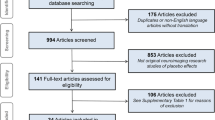
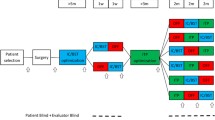
Samenvatting
Vanwege toegenomen inzichten in de pathofysiologie en de gerapporteerde effecten van diepe hersenstimulatie (‘deep brain stimulation’, DBS) op stemmingsklachten bij aandoeningen als de ziekte van Parkinson en de obsessieve-compulsieve stoornis, wordt DBS ook onderzocht als behandelmogelijkheid voor patiënten met een depressieve stoornis. Het gaat daarbij om therapieresistente depressieve patiënten die niet hersteld zijn met eerdere psychotherapeutische en farmacologische behandelingen. In tegenstelling tot eerder gepubliceerd open onderzoek, liet een gerandomiseerde klinische trial geen therapeutisch effect zien van stimulatie van de ventrale capsula interna/ventraal striatum (VC/VS). Ook eerder werden twee gerandomiseerde onderzoeken, één met betrekking tot stimulatie van de VC/VS en één met betrekking tot stimulatie van de subgenuale gyrus cinguli, voortijdig afgebroken vanwege gebrek aan effectiviteit. Hoewel de depressieve stoornis als potentiële behandelindicatie voor DBS aantrekkelijk blijft, past deze behandeling vooralsnog niet in een regulier behandelaanbod, en dient zij alleen aangeboden te worden als experimentele behandeling of in het kader van wetenschappelijk onderzoek.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatuur
Joyce PR. Epidemiology of mood disorders. In: Gelder MG, Lopez-Ibor Jr JJ, Andreassen NC, Eds. New Oxford textbook of psychiatry. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000. p. 695–700.
World Health Association. 2015. http://www.who.int/mental_health/management/depression/who_paper_depression_wfmh_2012.pdf. Geraadpleegd op 8 januari 2015.
Global Burden of Disease Study. collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2013;2015(386):743–800.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM IV). 4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders (DSM 5). 5th ed. Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Richtlijncommissie Depressie. Multidisciplinaire richtlijn depressie. Utrecht: Trimbos-instituut; 2005.
Richtlijncommissie elektroconvulsietherapie. Richtlijn elektroconvulsietherapie. Amsterdam: Nederlandse Vereniging voor Psychiatrie; 2000.
Baumeister AA. The Tulane Electrical Brain Stimulation Program; a historical case study in medical ethics. J Hist Neurosci. 2000;9:262–78.
Hariz MI, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L. Deep brain stimulation between 1947 and 1987: the untold story. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;29:E1.
Laitinen LV. Ethical aspects of psychiatric surgery. In: Sweet WH, Obrador S, Martin-Rodriguez JG, Eds. Neurosurgical treatment in psychiatry, pain and epilepsy. Baltimore: University Park Press; 1977. p. 483–8.
Bejjani BP, Arnulf I, Thivard L, et al. Transient acute depression by high-frequency deep-brain stimulation. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1476–80.
Temel Y, Kessels A, Tan S, Topdag A, Boon P, Visser-Vandewalle V. Behavioural changes after bilateral subthalamic stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006;12:265–72.
Berney A, Vingerhoets F, Perrin A, et al. Effect on mood of subthalamic DBS for Parkinson’s disease: a consecutive series of 24 patients. Neurology 2002;5:1427–9.
Tan SKH, Hartung H, Visser-Vandewalle V, Steinbusch HWM, Temel Y, Sharp T. A combined in vivo neurochemical and electrophysiological analysis of the effect of high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on 5-HT transmission. Exp Neurol. 2012;233:145–53.
Temel Y, Boothman LJ, Blokland A, et al. Inhibition of 5-HT neuron activity and induction of depressive-like behavior by high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:17087–92.
Voon V, Kubu C, Krack P, Houeto JL, Tröster AI. Deep brain stimulation: neuropsychological and neuropsychiatric issues. Mov Disord. 2006;21(suppl 14):S305–27.
Gabriëls L, Cosyns P, Nuttin B, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: psychopathological and neuropsychological outcome in three cases. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2003;107:275–82.
Greenberg BD, Malone DA, Friehs GM, et al. Three-year outcomes in deep brain stimulation for highly resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006;31:2384–93.
Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–81.
Mayberg HS. Limbic-cortical dysregulation: a proposed model of depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997;9:471–81.
Morishita T, Fayad SM, Higuchi MA, Nestor KA, Foote KD. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: systematic review of clinical outcomes. Neurotherapeutics. 2014;11:475–84.
Fitzgerald PB, Laird AR, Maller J, Daskalakis ZJ. A meta-analytic study of changes in brain activation in depression. Human Brain Mapp. 2008;29:683–95.
Sacher J, Neumann J, Funfstuck T, Soliman A, Villringer A, Schroeter ML. Mapping the depressed brain: a meta-analysis of structural and functional alterations in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 2012;140:142–8.
Bewernick BH, Hurlemann R, Matusch A, et al. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:110–6.
Delaveau P, Jabourian M, Lemogne C, Guionnet S, Bergouignan L, Fossati P. Brain effects of antidepressants in major depression: a meta-analysis of emotional processing studies. J Affect Disord. 2011;130:66–74.
Berlim MT, McGirr A, Eynde F van den, Fleck MP, Giacobbe P. Effectiveness and acceptability of deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subgenual cingulate cortex for treatment-resistant depression: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2014;159:31–8.
Hamani C, Mayberg H, Snyder B, Giacobbe P, Kennedy S, Lozano AM. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus for depression: anatomical location of active contacts in clinical responders and a suggested guideline for targeting. J Neurosurg. 2009;111:1209–15.
Kennedy SH, Giacobbe P, Rizvi SJ, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: follow-up after 3 to 6 years. Am J Psychiatry 2011;168:502–10.
Lozano AM, Mayberg HS, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Craddock RC, Kennedy SH. Subcallosal cingulate gyrus deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:461–7.
Malone DA Jr. Use of deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression. Clevel Clin J Med. 2010;77(Suppl 3):S77–80.
Malone DA Jr, Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:267–75.
Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Howland RH, Bhati MT, O’Reardon JP, et al. A randomized sham-controlled trial of deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for chronic treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;78:240–8.
Strong DR, Haber SN, Tyrka AR, Bernier JA, Rassmussen SA, Greenberg BD. Reversible increase in smoking after withdrawal of ventral capsule/ventral striatum deep brain stimulation in a depressed smoker. J Addict Med. 2012;6:94–5.
Underwood E. Short-circuiting depression. Science. 2013;342(6158):548–51.
Jimenez F, Velasco F, Salin-Pascual R, et al. A patient with a resistant major depression disorder treated with deep brain stimulation in the inferior thalamic peduncle. Neurosurgery 2005;57:585–93.
Sartorius A, Kiening KL, Kirsch P, et al. Remission of major depression under deep brain stimulation of the lateral habenula in a therapy-refractory patient. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:e9–e11.
Schlaepfer TE, Bewernick BH, Kayser S, Madler B, Coenen VA. Rapid effects of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:1204–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Copyright information
© 2016 Bohn Stafleu van Loghum
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Leentjens, A., Temel, Y. (2016). Diepe hersenstimulatie bij medicatieresistente depressies. In: Temel, Y., Leentjens, A., de Bie, R. (eds) Handboek diepe hersenstimulatie bij neurologische en psychiatrische aandoeningen. Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-368-0959-7_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-368-0959-7_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum, Houten
Print ISBN: 978-90-368-0958-0
Online ISBN: 978-90-368-0959-7
eBook Packages: Dutch language eBook collection