Abstract
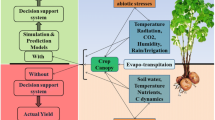
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is the most significant food crop next to rice and wheat. Climate change could exert critical influences on supply of food; consequently, key challenge for modern agriculture is to develop approaches to handle its harmful impacts for confirming food security by 2050 as well as afterward. Climate variability in the form of higher temperature, rainfall variability, and increased frequency of drought have shown significant impact on potato production. Thus, it is essential to design adaptation strategies that can mitigate influence of climate change for long-term basis. Different process-based models such as Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT), Agricultural Production Systems Simulator (APSIM), CropSyst (CropSyst VB–Simpotato), and STICS (Simulateur mulTIdisciplinaire pour les Cultures Standard) have shown great potential to develop sustainable agronomic practices as well as virtual potato cultivars to have good potato crop for future.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed M (2020) Introduction to modern climate change. Andrew E. Dessler: Cambridge University Press, 2011, 252 pp, ISBN-10: 0521173159. Sci Total Environ 734:139397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139397
Alva A, Marcos J, Stockle C, Reddy V, Timlin D (2004) CropSyst VB–Simpotato, a crop simulation model for potato-based cropping systems: II. Evaluation of nitrogen dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Crop Science Congress, Brisbane, Australia, 2004
Brown HE, Huth N, Holzworth D (2011) A potato model build using the APSIM Plant. NET framework, pp 961–967
Brown HE, Huth NI, Holzworth DP, Teixeira EI, Zyskowski RF, Hargreaves JNG, Moot DJ (2014) Plant modelling framework: software for building and running crop models on the APSIM platform. Environ Model Softw 62:385–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.09.005
Brown H, Huth N, Holzworth D (2018) 1 The APSIM Potato Model. http://apsimdev.apsim.info/ApsimxFiles/Potato4403.pdf
Costa LD, Vedove GD, Gianquinto G, Giovanardi R, Peressotti A (1997) Yield, water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in potato: influence of drought stress. Potato Res 40:19–34
Crosslin JM, Munyaneza JE, Brown JK, Liefting LW (2010) A history in the making: Potato Zebra chip disease associated with a new Psyllid-borne Bacterium – a tale of striped potatoes. APSnet Features. https://doi.org/10.1094/APSnet-Feature-2010-0110
Dalla Costa L, Delle Vedove G, Gianquinto G, Giovanardi R, Peressotti A (1997) Yield, water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in potato: influence of drought stress. Potato Res 40:19–34
Davies A, Jenkins T, Pike A, Shaq J, Carson I, Pollock CJ, Parry MI (1996) Modelling the predicted geographic and economic response of UK cropping systems to climate change scenarios: the case of potatoes. Asp Appl Biol 45:63–69
El-Abedin TKZ, Mattar MA, Alazba AA, Al-Ghobari HM (2017) Comparative effects of two water-saving irrigation techniques on soil water status, yield, and water use efficiency in potato. Sci Hortic 225:525–532
Eriksson D, Carlson-Nilsson U, Ortíz R, Andreasson E (2016) Overview and breeding strategies of table potato production in Sweden and the Fennoscandian region. Potato Res 59(3):279–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-016-9328-6
Eshel D, Tepel-Bamnolker P (2012) Can loss of apical dominance in potato tuber serve as a marker of physiological age? Plant Signal Behav 7:1158–1162
FAO (2017). http://faostat.fao.org/. Accessed in Jan 2017
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), World crop production statistics (2016). http://www.faostat.fao.org. Accessed 10th Sept 2016
Gao X, Li C, Zhang M, Wang R, Chen B (2015) Controlled release urea improved the nitrogen use efficiency, yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) on silt loamy soil. Field Crop Res 181:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.07.009
Geisseler D, Wilson R (2020) Nitrogen in potato rotations with cover crops: field trial and simulations using DSSAT. Agron JAccepted Author Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20177
Hack H, Gall H, Klemke Th., Klose R, Meier U, Stauss R, Witzenberger A (2001) The BBCH scale for phonological growth stages of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). In: Meier U (ed) Growth stages of mono and dicotyledonous Plants, BBCH Monograph, Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry
Haverkort AJ, Franke AC, Steyn JM, Pronk AA, Caldiz DO, Kooman PL (2015) A robust potato model: LINTUL-POTATO-DSS. Potato Res 58(4):313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-015-9303-7
Hijmans RJ (2003) The effect of climate change on global potato production. Am J Pot Res 80:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02855363
Hodges T, Johnson S, Johnson B (1992) SIMPOTATO: a highly modular program structure for an IBSNAT style crop simulation. Agron J 84:911–915
Hoogenboom G, Porter CH, Shelia V, Boote KJ, Singh U, White JW, Hunt LA, Ogoshi R, Lizaso JI, Koo J, Asseng S, Singels A, Moreno LP, Jones JW (2019) Decision support system for agrotechnology transfer (DSSAT) version 4.7.5 (www.dssat.net). DSSAT Foundation, Gainesville, FL
Jackson BC, Goolsby J, Wyzykowski A, Vitovsky N, Bextine B (2009) Analysis of genetic relationships between potato psyllid (Bactericera cockerelli) populations in the United States, Mexico and Guatemala using ITS2 and Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) data. Subtrop Plant Sci 61:1–5
Jégo G, Martínez M, Antigüedad I, Launay M, Sanchez-Pérez JM, Justes E (2008) Evaluation of the impact of various agricultural practices on nitrate leaching under the root zone of potato and sugar beet using the STICS soil–crop model. Sci Total Environ 394(2):207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.01.021
Jones JW, Hoogenboom G, Porter CH, Boote KJ, Batchelor WD, Hunt LA, Wilkens PW, Singh U, Gijsman AJ, Ritchie JT (2003) The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur J Agron 18(3–4):235–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1161-0301(02)00107-7
Khan MA, Gemenet DC, Villordon A (2016) Root system architecture and abiotic stress tolerance: current knowledge in root and tuber crops. Front Plant Sci 7(1584). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01584
Khan MS, Struik PC, van der Putten PEL, Jansen HJ, van Eck HJ, van Eeuwijk FA, Yin X (2019) A model-based approach to analyse genetic variation in potato using standard cultivars and a segregating population. I. Canopy cover dynamics. Field Crop Res 242:107581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.107581
Kooman PL, Haverkort AJ (1995) Modelling development and growth of the potato crop influenced by temperature and daylength: LINTUL-POTATO. In: Haverkort AJ, MacKerron DKL (eds) Potato ecology and modelling of crops under conditions limiting growth: proceedings of the second international potato modeling conference, held in Wageningen 17–19 May, 1994. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 41–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0051-9_3
Kooman PL, Fahem M, Tegera P, Haverkort AJ (1996a) Effects of climate on different potato genotypes 2. Dry matter allocation and duration of the growth cycle. Eur J Agron 5:207–217
Kooman PL, Fahem M, Tegera P, Haverkort AJ (1996b) Effects of climate on different potato genotypes 1. Radiation interception, total and tuber dry matter production. Eur J Agron 5:193–205
Lafta AM, Lorenzen JH (1995) Effect of high temperature on plant growth and carbohydrate metabolism in potato. Plant Physiol 109(2):637–643. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.2.637
Leiminger JH, Hausladen H (2011) Early blight control in potato using diseaseorientated threshold values. Plant Dis 96:124–130
Linker R, Ioslovich I, Sylaios G, Plauborg F, Battilani A (2016) Optimal model-based deficit irrigation scheduling using AquaCrop: a simulation study with cotton, potato and tomato. Agric Water Manag 163:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.09.011
Lizana XC, Avila A, Tolaba A, Martinez JP (2017) Field responses of potato to increased temperature during tuber bulking: projection for climate change scenarios, at high-yield environments of Southern Chile. Agric For Meteorol 239:192–201
Lutaladio N, Castaidi L (2009) Potato: the hidden treasure. J Food Compos Anal 22(6)
Lutz W, Samir KC (2010) Dimensions of global population projections: what do we know about future population trends and structures? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B-Biol Sci 365(1554):2779–2791
Martínez-Romero A, Domínguez A, Landeras G (2019) Regulated deficit irrigation strategies for different potato cultivars under continental Mediterranean-Atlantic conditions. Agric Water Manag 216:164–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.01.030
Miglietta F, Magliulo V, Bindi M, Cerio L, Vaccari FP, Loduca V, Peressotti A (1998) Free air CO2 enrichment of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): development, growth and yield. Glob Chang Biol 4:163–172
Mihovilovich E, Carli C, De Mendiburu F, Hualla V, Bonierbale M (2014) Protocol for tuber bulking maturity assessment of elite and advanced potato clones. Int. Potato Center, Lima, Peru. 18–19
Montoya F, Camargo D, Ortega JF, Córcoles JI, Domínguez A (2016) Evaluation of Aquacrop model for a potato crop under different irrigation conditions. Agric Water Manag 164:267–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.10.019
Montoya F, Camargo D, Domínguez A, Ortega JF, Córcoles JI (2018) Parametrization of Cropsyst model for the simulation of a potato crop in a Mediterranean environment. Agric Water Manag 203:297–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.03.029
Montoya F, Camargo D, Córcoles JI, Domínguez A, Ortega JF (2020) Analysis of deficit irrigation strategies by using SUBSTOR-potato model in a semi-arid area. J Agric Sci:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002185961900090X
Morissette R, Jégo G, Bélanger G, Cambouris AN, Nyiraneza J, Zebarth BJ (2016) Simulating potato growth and nitrogen uptake in eastern Canada with the STICS model. Agron J 108(5):1853–1868. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.02.0112
Munyaneza JE, Henne DC (2013) Chapter 4 – Leafhopper and psyllid pests of potato. In: Alyokhin A, Vincent C, Giordanengo P (eds) Insect pests of potato. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 65–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386895-4.00004-1
Ojeda JJ, Rezaei EE, Remenyi TA, Webb MA, Webber HA, Kamali B, Harris RMB, Brown JN, Kidd DB, Mohammed CL, Siebert S, Ewert F, Meinke H (2020) Effects of soil- and climate data aggregation on simulated potato yield and irrigation water requirement. Sci Total Environ 710:135589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135589
Paredes P, D’Agostino D, Assif M, Todorovic M, Pereira LS (2018) Assessing potato transpiration, yield and water productivity under various water regimes and planting dates using the FAO dual Kc approach. Agric Water Manag 195(Supplement C):11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.09.011
Parent S-É, Leblanc MA, Parent A-C, Coulibali Z, Parent LE (2017) Site-specific multilevel modeling of potato response to nitrogen fertilization. Front Environ Sci 5(81). https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2017.00081
Peins DR, Crawford JW, Grashoff C, Jefferies RA, Parter JR, Marshall B (1996) A simulation study of crop growth ahd development under climate change. Agric For Meteorol 79:271–887
Peiris DR, Crawford JW, Grashoff C, Jefferies RA, Porter JR, Marshall B (1996) A simulation study of crop growth and development under climate change. Agric For Meteorol 79(4):271–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(95)02286-4
Pelletier Y, Michaud D (1995). Insect pest control on potato: genetically-based control. In: Duchesne RM, Boiteau G (eds) Potato insect pest control: development of a sustainable approach, Gouvernement du Que’bec. 69–79
Pinhero RG, Coffin R, Yada RY (2009) Post-harvest storage of potatoes. Advances in potato chemistry and technology. Academic Press (Elsevier), New York, pp 339–370
Rajsic P, Weersink A (2008) Do farmers waste fertilizer? A comparison of ex post optimal nitrogen rates and ex ante recommendations by model, site and year. Agric Syst 97(1):56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2007.12.001
Raymundo R, Kleinwechter U, Asseng S (2014). Virtual potato crop modeling A comparison of genetic coefficients of the DSSAT-SUBSTOR potato model with breeding goals for developing countries. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7687
Raymundo R, Asseng S, Prassad R, Kleinwechter U, Concha J, Condori B, Bowen W, Wolf J, Olesen JE, Dong Q, Zotarelli L, Gastelo M, Alva A, Travasso M, Quiroz R, Arora V, Graham W, Porter C (2017) Performance of the SUBSTOR-potato model across contrasting growing conditions. Field Crop Res 202:57–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.04.012
Razzaghi F, Zhou Z, Andersen MN, Plauborg F (2017) Simulation of potato yield in temperate condition by the AquaCrop model. Agric Water Manag 191:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.06.008
Rens LR, Zotarelli L, Rowland DL, Morgan KT (2018) Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer rates and time of application for potatoes under seepage irrigation. Field Crop Res 215:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.10.004
Ritchie J, Griffin TS, Johnson BS (1995) SUBSTOR: functional model of potato growth, development and yield. In: Modelling and parameterization of the soil-plant-atmosphere system: a comparison of potato growth models, pp 401–435
Romanucci V, Di Fabio G, Di Marino C, Davinelli S, Scapagnini G, Zarrelli A (2018) Evaluation of new strategies to reduce the total content of α-solanine and α-chaconine in potatoes. Phytochem Lett 23:116–119
Rosenzweig C, Phillips J, Goldberg R, Carroll J, Hodges T (1996) Potential impacts of climate change on citrus and potato production in the US. Agric Syst 52(4):455–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-521X(95)00059-E
Rykaczewska K (2015) The effect of high temperature occurring in subsequent stages of plant development on potato yield and tuber physiological defects. Am J Potato Res 92(3):339–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-015-9436-x
Singh U, Matthews RB, Griffin TS, Ritchie JT, Hunt LA, Goenaga R (1998) Modeling growth and development of root and tuber crops. In: Tsuji G, Hoogenboom G, Thornton P (eds) Understanding options for agricultural production, vol 7. Systems approaches for sustainable agricultural development. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 129–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3624-4_7
Shillito RM, Timlin DJ, Fleisher D, Reddy VR, Quebedeaux B (2009) Yield response of potato to spatially patterned nitrogen application. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129(1):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.07.010
Šrek P, Hejcman M, Kunzová E (2010) Multivariate analysis of relationship between potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) yield, amount of applied elements, their concentrations in tubers and uptake in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Field Crop Res 118(2):183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.05.009
Stevenson WR, Loria R, Franc GD, Weingartner DP (2001) Compendium of potato diseases, 2nd edn. The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul
Tang J, Xiao D, Bai H, Wang B, Liu DL, Feng P, Zhang Y, Zhang J (2020) Potential benefits of potato yield at two sites of agro-pastoral ecotone in North China under future climate change. Int J Plant Prod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-020-00092-7
Tang J, Wang J, Fang Q, Dayananda B, Yu Q, Zhao P, Yin H, Pan X (2019) Identifying agronomic options for better potato production and conserving water resources in the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China. Agric For Meteorol 272-273:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.04.001
Tryjanowski P, Sparks TH, Blecharczyk A, Małecka-Jankowiak I, Switek S, Sawinska Z (2017) Changing phenology of potato and of the treatment for its major pest (Colorado potato beetle) – a long-term analysis. Am J Potato Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-017-9611-3
Van Der Waals JE, Korsten L, Aveling TAS (2001) A review of early blight of potato. Afr Plant Prot 7:91–102
van Oort PAJ, Timmermans BGH, van Swaaij ACPM (2012) Why farmers’ sowing dates hardly change when temperature rises. Eur J Agron 40:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2012.02.005
Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot 61(3):199–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.05.011
Wang L, Coulter JA, Palta JA, Xie J, Luo Z, Li L, Carberry P, Li Q, Deng X (2019) Mulching-induced changes in tuber yield and nitrogen use efficiency in potato in China: a meta-analysis. Agronomy 9(12):793
Woli P, Hoogenboom G (2018) Simulating weather effects on potato yield, nitrate leaching, and profit margin in the US Pacific Northwest. Agric Water Manag 201:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.01.023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ahmed, M. et al. (2020). Potato Modeling. In: Ahmed, M. (eds) Systems Modeling. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4728-7_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4728-7_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4727-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4728-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)