Abstract
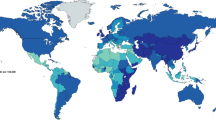
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer worldwide and the sixth most common cause of death from cancer. More than 80 % of esophageal cancer cases and deaths occur in developing countries, and approximately 90 % are squamous cell carcinomas in the high-incidence regions. The incidence rates of esophageal cancer show wide variation internationally. It has been shown to be two to four times more common among men than women in general; however in Japan it is approximately seven times more common among males. Both incidence and mortality are on the rise since 1960 due to the aging Japanese population, while age-adjusted rates are consistently decreasing with the exception of the increasing male incidence rate. Established risk factors for esophageal squamous carcinoma include tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption, while fruit and vegetable intake show high probability in preventing esophageal cancer. Likewise, intake of high-temperature beverages and foods show high probability of increasing risk through heat damage in the esophagus. Approximately 88 % of male esophageal cancer (52 % for females) in Japan is thought to have been avoidable by lifestyle improvement such as refraining from smoking of tobacco and alcohol use, while maintaining sufficient fruit and vegetable intake.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) GLOBOCAN 2008 v2.0, Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 10 [Internet]. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. http://globocan.iarc.fr. Accessed 15 Aug 2013
Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, Storm H, Ferlay J, Heanue M, Boyle P (eds) (2007) Cancer incidence in five continents, vol IX. IARC Scientific Publications No. 160, International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. http://ci5.iarc.fr/CI5i-ix/ci5i-ix.htm. Accessed 15 Aug 2013
Shibata A, Matsuda T, Ajiki W, Sobue T (2008) Trend in incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus in Japan, 1993–2001. Jpn J Clin Oncol 38:464–468
Kusano C, Gotoda T, Khor CJ et al (2008) Changing trends in the proportion of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction in a large tertiary referral center in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:1662–1665
World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (2007) Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective. World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research, Washington, DC
Adami HO, Hunter DJ, Trichopoulos D (2002) Textbook of cancer epidemiology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Oze I, Matsuo K, Ito H et al (2012) Cigarette smoking and esophageal cancer risk: an evaluation based on a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence among the Japanese population. Jpn J Clin Oncol 42:63–73
Oze I, Matsuo K, Wakai K et al (2011) Alcohol drinking and esophageal cancer risk: an evaluation based on a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence among the japanese population. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:677–692
Ishiguro S, Sasazuki S, Inoue M et al (2009) Effect of alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking and flushing response on esophageal cancer risk: a population-based cohort study (JPHC study). Cancer Lett 275:240–246
Yang S-J, Yokoyama A, Yokoyama T et al (2010) Relationship between genetic polymorphisms of ALDH2 and ADH1B and esophageal cancer risk: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 16:4210–4220
Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K et al (2012) Genome-wide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple. Nat Genet 44:1090–1098
Yamaji T, Inoue M, Sasazuki S et al (2008) Fruit and vegetable consumption and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus in Japan: the JPHC study. Int J Cancer 123:1935–1940
Sharp L, Chilvers CE, Cheng KK et al (2001) Risk factors for squamous-cell carcinoma of the oesophagus in women: a case–control study. Br J Cancer 85:1667–1670
Kinjo Y, Cui Y, Akiba S et al (1998) Mortality risks of oesophageal cancer associated with hot tea, alcohol, tobacco and diet in Japan. J Epidemiol 8:235–243
Ishikawa A, Kuriyama S, Tsubono Y et al (2006) Smoking, alcohol drinking, green tea consumption and the risk of esophageal cancer in Japanese men. J Epidemiol 16:185–192
Inoue M, Sawada N, Matsuda T et al (2012) Attributable causes of cancer in Japan in 2005—systematic assessment to estimate current burden of cancer attributable to known preventable risk factors in Japan. Ann Oncol 23:1362–1369
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Japan
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tsugane, S. (2015). Epidemiology of ESCC. In: Ando, N. (eds) Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54977-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-54977-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-54976-5
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-54977-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)