Abstract
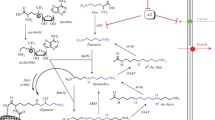
Long-chain and/or branched polyamines such as N 4-aminopropylspermidine [3(3)4] (abbreviation for the number of methylene CH2 chain units between NH2, NH, N, or N+), N 4-bis(aminopropyl)spermidine [3(3)(3)4], and tetrakis(3-aminopropyl)ammonium [3(3)(3)3] are polycations of biotic origin that are only found in thermophiles. The thermophilic bacterium Thermus thermophilus and the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis synthesize a polyamine, spermidine, via conversion of arginine to agmatine (a step catalyzed by arginine decarboxylase), aminopropylation of agmatine to N 1-aminopropylagmatine (catalyzed by aminopropyl transferase), and hydrolysis of N 1-aminopropylagmatine to spermidine by N 1-aminopropylagmatine ureohydrolase. It is noteworthy that thermophiles synthesize spermidine without producing putrescine as an intermediate. Spermidine can be modified to produce further polyamides such as N 4-aminopropylspermidine [3(3)4] and then N 4-bis(aminopropyl)spermidine by an enzyme coded by the TK1691 gene in T. kodakarensis. TK1691 and its orthologues are found in (hyper)thermophilic Archaea and Bacteria, but not in mesophilic Bacteria. TK1691 is a recently characterized aminopropyl transferase involved in the synthesis of branched polyamines, which are essential for the stabilization and structural protection of nucleic acids and which enhance polypeptide synthesis at high temperature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bale S, Ealick SE (2010) Structural biology of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase. Amino Acids 38:451–460
Cacciapuoti G, Porcelli M, De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Bertoldo C, Zappia V (1991) S-Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase from the thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Purification, molecular properties and studies on the covalently bound pyruvate. Eur J Biochem 199:395–400
Cacciapuoti G, Porcelli M, Moretti MA, Sorrentino F, Concilio L, Zappia V et al (2007) The first agmatine/cadaverine aminopropyl transferase: biochemical and structural characterization of an enzyme involved in polyamine biosynthesis in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Bacteriol 189:6057–6067
Fukuda W, Morimoto N, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2008) Agmatine is essential for the cell growth of Thermococcus kodakaraensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 287:113–120
Fukui T, Atomi H, Kanai T, Matsumi R, Fujiwara S, Imanaka T (2005) Complete genome sequence of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1 and comparison with Pyrococcus genomes. Genome Res 15:352–363
Giles TN, Graham DE (2008) Crenarchaeal arginine decarboxylase evolved from an S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase enzyme. J Biol Chem 283:25829–25838
Graham DE, Xu H, White RH (2002) Methanococcus jannaschii uses a pyruvoyl-dependent arginine decarboxylase in polyamine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 277:23500–23507
Hamana K, Matsuzaki S (1985) Further study on polyamines in primitive unicellular eukaryotic algae. J Biochem 97:1311–1315
Hamana K, Matsuzaki S (1992) Polyamines as a chemotaxonomic marker in bacterial systematics. Crit Rev Microbiol 18:261–283
Ikeuchi Y, Kimura S, Numata T, Nakamura D, Yokogawa T, Ogata T et al (2010) Agmatine-conjugated cytidine in a tRNA anticodon is essential for AUA decoding in archaea. Nat Chem Biol 6:277–282
Imai A, Matsuyama T, Hanzawa Y, Akiyama T, Tamaoki M, Saji H et al (2004) Spermidine synthase genes are essential for survival of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 135:1565–1573
Kim AD, Graham DE, Seeholzer SH, Markham GD (2000) S-Adenosylmethionine decarboxylase from the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii: identification of a novel family of pyruvoyl enzymes. J Bacteriol 182:6667–6672
Knott JM (2009) Biosynthesis of long-chain polyamines by crenarchaeal polyamine synthases from Hyperthermus butylicus and Pyrobaculum aerophilum. FEBS Lett 583:3519–3524
Knott JM, Romer P, Sumper M (2007) Putative spermine synthases from Thalassiosira pseudonana and Arabidopsis thaliana synthesize thermospermine rather than spermine. FEBS Lett 581:3081–3086
Lu ZJ, Markham GD (2004) Catalytic properties of the archaeal S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase from Methanococcus jannaschii. J Biol Chem 279:265–273
Morimoto N, Fukuda W, Nakajima N, Masuda T, Terui Y, Kanai T et al (2010) Dual biosynthesis pathway for longer-chain polyamines in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. J Bacteriol 192:4991–5001
Ohnuma M, Terui Y, Tamakoshi M, Mitome H, Niitsu M, Samejima K et al (2005) N1-Aminopropylagmatine, a new polyamine produced as a key intermediate in polyamine biosynthesis of an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus. J Biol Chem 280:30073–30082
Okada K, Hidese R, Fukuda W, Niitsu M, Takao K, Horai Y, Umezawa N, Higuchi T, Oshima T, Yoshikawa Y, Imanaka T, Fujiwara S (2014) Identification of a novel aminopropyltransferase involved in the synthesis of branched-chain polyamines in hyperthermophiles. J Bacteriol 196:1866–1876
Rhee HJ, Kim EJ, Lee JK (2007) Physiological polyamines: simple primordial stress molecules. J Cell Mol Med 11:685–703
Sato T, Atomi H (2011) Novel metabolic pathways in Archaea. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:307–314
Schneider J, Wendisch VF (2011) Biotechnological production of polyamines by bacteria: recent achievements and future perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:17–30
Stetter KO (1996) Hyperthermophilic procaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 18:149–158
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1985) Polyamines in microorganisms. Microbiol Rev 49:81–99
Terui Y, Ohnuma M, Hiraga K, Kawashima E, Oshima T (2005) Stabilization of nucleic acids by unusual polyamines produced by an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus. Biochem J 388:427–433
Tolbert WD, Graham DE, White RH, Ealick SE (2003) Pyruvoyl-dependent arginine decarboxylase from Methanococcus jannaschii: crystal structures of the self-cleaved and S53A proenzyme forms. Structure 11:285–294
Uzawa T, Hamasaki N, Oshima T (1993) Effects of novel polyamines on cell-free polypeptide synthesis catalyzed by Thermus thermophilus HB8 extract. J Biochem (Tokyo) 114:478–486
van Poelje PD, Snell EE (1990) Pyruvoyl-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 59:29–59
Wallace HM, Fraser AV, Hughes A (2003) A perspective of polyamine metabolism. Biochem J 376:1–14
Yang Z, Lu CD (2007) Functional genomics enables identification of genes of the arginine transaminase pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:3945–3953
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Fukuda, W., Hidese, R., Fujiwara, S. (2015). Long-Chain and Branched Polyamines in Thermophilic Microbes. In: Kusano, T., Suzuki, H. (eds) Polyamines. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55212-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55212-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-55211-6
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-55212-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)