Abstract
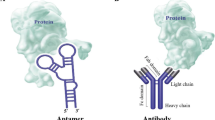
In the emerging class of synthetic molecules, aptamers have shown both diagnostics & therapeutics potentials. In past few years a new concept has come that justify the use of aptamer conjugated drugs or ApDC. This approach is not new and already in use through monoclonal antibody conjugated drugs for treatment of certain diseases. However due to certain advantages of aptamers over antibody, more interest has been shifted towards ApDC. Drugs can be conjugated to aptamers by non-covalent and covalent approaches. Doxorubicin an anticancer drug has been conjugated to aptamers and the complex has shown better efficacy and reduced cell toxicity in comparison to drug that was administered alone. Other approaches used addition of complement protein or Fc region of antibody to aptamer for activating host immune system for killing antibiotics resistant bacteria etc. This gives a promising scenario for ApDC future but at the same time efficient ApDC production and its use is still a big challenge.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagalkot V, Zhang L, Levy-Nissenbaum E, Jon S, Kantoff PW, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2007) Quantum dot− aptamer conjugates for synchronous cancer imaging, therapy, and sensing of drug delivery based on bi-fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nano Lett 7(10):3065–3070
Bayrac AT, Akça OE, Eyidoğan Fİ, Öktem HA (2018) Target-specific delivery of doxorubicin to human glioblastoma cell line via ssDNAaptamer. J Biosci 43(1):97–104
Blind M, Blank M (2015) Aptamer selection technology and recent advances. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4:e223
Bruno JG (2013) A review of therapeutic aptamer conjugates with emphasis on new approaches. Pharmaceuticals 6(3):340–357
Catuogno S, Esposito CL, de Franciscis V (2016) Aptamer-mediated targeted delivery of therapeutics: an update. Pharmaceuticals 9(4):69
Chen X, Estévez MC, Zhu Z, Huang YF, Chen Y, Wang L, Tan W (2009) Using aptamer-conjugated fluorescence resonance energy transfer nanoparticles for multiplexed cancer cell monitoring. Anal Chem 81(16):7009–7014
Chen H, Xie S, Liang H, Wu C, Cui L, Huan SY, Zhang X (2017a) Generation of biostable L-aptamers against achiral targets by chiral inversion of existing D-aptamers. Talanta 164:662–667
Chen K, Liu B, Yu B, Zhong W, Lu Y, Zhang J, Liao J, Liu J, Pu Y, Qiu L, Zhang L (2017b) Advances in the development of aptamer drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 9(3):e 1438
Chu TC, Marks JW, Lavery LA, Faulkner S, Rosenblum MG, Ellington AD, Levy M (2006) Aptamer: toxin conjugates that specifically target prostate tumor cells. Cancer Res 66(12):5989–5992
Damiani RM, Moura DJ, Viau CM, Caceres RA, Henriques JAP, Saffi J (2016) Pathways of cardiac toxicity: comparison between chemotherapeutic drugs doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. Arch Toxicol 90(9):2063–2076
Dougan H, Lyster DM, Vo CV, Stafford A, Weitz JI, Hobbs JB (2000) Extending the lifetime of anticoagulant oligodeoxynucleotide aptamers in blood. Nucl Med Biol 27(3):289–297
Huang YF, Sefah K, Bamrungsap S, Chang HT, Tan W (2008) Selective photothermal therapy for mixed cancer cells using aptamer-conjugated nanorods. Langmuir 24(20):11860–11865
Khanna P, Ong C, Bay BH, Baeg GH (2015) Nanotoxicity: an interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death. Nano 5(3):1163–1180
Liu H, Lv C, Ding B, Wang J, Li S, Zhang Y (2014) Antitumor activity of G-quadruplex-interactive agent TMPyP4 with photodynamic therapy in ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett 8(1):409–413
Mallikaratchy P, Tang Z, Tan W (2008) Cell specific aptamer–photosensitizer conjugates as a molecular tool in photodynamic therapy. ChemMedChem 3(3):425–428
McNamara JO II, Andrechek ER, Wang Y, Viles KD, Rempel RE, Gilboa E, Sullenger BA, Giangrande PH (2006) Cell type–specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nat Biotechnol 24(8):1005
Ni S, Yao H, Wang L, Lu J, Jiang F, Lu A, Zhang G (2017) Chemical modifications of nucleic acid aptamers for therapeutic purposes. Int J Mol Sci 18(8):1683
Parashar A, Rajput YS, Sharma R (2015) Aptamer-based sensing of β-casomorphin-7. J Agric Food Chem 63(10):2647–2653
Perez HL, Cardarelli PM, Deshpande S, Gangwar S, Schroeder GM, Vite GD, Borzilleri RM (2014) Antibody–drug conjugates: current status and future directions. Drug Discov Today 19(7):869–881
Ricart AD (2011) Antibody-drug conjugates of calicheamicin derivative: gemtuzumabozogamicin and inotuzumabozogamicin. Clin Cancer Res 17(20):6417–6427
Tan L, Neoh KG, Kang ET, Choe WS, Su X (2011) PEGylated anti-MUC1 aptamer-doxorubicin complex for targeted drug delivery to MCF7 breast cancer cells. Macromol Biosci 11(10):1331–1335
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249(4968):505–510
Volk DE, Lokesh GL (2017) Development of phosphorothioate DNA and DNA thioaptamers. Biomedicine 5(3):41
Wang R, Zhu G, Mei L, Xie Y, Ma H, Ye M, Qing FL, Tan W (2014) Automated modular synthesis of aptamer–drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 136(7):2731–2734
Yoon S, Huang KW, Reebye V, Spalding D, Przytycka TM, Wang Y, Swiderski P, Li L, Armstrong B, Reccia I, Zacharoulis D (2017) Aptamer-drug conjugates of active metabolites of nucleoside analogs and cytotoxic agents inhibit pancreatic tumor cell growth. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 6:80–88
Zhou J, Rossi JJ (2014) Cell-type-specific, aptamer-functionalized agents for targeted disease therapy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 3:e169
Zhu G, Niu G, Chen X (2015) Aptamer–drug conjugates. Bioconjug Chem 26(11):2186–2197
Acknowledgments
National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), Karnal for providing laboratory & library support.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest amongst the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Parashar, A., Pandey, K.K., Yadav, M.L. (2019). Different Approaches for Aptamer Conjugated Drugs Preparation. In: Yadav, G., Kumar, V., Aggarwal, N. (eds) Aptamers. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8836-1_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8836-1_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-8835-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-8836-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)