Abstract
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that is not fully reversible. It is a highly complex disease in which both environmental exposures and host susceptibility factors should be taken into account in its management. Although cigarette smoke is the major risk factor, quitting smoking does not fully repress the airway inflammation and restore the lost lung function.
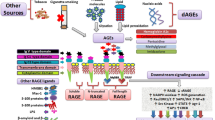
Our group has been interested in changes of glycosylation that are related to the onset, biomarker discovery, and therapeutics of various diseases including cancer, neurological disease, and lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes and COPD. Changes in glycan structures are currently being used as cancer biomarkers, prognosis, and treatment of the disease. Cell membrane receptors are mostly glycosylated proteins, and changes in the glycosylation of them have been shown to lead to dysfunctions in downstream signal pathways.
In COPD, alterations in the structures of glycans lead to dysfunction of receptor molecules, such as the TGF-beta receptor related to the upregulation of protease, or result in alterations in mucus viscosity and impaired mucociliary transport. Although the mechanism responsible for this is still uncertain, it appears that environmental factors such as exposure to cigarette smoke, pollutants, and bacteria/virus infections can alter the activities of some glycosyltransferases, and eventually this may affect the synthesis of glycans. Here, we show some glycan structures and relationships with the pathogenesis of COPD. Our recent findings regarding the role of glycan changes in COPD may open a new avenue toward the development of glycotherapeutics for COPD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang J, Patton JT, Sarkar A, Ernst B, Magnani JL, Frenette PS (2010) GMI-1070, a novel pan-selectin antagonist, reverses acute vascular occlusions in sickle cell mice. Blood 2010(116):1779–1786
Gao C, Maeno T, Ota F, Ueno M, Korekane H, Takamatsu S, Shirato K, Matsumoto A, Kobayashi S, Yoshida K, Kitazume S, Ohtsubo K, Betsuyaku T, Taniguchi N (2012) Sensitivity of heterozygous alpha1, 6-fucosyltransferase knock-out mice to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema: implication of aberrant transforming growth factor-beta signaling and matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Biol Chem 287:16699–16708
Ishibashi Y, Inouye Y, Okano T, Taniguchi A (2005) Regulation of sialyl-Lewis x epitope expression by TNF-alpha and EGF in an airway carcinoma cell line. Glycoconj J 22:53–62
Kamio K, Yoshida T, Gao C, Ishii T, Ota F, Motegi T, Kobayashi S, Fujinawa R, Ohtsubo K, Kitazume S, Angata T, Azuma A, Gemma A, Nishimura M, Betsuyaku T, Kida K, Taniguchi N (2012) alpha1, 6-Fucosyltransferase (Fut8) is implicated in vulnerability to elastase-induced emphysema in mice and a possible non-invasive predictive marker for disease progression and exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 424:112–117
Knezevic A, Gornik O, Polasek O, Pucic M, Redzic I, Novokmet M, Rudd PM, Wright AF, Campbell H, Rudan I, Lauc G (2010) Effects of aging, body mass index, plasma lipid profiles, and smoking on human plasma N-glycans. Glycobiology 20:959–969
Nonaka M, Bao X, Matsumura F, Götze S, Kandasamy J, Kononov A, Broide DH, Nakayama J, Seeberger PH, Fukuda M (2014) Synthetic di-sulfated iduronic acid attenuates asthmatic response by blocking T-cell recruitment to inflammatory sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(22):8173–8178
Shinkawa T, Nakamura K, Yamane N, Shoji-Hosaka E, Kanda Y, Sakurada M, Uchida K, Anazawa H, Satoh M, Yamasaki M, Hanai N, Shitara K (2003) The absence of fucose but not the presence of galactose or bisecting N-acetylglucosamine of human IgG1 complex-type oligosaccharides shows the critical role of enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 278:3466–3473
Shirato K, Gao C, Ota F, Angata T, Shogomori H, Ohtsubo K, Yoshida K, Lepenies B, Taniguchi N (2013) Flagellin/Toll-like receptor 5 response was specifically attenuated by keratan sulfate disaccharide via decreased EGFR phosphorylation in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435:460–465
Wang X, Inoue S, Gu J, Miyoshi E, Noda K, Li W, Mizuno-Horikawa Y, Nakano M, Asahi M, Takahashi M, Uozumi N, Ihara S, Lee SH, Ikeda Y, Yamaguchi Y, Aze Y, Tomiyama Y, Fujii J, Suzuki K, Kondo A, Shapiro SD, Lopez-Otin C, Kuwaki T, Okabe M, Honke K, Taniguchi N (2005) Dysregulation of TGF-beta1 receptor activation leads to abnormal lung development and emphysema-like phenotype in core fucose-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15791–15796
Wang X, Gu J, Ihara H, Miyoshi E, Honke K, Taniguchi N (2006) Core fucosylation regulates epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated intracellular signaling. J Biol Chem 281:2572–2577
Wang X, Fukuda T, Li W, Gao CX, Kondo A, Matsumoto A, Miyoshi E, Taniguchi N, Gu J (2009) Requirement of Fut8 for the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: a new mechanism for the emphysema-like changes observed in Fut8-deficient mice. J Biochem 145:643–651
Xia B, Royall JA, Damera G, Sachdev GP, Cummings RD (2005) Altered O-glycosylation and sulfation of airway mucins associated with cystic fibrosis. Glycobiology 15:747–775
Yamada M, Ishii T, Ikeda S et al (2011) Association of fucosyltransferase 8 (FUT8) polymorphism Thr267Lys with pulmonary emphysema. J Hum Genet 56(12):857–860
Zhao Y, Itoh S, Wang X, Isaji T, Miyoshi E, Kariya Y, Miyazaki K, Kawasaki N, Taniguchi N, Gu J (2006) Deletion of core fucosylation on alpha3beta1 integrin down-regulates its functions. J Biol Chem 281:38343–38350
Acknowledgments
Most of the studies on COPD were supported in part by the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gao, C., Taniguchi, N. (2015). Glycans and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). In: Suzuki, T., Ohtsubo, K., Taniguchi, N. (eds) Sugar Chains. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55381-6_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55381-6_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55380-9
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55381-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)