Abstract
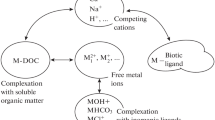
Critical loads of heavy metals address not only ecotoxicological effects on organisms in soils and surface waters, but also food quality in view of public health. A critical load for metals is the load resulting at steady state in a metal concentration in a compartment (e.g. soil solution, surface water) that equals the critical limit for that compartment. This chapter presents an overview of methods to derive critical loads of metals, with a focus on cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), using critical limits for dissolved total metal concentrations based on impacts on food crops, soil organisms and aquatic organisms. Unlike nitrogen and sulphur, the time to reach steady state can be very long and therefore dynamic models are needed to estimate the times involved in attaining a certain chemical state in response to heavy metal inputs. Therefore, simple approaches are also presented to calculate target loads, i.e. deposition levels at which a critical limit is attained within a predefined time horizon. Results are presented for critical loads of Cd in view of food quality, critical loads and target loads of Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in view of soil biodiversity and a critical limit for Hg in precipitation in view of impacts on fish and soil organisms. Results are discussed in view of the uncertainty and potential applicability for policy support.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments: Biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Anderson, A., & Bingefors, S. (1985). Trends and annual variations in Cd concentrations in grain of winter wheat. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 35, 339–344.
Ashmore, M., Shotbolt, L., Hill, M., Hall, J., Spurgeon, D., Svendsen, C., Fawehinimi, J., Heywood, E., Tipping, E., Lofts, S., Lawlor, A., & Jordan, C. (2004). Further development of an effects (critical loads) based approach for cadmium, copper, lead and zinc. Final Report, EPG 1/3/188.
Baatrup, E. (1991). Structural and functional-effects of heavy-metals on the nervous-system, including sense-organs, of fish. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 199, 253–257.
Bringmark, L., Bringmark, E., & Samuelsson, B. (1998). Effects on mor layer respiration by small experimental additions of mercury and lead. Science of the Total Environment, 213, 115–119.
Bryan, S. E., Tipping, E., & Hamilton-Taylor, J. (2002). Comparison of measured and modelled copper binding by natural organic matter in freshwaters. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 133, 37–49.
Clark, R. B. (2001). Marine pollution (Metals, pp. 98–125). Oxford: Oxford Science Publishers.
Crommentuijn, T., Polder, M. D., & van de Plassche, E. J. (1997). Maximum permissible concentrations and negligible concentrations for metals, taking background concentrations into account. Report no. 601501 001. Bilthoven, The Netherlands: National Institute of Public Health and the Environment.
De Vries, W., & Bakker, D. J. (1998). Manual for calculating critical loads of heavy metals for terrestrial ecosystems. Guidelines for critical limits, calculation methods and input data. (Report 166). Wageningen, The Netherlands: DLO Winand Staring Centre.
De Vries, W., & Groenenberg, J. E. (2009). Evaluation of approaches to calculate critical metal loads for forest ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3422–3432.
De Vries, W., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2013). Modeling the cadmium balance in Australian agricultural systems in view of possible impacts on food quality. Science of the Total Environment, 461–462, 240–257.
De Vries, W., Bakker, D. J., & Sverdrup, H. U. (1998). Manual for calculating critical loads of heavy metals for aquatic ecosystems. Guidelines for critical limits, calculation methods and input data. (Report 165). Wageningen, The Netherlands: DLO Winand Staring Centre.
De Vries, W., Schütze, G., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., Meili, M., Römkens, P. F. A. M., & Groenenberg, J. E. (2005). Calculation of critical loads for cadmium, lead and mercury. Background document to a mapping manual on critical loads of cadmium, lead and mercury. (Report 1104). Wageningen, The Netherlands: Alterra.
De Vries, W., Römkens, P. F. A. M., & Schütze, G. (2007a). Critical soil concentrations of cadmium, lead and mercury in view of health effects on humans and animals. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 191, 91–130.
De Vries, W., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., Meili, M., Groenenberg, B. J., & Schütze, G. (2007b). Impact of soil properties on critical concentrations of cadmium, lead, copper, zinc and mercury in soil and soil solution in view of ecotoxicological effects. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 191, 47–89.
De Vries, W., Groenenberg, J. E., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., & Posch, M. (2012). Critical loads of heavy metals for soils. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils. Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (Chap. 8, pp. 211–237). Dordrecht: Springer.
Doyle, P. J., Gutzman, D. W., Sheppard, M. I., Sheppard, S. C., Bird, G. A., & Hrebenyk, D. (2003). An ecological risk assessment of air emissions of trace metals from copper and zinc production facilities. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 9, 607–636.
Dwane, G. C., & Tipping, E. (1998). Testing a humic speciation model by titration of copper-amended natural waters. Environment International, 24, 609–616.
Groenenberg, J. E., Koopmans, G. F., & Comans, R. N. J. (2010a). Uncertainty analysis of the nonideal competitive adsorption-donnan model: Effects of dissolved organic matter variability on predicted metal speciation in soil solution. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 1340–1346.
Groenenberg, J. E., Römkens, P. F. A. M., Comans, R. N. J., Luster, J., Pampura, T., Shotbolt, L., Tipping, E., & De Vries, W. (2010b). Transfer functions for solid-solution partitioning of cadmium, copper, nickel, lead and zinc in soils: Derivation of relationships for free metal ion activities and validation with independent data. European Journal of Soil Science, 61, 58–73.
Jones, K. C., Jackson, A., & Johnston, A. E. (1992). Evidence of an increase in cadmium content of herbage since the 1860s. European Journal of Soil Science, 26, 834–836.
Kawada, T., & Suzuki, S. (1998). A review on the cadmium content of rice, daily cadmium intake, and accumulation in the kidneys. Journal of Occupational Health, 40, 264–269.
Meili, M. (1997). Mercury in lakes and rivers. In A. Sigel & H. Sigel (Eds.), Mercury and its effects on environment and biology (pp. 21–51). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Meili, M., Bishop, K., Bringmark, L., Johansson, K., Munthe, J., Sverdrup, H., & De Vries, W. (2003). Critical levels of atmospheric pollution: Criteria and concepts for operational modelling of mercury in forest and lake ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 304, 83–106.
Paces, T., Corcimaru, S., Emmanuel, S., Erel, Y., Novak, M., Plyusnin, A., Veron, A., & Wickham, S. (2002). Critical loads of hazardous trace elements in soil-water system. Journal of Field Science, 1, 15–22.
Palmborg, C., Bringmark, L., Bringmark, E., & Nordgren, A. (1998). Multivariate analysis of microbial activity and soil organic matter at a forest site subjected to low-level heavy metal pollution. Ambio, 27, 53–57.
Pampura, T., Groenenberg, J. E., & Rietra, R. P. T. M. (2006). Comparison of methods for copper free ion activity determination in soil solutions of contaminated and background soils. Forest Snow Landscape Research, 80, 305–322.
Pampura, T., Groenenberg, J. E., Lofts, S., & Priputina, I. (2007). Validation of transfer functions predicting Cd and Pb free metal ion activity in soil solution as a function of soil characteristics and reactive metal content. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 184, 217–234.
Posch, M., & De Vries, W. (2009). Dynamic modelling of metals—Time scales and target loads. Environmental Modelling & Software, 24, 86–95.
Posch, M., Hettelingh, J.-P., & Slootweg, J. (2003). Manual for dynamic modelling of soil response to atmospheric deposition. (RIVM report 259101 012). Bilthoven, The Netherlands: National Institute for Public Health and the Environment.
Satarug, S., Haswell-Elkins, M. R., & Moore, M. R. (2000). Safe levels of cadmium intake to prevent renal toxicity in human subjects. British Journal of Nutrition, 84, 791–802.
Slootweg, J., Hettelingh, J.-P., Posch, M., Schütze, G., Spranger, T., De Vries, W., Reinds, G. J., van ’t Zelfde, M., Dutchak, S., & Ilyin, I. (2007). European critical loads of cadmium, lead and mercury and their exceedances. Water Air & Soil Pollution: Focus, 7, 371–377.
Sola, F., Isaia, J., & Masoni, A. (1995). Effects of copper on gill structure and transport function in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 15, 391–398.
Tipping, E. (1994). WHAM—A chemical equilibrium model and computer code for waters, sediments, and soils incorporating a discrete site/electrostatic model of ion-binding by humic substances. Computers & Geosciences, 20, 973–1023.
Tipping, E. (1998). Humic ion-binding Model VI: An improved description of the interactions of protons and metal ions with humic substances. Aquatic Geochemistry, 4, 3–47.
Tipping, E. (2002). Cation binding by humic substances. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Tipping, E. (2005). Modelling Al competition for heavy metal binding by dissolved organic matter in soil and surface waters of acid and neutral pH. Geoderma, 127, 293–304.
Tipping, E., Woof, C., & Hurley, M. A. (1991). Humic substances in acid surface waters; modelling aluminium binding, contribution to ionic charge-balance, and control of pH. Water Research, 25, 425–435.
Tipping, E., Rey-Castro, C., Bryan, S. E., & Hamilton-Taylor, J. (2002). Al(III) and Fe(III) binding by humic substances in freshwaters, and implications for trace metal speciation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66, 3211–3224.
Tipping, E., Lawlor, A. J., & Lofts, S. (2006a). Simulating the long-term chemistry of an upland UK catchment: Major solutes and acidification. Environmental Pollution, 141, 151–166.
Tipping, E., Lawlor, A. J., Lofts, S., & Shotbolt, L. (2006b). Simulating the long-term chemistry of an upland UK catchment: Heavy metals. Environmental Pollution, 141, 139–150.
Tipping, E., Yang, H., Lawlor, A. J., Rose, N. L., & Shotbolt, L. (2007). Trace metals in the catchment, loch and sediments of Lochnagar: Measurements and modelling. In N. L. Rose (Ed.), Lochnagar: The natural history of a mountain lake (pp. 345–373). Dordrecht: Springer.
Vulkan, R., Zhao, F.-J., Barbosa-Jefferson, V., Preston, S., Paton, G. I., Tipping, E., & McGrath, S. P. (2000). Copper speciation and impacts on bacterial biosensors in the pore water of copper-contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 5115–5121.
Weng, L. P., Temminghoff, E. J. M., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2001). Determination of the free ion concentration of trace metals in soil solution using a soil column Donnan membrane technique. European Journal of Soil Science, 52, 629–637.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
de Vries, W., Groenenberg, J., Posch, M. (2015). Mass Balance Approaches to Assess Critical Loads and Target Loads of Metals for Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecosystems. In: de Vries, W., Hettelingh, JP., Posch, M. (eds) Critical Loads and Dynamic Risk Assessments. Environmental Pollution, vol 25. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9508-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9508-1_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-017-9507-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-9508-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)