Abstract
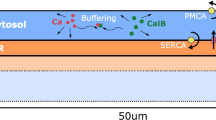
The fire-diffuse-fire model provides an idealized model of Ca2+ release within living cells. The effect of calcium pumps, which drive Ca2+ back into internal stores, is often neglected for mathematical simplicity. Here we show how to explicitly analyse such effects by extending the work of Keizer et al. [Keizer, J. E., G. D. Smith, S. Ponce Dawson and J. Pearson (1998). Saltatory propagation of Ca2+ waves by Ca2+ sparks. Biophys. J. 75, 595–600.]. For travelling waves, in which release events occur sequentially, we construct the speed of waves in terms of the time-scale at which pumps operate. An immediate consequence of this analysis is that the inclusion of calcium pumps leads to multiple solutions. A linear stability analysis determines those solution branches in parameter space which are stable. Numerical continuation is used to provide explicit examples of the bifurcation diagrams of the speed of waves as a function of physiologically significant system parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, M. J. (1997). Elementary and global aspects of calcium signalling. J. Neurophysiol. 499, 291–306.
Berridge, M. J. (1998). Neuronal calcium signalling. Neuron 21, 13–26.
Berridge, M. J. and G. Dupont (1994). Spatial and temporal signalling by calcium. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 6, 267–274.
Bootman, M. D., M. J. Berridge and P. Lipp (1997). Cooking with calcium: The recipes for composing global signals from elementary events. Cell 91, 367–373.
Bugrim, E. A., Zhabotinsky and I. R. Epstein (1997). Calcium waves in a model with a random spatially discrete distribution of Ca2+ release sites. Biophys. J. 73, 2897–2906.
Callamaras, N., J. S. Marchant, X. P. Sun and I. Parker (1998). Activation and co-ordination of InsP(3)-mediated elementary Ca2+ events during global Ca2+ signals in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiol. 509, 81–91.
Chopra, G. C., B. D. Sleeman, J. Brindley, D. G. Knapp and A. V. Holden (1999). Velocity and stability of solitary planar travelling wave solutions of intracellular [Ca2+]. Bull. Math. Biol. 61, 273–301.
Coombes, S. and P. C. Bressloff (2000). Solitary waves in a model of dendritic cable with active spines. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61, 432–453.
De Young, G. W. and J. Keizer (1992). A single pool IP3-receptor based model for agonist stimulated Ca2+ oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9895–9899.
DuPont, G. and A. Goldbeter (1994). Properties of intracellular Ca2+ waves generated by a model based on Ca2+-induced-Ca2+ release. Biophys. J. 67, 2191–2204.
Goldbeter, A. (1996). Biochemical Oscillations and Cellular Rhythms, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Jafri, M. S. and J. Keizer (1995). On the roles of Ca2+ diffusion, Ca2+ buffers, and the endoplasmic reticulum in IP3-induced Ca2+ waves. Biophys. J. 69, 2139–2153.
Jafri, M. S. and J. Keizer (1997). Agonist-induced calcium waves in oscillatory cells: A biological example of Burgers’ equation. Bull. Math. Biol. 59, 1125–1144.
Keizer, J. E., G. D. Smith, S. Ponce Dawson and J. Pearson (1998). Saltatory propagation of Ca2+ waves by Ca2+ sparks. Biophys. J. 75, 595–600.
Li, Y. X., J. Keizer, S. S. Stojilkovic and J. Rinzel (1995). Ca2+ excitability of the ER membrane: an explanation for IP3-induced Ca2+ oscillations. Am. J. Physiol. 269, C1079–C1092.
Parker, I. and Y. Yao (1991). Regenerative release of calcium from functionally discrete subcellular stores by inisitol trisphosphate. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 246, 269–274.
Pearson, J. E. and S. Ponce Dawson (1998). Crisis on skid row. Physica A 257, 141–148.
Pearson, J. E., S. Ponce Dawson, J. Keizer and G. Smith (1998). Crisis on skid row. Available online at http://www-xdiv.lanl.gov/XCM/pearson/skid_row_relay.ps.
Ponce Dawson, S., J. Keizer and J. E. Pearson (1999). Fire-diffuse-fire model of dynamics of intracellular calcium waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 6060–6063.
Rinzel, J. and K. Maginu (1984). Kinematic analysis of wave pattern formation in excitable media, Non-equilibrium Dynamics in Chemical Systems, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 107–113.
Rooney, T. A. and A. P. Thomas (1993). Intracellular calcium waves generated by Ins(1,4,5)P3-dependent mechanisms. Cell Calcium 14, 674–690.
Sneyd, J., P. D. Dale and A. Duffy (1998). Traveling waves in buffered systems: applications to calcium waves. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58, 1178–1192.
Sneyd, J., S. Girard and D. Clapham (1993). Calcium wave propagation by calcium-induced-calcium release: an unusual excitable system. Bull. Math. Biol. 55, 315–344.
Wagner, J. and J. Keizer (1994). Effects of rapid buffers on Ca2+ diffusion and Ca2+ oscillations. Biophys. J. 67, 447–456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coombes, S. The effect of ion pumps on the speed of travelling waves in the fire-diffuse-fire model of Ca2+ release. Bull. Math. Biol. 63, 1–20 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2000.0193
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2000.0193