Abstract
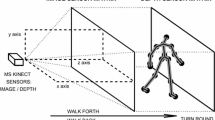
Traditional vision-based systems used for automatic gait pathology detection, associate high-cost. However, with the advent of Microsoft Kinect sensor, researchers tried to model some low-cost gait assessment systems; but they suffer from the device-specific generic constraints. This study attempted to mitigate those pitfalls by introducing a noble multi-Kinect setup for automated gait diagnosis. Ten healthy participants were recruited to simulate pathological gait. Extracted salient features were classified using supervised learning, leading to an overall accuracy of 93%, which outperformed state-of-the-art.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Figueiredo, C.P. Santos, J.C. Moreno, Automatic recognition of gait patterns in human motor disorders using machine learning: a review. Med. Eng. Phys. 53, 1–12 (2018)
W. Rueangsirarak, J. Zhang, N. Aslam, E.S.L. Ho, H.P.H. Shum, Automatic musculoskeletal and neurological disorder diagnosis with relative joint displacement from human gait. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 26(12), 2387–2396 (2018)
Y. Ma, K. Mithraratne, N.C. Wilson, X. Wang, Y. Ma, Y. Zhang, The validity and reliability of a Kinect v2-based gait analysis system for children with cerebral palsy. Sensors 19(7), 1660 (2019)
S. Bei, Z. Zhen, Z. Xing, L. Taocheng, L. Qin, Movement disorder detection via adaptively fused gait analysis based on kinect sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 18(17), 7305–7314 (2018)
E. Dolatabadi, B. Taati, A. Mihailidis, An automated classification of pathological gait using unobtrusive sensing technology. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 25(12), 2336–2346 (2017)
Q. Wang, G. Kurillo, F. Ofli, R. Bajcsy, Evaluation of pose tracking accuracy in the first and second generations of Microsoft Kinect, in 2015 International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (IEEE, 2015), pp. 380–389
B. Müller, W. Ilg, M.A. Giese, N. Ludolph, Validation of enhanced Kinect sensor based motion capturing for gait assessment. PLoS ONE 12(4), e0175813 (2017)
S. Chakraborty, A. Nandy, Trisha M. Kesar, Gait deficits and dynamic stability in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biomech. 71, 11–23 (2020)
Q. Li, Y. Wang, A. Sharf, Y. Cao, T. Changhe, B. Chen, Y. Shengyuan, Classification of gait anomalies from kinect. Vis. Comput. 34(2), 229–241 (2018)
T.-N. Nguyen, H.-H. Huynh, J. Meunier, Skeleton-based abnormal gait detection. Sensors 16(11), 1792 (2016)
M. Khokhlova, C. Migniot, A. Morozov, O. Sushkova, A. Dipanda, Normal and pathological gait classification LSTM model. Artif. Intell. Med. 94, 54–66 (2019)
K. Desai, B. Prabhakaran, S. Raghuraman, Combining skeletal poses for 3d human model generation using multiple kinects, in Proceedings of the 9th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference (ACM, 2018), pp. 40–51
J.P. Vieira, D. Carmo, Y. Jovita, L. Oliveira, A proposal of a non-intrusive, global movement analysis of hemiparesis treatment. J. Commun. Inf. Syst. 30(1) (2015)
S. Hong, Y. Kim, Dynamic pose estimation using multiple RGB-D cameras. Sensors 18(11), 3865 (2018)
Y. Kim, S. Baek, B.-C. Bae, Motion capture of the human body using multiple depth sensors. ETRI J. 39(2), 181–190 (2017)
M. Rietzler, F. Geiselhart, J. Thomas, E. Rukzio, Fusionkit: a generic toolkit for skeleton, marker and rigid-body tracking, in Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGCHI Symposium on Engineering Interactive Computing Systems (ACM, 2016), pp. 73–84
Acknowledgements
We would like to be extremely thankful to Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), DST, Govt. of India to partially support this research work. The Kinect V2 sensors used in our research experiment were purchased from the project, funded by SERB with FILE NO: ECR/2017/000408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chakraborty, S., Mishra, R., Dwivedi, A., Das, T., Nandy, A. (2020). A Low-Cost Pathological Gait Detection System in Multi-Kinect Environment. In: Bhattacharya, I., Otani, Y., Lutz, P., Cherukulappurath, S. (eds) Progress in Optomechatronics. Springer Proceedings in Physics, vol 249. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6467-3_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6467-3_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-6466-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-6467-3
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)