocturnal dyspnea) while the other 50% had both digestive and respiratory symptoms. Among the 17 subjects with GER, 9 were on theophylline treatment, but only 2 received sympathomimetic agents [5].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CJ, Newhouse MT (1984) Gastroesophageal reflux and chronic respiratory disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:645–647
Harding SM, Richter JE (1997) The role of gastroesophageal reflux in chronic cough and asthma. Chest 111:1389–1402
Ledson MJ, Wilson GE, Tran J, Walshaw MJ (1998) Tracheal microaspiration in adult cystic fibrosis. J R Soc Med 91:10–12
Mays EE, Dubois JJ, Hamilton GB (1976) Pulmonary fibrosis associated with tracheobronchial aspiration. Chest 69:512–515
Ducoloné A, Vandevenne A, Jouin H, Grob J-C, Coumaros D, Meyer C, Burghard G, Methlin G, Hollender L (1987) Gastroesophageal reflux in patients with asthma and chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:327–332
Kahrilas PJ, Gupta RR (1990) Mechanisms of acid reflux associated with cigarette smoking. Gut 31:4–10
Kahrilas PJ (1992) Cigarette smoking and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis 10:61–71
Berquist WE, Rachelefsky GS, Kadden M, Siegel SC, Katz RM, Mickey MR, Ament ME (1981) Effect of theophylline on gastroesophageal reflux in normal adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 67:407–411
Johannesson N, Andersson K-E, Joelsson B, Persson CGA (1985) Relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter and stimulation of gastric secretion and diuresis by antiasthmatic xanthines. Role of adenosine antagonism. Am Rev Respir Dis 131:26–31
Schindlbeck NE, Heinrich C, Huber RM, Muller-Lissner SA (1998) Effects of albuterol (salbutamol) on esophageal motility and gastroesophageal reflux in healthy volunteers. JAMA 260:3156–3158
Michoud MC, Leduc T, Proulx F, Perreault S, Du Souich P, Duranceau A, Amyot R (1991) Effect of salbutamol on gastroesophageal reflux in healthy volunteers and patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 87:762–767
Roussos C, Macklem PT (1982) The respiratory muscles. N Engl J Med 307:786–797
Moote DW, Lloyd DA, McCourtie DR, Wells GA (1986) Increase in gastroesophageal reflux during methacholine-induced bronchospasm. J Allergy Clin Immunol 78:619–623
Ekstrom TKA, Tibbling LIE (1989) Can mild bronchospasm reduce gastroesophageal reflux? Am Rev Respir Dis 139:52–55
Orr WC, Shamma-Othman Z, Allen M, Robinson MG (1992) Esophageal function and gastroesophageal reflux during sleep and waking in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 101:1521–1525
Reid KR, McKenzie FN, Menkis AH, Novick RJ, Pflugfelder PW, Kostuk WJ, Ahmad D (1990) Importance of chronic aspiration in recipients of heart-lung transplants. Lancet 336:206–208
Lusuardi M, Capelli A, Cerutti CG, Spada EL, Donner CF (1994) Airways inflammation in subjects with chronic bronchitis who have never smoked. Thorax 49:1211–1216
Ruth M, Carlsson S, Mansson I, Bengtsson U, Sandberg N (1993) Scintigraphic detection of gastro-pulmonary aspiration in patients with respiratory disorders. Clin Physiol 13:19–33
Tibbling L (1993) Wrong-way swallowing as a possible cause of bronchitis in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 113:405–408
Tibbling L, Gibellino FM, Johansson KE (1995) Is mis-swallowing or smoking a cause of respiratory symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease? Dysphagia 10:113–116
David P, Denis P, Nouvet G, Pasquis G, Lefrancois R, Morere P (1982) Fonction respiratoire et reflux gastro-oesophagien au cours de la bronchite chronique. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 18:81–86
Pellegrini CA, DeMeester TR, Johnson LF, Skinner DB (1979) Gastroesophageal reflux and pulmonary aspiration: incidence, functional abnormality, and results of surgical therapy. Surgery 86:110–119
Boeree MJ, Peters FTM, Postma DS, Kleibeuker JH (1998) No effect of high-dose omeprazole in patients with severe airway hyperresponsiveness and (a) symptomatic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Eur Respir J 11:1070–1074
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer-Verlag Italia
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lusuardi, M., Donner, C.F. (1999). Gastroesophageal Reflux in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. In: Dal Negro, R.W., Allegra, L. (eds) Pneumological Aspects of Gastroesophageal Reflux. Springer, Milano. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-2147-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-88-470-2147-1_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Milano
Print ISBN: 978-88-470-0049-0
Online ISBN: 978-88-470-2147-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive