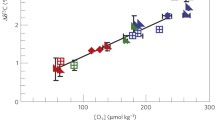
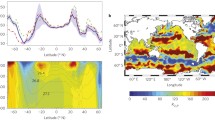
Abstract
Measured rates of sediment oxygen consumption are extrapolated throughout the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean basins from 61° N to 61° S latitude. Because benthic respiration must be supported predominantly by the rain of organic matter from surface waters, the pattern of oxygen consumption in the surface sediments reveals the distribution of particle fluxes in the deep ocean. Benthic oxygen consumption in the Atlantic and Pacific basins appears to account for the remineralization of 1 to 2& of global oceanic primary production and 4 to 10% of global new production. These values are minimum estimates of the role of the sea floor in global cycles because the contributions from the Arctic, Antarctic and Indian Oceans are not included. Comparison of total respiration estimated for the deep Atlantic from AOU and 14C relationships and from benthic respiration indicates that sea floor processes account for 33 to 40% of the organic matter remineralization occurring below 1000 m. Introduction
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broecker, W.S., S. Blanton, W.M. Smethie, Jr., and G. Ostlund (1991) Radiocarbon decay and oxygen utilization in the deep Atlantic Ocean, Global Biogeochem. Cycles 5, 87–117.
Cole, J.J., S. Honjo, and J. Erez (1987) Benthic decomposition of organic matter at a deep-water site in the Panama Basin. Nature 327, 703–704.
Cwienk, D.S. (1986) Recent and glacial age organic carbon and biogenic silica accumulation in marine sediments. Master’s thesis, School of Oceanography, University of Rhode Island. 237p.
Eppley, R.W. and B.J. Peterson (1979) Particulate organic matter flux and planktonic new production in the deep ocean. Nature 282, 677–680.
Froelich, P.N., and others (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43, 1075–1090.
Francois, R, M.P. Bacon and D.O. Suman (1990) Thorium 230 profiling in deep-sea sediments: High-resolution records of flux and dissolution of carbonate in the equatorial Atlantic during the last 24,000 years, Paleoceanogr. 5, 761–788.
Goloway, F., and M. Bender (1982) Diagenetic models of interstitial nitrate profiles in deep-sea suboxic sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 624–638.
Grundmanis, V., and J.W. Murray (1982) Aerobic respiration in pelagic marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46, 1101–1120.
Heggie, D., C. Maris, A. Hudson, J. Dymond, R. Beach, and J. Cullen (1987) Organic carbon oxidation and preservation in NW Atlantic continental margin sediments., in: Geology and Geochemistry of Abyssal Plains, P.P.E. Weaver and J. Thomson, eds., Geological Society Special Publication 31, 215–236.
Jahnke, R.A. (1990) Ocean flux studies: A status report. Reviews of Geophysics 28, 381–398.
Jahnke, R.A., S.R. Emerson, and J.W. Murray (1982) A model of oxygen reduction, denitrification, and organic matter mineralization in marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 610–623.
Jahnke, R.A. and G.A. Jackson (1987) Role of sea floor organisms in oxygen consumption in the deep North Pacific Ocean. Nature 329, 621–623.
Jahnke, R.A., S.R Emerson, C.E. Reimers, J. Schuffert, K. Ruttenberg, and D. Archer (1989) Benthic recycling of biogenic debris in the eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 2947–2960.
Jahnke, R.A., C.E. Reimers, and D.B. Craven (1990) Intensification of recycling of organic matter at the sea floor near ocean margins. Nature 348, 50–54.
Lyle, M., D.W. Murray, B.P. Finney, J. Dymond, J.M. Robbins, and K. Brooksforce (1988) The record of late Pleistocene biogenic sedimentation in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, Paleoceangr. 3, 39–60.
Martin, J.H., G.A. Knauer, D.M. Karl and W.W. Broenkow (1987) VERTEX: carbon cycling in the northeast Pacific, Deep-Sea Res. 34, 267–285.
Martin, W.R. and M.L. Bender (1988) The variability of benthic fluxes and sedimentary remineralization rates in response to seasonally variable organic carbon rain rates in the deep sea: A modeling study. Am. J. Sci. 288, 561–574.
Martin, W.R., M. Bender, M. Leinen, and J. Orchardo (submitted) Benthic organic carbon degradation and biogenic silica dissolution in the central equatorial Pacific. Deep-Sea Res.
Muller, P.J. and E. Suess (1979) Productivity, sedimentation rate, and sedimentary organic matter in the oceans-I. Organic carbon preservation. Deep-Sea Res. 24, 1347–1367.
Murray, J.W. and K.M. Kuivila (1990) Organic matter diagenesis in the northeast Pacific: transition from aerobic red clay to suboxic hemipelagic sediments. Deep-Sea Res. 37, 59–80.
Patching, J.W., R.C.T. Raine, P.R.O. Barnett, and J. Watson (1986) Abyssal benthic oxygen consumption in the Northeast Atlantic: measurements using the suspended core technique. Oceanol. Acta 9, 1–7.
Premuzic, E.T., C.M. Benkovitz, J.S. Gaffney, and J.J. Walsh (1982) The nature and distribution of organic matter in the surface sediments of world oceans and seas. Org. Geochem. 4, 63–77.
Reimers, C.E., S. Kalhom, S.R. Emerson and K.H. Nealson (1984) Oxygen consumption rates in pelagic sediments from the central Pacific: First estimates from microelectrode profiles. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 48, 903–910.
Romankevich, E.A. (1984) Geochemistry of organic matter in the ocean. Springer Verlag, 334p.
Smith, K.L. Jr. (1987) Food energy supply and demand: A discrepancy between particulate organic carbon flux and sediment community oxygen consumption in the deep ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 32, 201–220.
Smith, K.L. Jr. and K.R. Hinga (1983) Sediment community respiration in the sea, in: The Sea, vol. 8, G. T. Rowe, ed., Wiley, New York.. pp. 331–370
Suess, E., P.J. Muller, H.S. Powell, and C.E. Reimers (1980) A closer look at nitrification in pelagic sediments. Geochem. J. 14, 129–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jahnke, R.A., Jackson, G.A. (1992). The Spatial Distribution of Sea Floor Oxygen Consumption in The Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. In: Rowe, G.T., Pariente, V. (eds) Deep-Sea Food Chains and the Global Carbon Cycle. NATO ASI Series, vol 360. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2452-2_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2452-2_18
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5082-1
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-2452-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive