Abstract
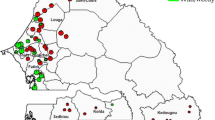
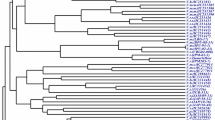
The Mediterranean Basin is a major region of lucerne (Medicago sativa) cultivation. We used seven microsatellite markers to evaluate within-population diversity and test differentiation among lucerne populations from the Mediterranean Basin. A set of 16 populations from France, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Australia and the USA, each represented by 30 individuals, was analysed for seven microsatellite markers. One marker was excluded from the analyses because of presence of null alleles. Number of alleles and expected heterozygozity were calculated to evaluate within-population diversity. FIS was calculated to test departure of populations from panmictic equilibrium. Population structure was analysed by the calculation of FST index. Within-population genetic diversity was large in all populations, and the populations appeared to be at panmictic equilibrium. Global FST was significant but very low (0.016). Three groups were identified, one composed by only Gabes, a second group composed by three North African populations, the two Australian cultivars, one American cultivar and one European population and a third group with six European populations, one Moroccan population and one American cultivar. Differentiation among populations was limited, which could be explained by the numerous possibilities of gene flow among populations, such as seed exchange or pollen flux. Reproductive biology (allogamy) and genetics (autotetraploidy) favour the maintenance of large within-population diversity and limits the possibility of population differentiation for neutral markers. This relative lack of differentiation with neutral markers is observed while the populations are known to noticeably differ for agronomic traits.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flajoulot, S., Ronfort, J., Baudouin, P., Barre, P., Huguet, T., Huyghe, C., Julier, B. 2008. Genetic diversity among alfalfa (Medicago sativa) cultivars coming from a breeding program, using SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 111:1420–1429.
Hardy, O.J., Vekemans X. 2002. SPAGeDi: A versatile computer program to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2:618–620.
Herrmann, D., Flajoulot, S., Barre, P., Huyghe, C., Ronfort, J., Julier, B. 2008. Comparison of morphological traits and SSR to analyse diversity and structure of alfalfa cultivars. North American Alfalfa Improvement Conference, Dallas.
Julier, B., Porcheron, A., Ecalle, C., Guy, P. 1995. Genetic variability for morphology, growth and forage yield among perennial diploid and tetraploid lucerne populations (Medicago sativa L.). Agronomie 15:295–304.
Ronfort, J., Jenczewski, E., Bataillon, T., Rousset, F. 1998. Analysis of population structure in autotetraploid species. Genetics 150:921–930.
Thrall, P.H., Young, A. 2000. AUTOTET: A program for analysis of autotetraploid genotypic data. J. Hered. 91:348–349.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by European Union, program INCO PERMED (Improvement of native PERennial forage plants for sustainibility of MEDiterranean farming systems), 2004–2009. We thank Mounawer Badri (CBBC, Tunisia) for DNA extraction, Chrystel Gibelin and Denise Cadier for genotyping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Julier, B., Semiani, Y., Laouar, M. (2010). Genetic Diversity in a Collection of Lucerne Populations from the Mediterranean Basin Evaluated by SSR Markers. In: Huyghe, C. (eds) Sustainable use of Genetic Diversity in Forage and Turf Breeding. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-8706-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-8706-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-8705-8
Online ISBN: 978-90-481-8706-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)