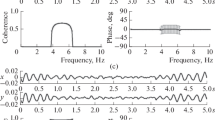
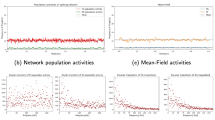
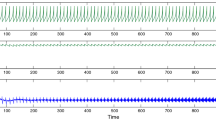
Abstract
The effect of a periodic signal and a time correlated Gaussian noise on the modified Morris-Lecar model of the CA3 region of the hippocampus is analyzed. Spatially correlated and uncorrelated forcings are used to investigate the possibility to ”anticontrol” the synchronized behavior, typical of epileptic seizures, in order to lead the system dynamics to a disordered pattern characteristic of normal brain functioning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bélair J., Glass L., Heiden U. & Milton J. [1995] “Dynamical disease: identification, temporal aspects and treatment strategies of human illness”, Chaos 5, 1–7.
Bjork, E.A. & Tacke, U. [1985] “Sounds with harmonic spectra are more effective than pure tones in inducing audiogenic seizure in rats”, Hear Res. 17, 95–98.
Bondarcnko V.E. [2002] “Control and ‘anticontrol’ of chaos in an analog neuronal network with time delay”, Chaos, Solitons and Fractals 13, 139–154.
Dabrowski A., Galias Z. & Ogorzalek M. [2000] “Observations of phase synchronization phenomena in one-dimensional arrays of coupled chaotic electronic circuits”, Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 10, 2391–2398.
Christini D.J. & Collins J.J. [1995] “Controlling nonchaotic neuronal noise using chaos control techniques”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2782–2785.
Freeman W. J. [1988] Nonlinear neural dynamics in olfaction as a model for cognition. In Dynamics of Sensory and Cognitive Processing by the Brain, E. Basar, ed. (Springer, Berlin, 1988), pp. 19–29.
Engel A.K., Roelfsema P.R., König P. & Singer W. [1997] Neurophysiological relevance of time. In Time, Temporality, Now, H. Atmanspacher and E. Ruhnau, ed., (Springer, Berlin), pp. 133–157.
Freeman W.J. & Skarda C. A. [1985] “Spatial EEG patterns, nonlinear dynamics and perception: The Neo-Sherrington view”, Brain Res. Rev. 10, 147–175.
Freeman W. J. [1994] “Neural networks and chaos”, J. Theor. BioI. 171, 13–18.
García-Ojalvo J. & Sancho J.M. Noise in spatially extended systems, (Springer-Verlag, New-York, 1999).
Glanz J. [1997] “Mastering the nonlinear brain”, Science 277, 1758–1760.
Grillner S., Wallén P., Brodin L. & Lansner A. [1991] “Neuronal network generating locomotor behavior in lamprey: circuitry, transmitters, membrane properties, and simulation”, Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 169–199.
Kelso S.J. & Fuchs A. [1995] “Self-organizing dynamics of the human brain: critical instabilities and Sil’nikov chaos”, Chaos 5, 64–69.
Kristeva-Feige R., Feige B., Makeig S., Ross B. & Elbert T. [1993] “Oscillatory brain activity during a motor task”, Neuroreport 4, 1291–1294.
Larter R., Speelman B. & Worth R.M. [1999] “A coupled ordinary differential equation lattice model for the simulation of epileptic seizures”, Chaos 9, 795–804.
Le Van Qnyen M., Martinerie J., Adam C. & Varela F.J. [1997] “Unstable periodic orbits in human epileptic seizures”, Phys. Rev. E 56, 3401–3411.
Lorenzo M.N. & Pérez-Muñuzuri V. [2001] “Influence of low intensity noise on assemblies of diffusively coupled chaotic cells”, Chaos 11, 371–376.
Montejo N., Lorenzo M.N., Pérez-Muñuzuri V. & Pérea-Villar V. [2002] “Clustering and Synchronization in a One-Dimensional Model for the CA3 Region of the Hippocampus”, Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 12.
Morris C. & Lecar H. [1981] “Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber”, Biophys. J. 35, 193–213.
Murthy V.N. & Fetz E.E. [1992] “Coherent 25-to 35-Hz oscillations in the sensorimotor cortex of the awake monkeys”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5670–5674.
Pierson, M. & Liebman, S.L. [1992] “Noise exposure-induced audiogenic seizure susceptibility in Sprague-Dawley rats”, Epilepsy Res. 13, 35–42.
Schiff S.J., Jerger H., Duong D.H., Chang T., Spano M.L. & Ditto W.L. [1994] “Controlling chaos in the brain”, Nature 370, 615–620.
Singer W., and Gray C.M. [1995] “Visual feature integration and temporal correlation hypothesis”, Anon. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 555–586.
Traub R.D. & Miles R. [1991] Neuronal Networks of the hippocampus Cambridge University Press.
Wilson H.R. & Cowan J. D. [1972] “Excitatory and inhibitory interaction of localized populations of model neurons”, Biophys. J. 12, 1–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Montejo, N., Lorenzo, M.N., Pérez-Muñuzuri, V., Pérez-Villar, V. (2004). On the Effect of Time Correlated Noise and Periodic Forcing on a Neuronal System. In: Descalzi, O., Martínez, J., Rica, S. (eds) Instabilities and Nonequilibrium Structures IX. Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems, vol 9. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0991-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0991-1_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-3760-0
Online ISBN: 978-94-007-0991-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive