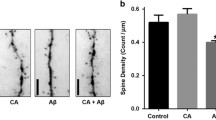
Summary
Several lines of evidence indicate that Aβ may play an important role in the pathogenesis of AD. However, there are several discrepancies between the production of Aβ and the development of the disease.
Thus, Aβ may not be the sole active fragment of β-amyloid precursor protein (βAPP) in the neurotoxicity assiciated with AD.
We focused on the amyloidegenic carboxyl terminal fragments of βAPP containing the full length of Aβ (CT105). We synthesized a recombinant carboxyl-terminal 105 amino acid fragment of βAPP and examined the effects of CT105 and Aβ on cultured neurons, Ca++ uptake into rat brain microsomes, Na+ -Ca++ exchange activity, ion channel forming activity in lipid bilayers and passive avoidance performance of mice.
Our results suggest that the cytotoxic and channel inducing effects of CT105 are much more potent than that of Aβ and toxic mechanisms of CT105 are different from those of Aβ.
Taken together, these lines of evidence postulate that CT is an alternative toxic element important in the generation of the symptoms common to AD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arispe N, Rojas E, Pollard H.B. (1993) Alzheimer disease amyloid beta protein forms calcium channels in bilayer membranes: blockade by tromethamine and aluminum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(2): 567–571
Bhadkdi S, Tranum J.J. (1987) Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 107: 147–223
Caputo C.B., Sobel I.R., Scott C.W., Brunner W.F., Barth P.T., Blowers D.P. (1992) Association of the carboxy-terminus of beta-amyloid protein precursor with Alzheimer paired helical filaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 185: 1034–1040
Cheder F (1995) Processing of the β-amyloid precursor protein and its regulation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 65: 1431–1444
Chung Y.H., Jung J.M., Choi W, Park C.H., Choi K.S., Suh Y.H. (1994) Bacterial expression, purification of full length and carboxy terminal fragment of Alzheimer’s precusor protein and their proteolytic processing by thrombin. Life Sci 54: 1259–1268
Cullen W.K., Suh Y.H., Anwyl R, Rowan M.J. (1997) Block of late-phase long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus in vivo by β-amyloid precursor protein fragments. Neuroreport 8: 3213–3217
Chow N, Korenberg J.R., Chen X.N., Neve R.L. (1996) APP-BPI, a novel protein that binds to the caryboxy-teriminal region of the amyloid protein precusor. J Biol Chem 271:11339-11346
Clemens J.A., Stephenson DT (1992) Implants containing beta-amyloid protein are not neurotoxic to young and old rat brain. Neurobiol Aging 13: 581–586
Drake L, Korchev Y, Bashford L, Djamgoz M, Wakelin D, Ashall F, Bundy D (1994) The major secreted product of the whipworm, Trichuris, is a pore-forming protein. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 257: 255–261
Duffy P.E., Rapport M, Graf L (1980) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and Alzheimer-type senile dementia. Neurology 30: 778–782
Dyrks T, Dyrks E, Hartmann T, Masters C, Bryreuther K (1992) Amyloidogenicity of βA4 and βA4-bearing amyloid protein precursor fragments by metal-catalyzed oxidation. J Biol Chem 267: 18210–18217
Edelman A.M., Hunter D.D., Hendrickson A.E., Krebs E.G. (1985) Subcellular distribution of calcium- and calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain phosphorylating activity in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 5(10): 2609–2617
Estus S, Coide T.E., Kunishita T.L., Blades D, Lowery D, Eisen J, Usiak M, Tabira T.L., Greenberg B.D., Younkin S.G. (1992) Potentially amyloidogenic, carboxyl-terminal derivatives of the amyloid protein precursor. Science 255: 726–728
Fraser S, Suh Y.H., Chong Y.H., Djamgoz M.A. (1996) Membrane currents induced in Xenopus oocytes by the carboxyl terminal fragment of the β-amyloid precursor protein. J Neurochem 66: 2034–2040
Fraser S.P., Suh Y.H., Djamgoz M.B.A. (1997) Ionic effects of the Alzheimer’s disease βamyloid precursor protein and its metabolic fragments. Trends Neurosci 20: 67–72
Fukuchi K, Kamino K, Deeb S.S., Furlong C.E., Sundstrom J.A., Smith A.C., Martin G.M. (1992) Expression of a carboxy-terminal region of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in a heterogeneous culture of neuroblastoma cells: evidence for altered processing and selective neurotoxicity. Mol Brain Res 16: 37–46
Fukuchi K, Sopher B, Martin G.M. (1993a) Neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid. Nature 361:122–123
Fukuchi K, Sopher B, Furlong C.E., Smith A.C., Dnag T, Martin G.M. (1993b) Selective neurotoxicity of COOH-terminal fragments of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in mouse brains by transplantation of transformed neuronal cells. Exp Neurol 127: 253–264
Fukuchi K, Kunkel D.D., Schwartzkroin P.A., Kamino K, Ogburn C.E., Furlong C.E., Martin G.M. (1994) Overexpression of a C-terminal portion of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in mouse brains by transplantation of transformed neuronal cells. Exp Neurol 127:253–264
Games D, Khan K.M., Soriano F.G., Keirn P.S., Davis D.L., Bryant K, Lieberburg I (1992) Lack of Alzheimer’s pathology after β-amyloid protein injections in rat brain.Neurobiol Aging 13: 569–576
Glenner G.G., Wong C.W. (1984) Alzheimer’s disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120: 885–890
Golde T.E., Estus S, Younkin L.H., Selkoe D.J., Younkin S.G. (1992) Processing of the amyloid protein precursor to potentially amyloidogenic derivatives. Sciences 255:728–730
Hartell N.A., Suh Y.H., Lee K.W. (1996) Effects of peptide fragments of APP on parallel fiber-purkinje cell synaptic transmission in rat cerebellum. Degenerative disease: Alzheimer’s Beta-Amyloid-Membrane Interactions. 26th Annual Meeting of Society for Neuroscience, Washington 1996, Abstract 22 (Part 3): p 2110
Kametani F, Tanaka K, Tokuda T, Ikeda S (1994) Secretory cleavage site of Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein in heterogeneous in Down’s syndrome brain. FEBS Lett 351: 165–167
Kammeshidt A, Boyce F.M., Spanoyannis A.F., Cummings B.J., Ortegon J, Cotman C, Vaught J.L., Neve R.L. (1992) Desposition of beta/A4 immunoreactivity and neuronal pathology in transgenic mice expressing the carboxyl-terminal fragment of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10857–10861
Kang J, Lemaire H.G., Unterbeck A, Salbaum M.N., Masters C.L., Grzeschik K.H., Multhaup C, Beyreuther K, Muller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell surface receptor. Nature 325: 733–736
Kijima Y, Ogunbummi E, Fleischer S (1991) Drug action of thapsigargin on the Ca2+ pump protein of Sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 266(34): 22912–22918
Kim H.J., Suh Y.H., Lee M.H., Ryu P.D. (1996) C-terminal fragment of the β amyloidal precursor protein forms cation selective channels in planar lipid bilayer. Degenerative disease: Alzheimer’s Beta-Amyloid-Membrane Interactions. 26th Annual Meeting of Society for Neuroscience, Washington 1996, Abstract 22 (Part 3): p 2110
Kim S.H., Suh Y.H. (1996) Neurotoxicity of a caroboxy teiminal fragment of the Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. J Neurochem 67: 1172–1182
Kozlowski M.R., Spanoyannis A.L., Manly S.P., Fidel S.A., Neve R.L. (1992) The neurotoxic carboxy-terminal fragment of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor binds specifically to a neuronal cell surface molecule: pH dependence of the neurotoxicity and the binding. J Neurosci 12: 1679–1687
Laursen S.E., Belknap J.K. (1986) Intracerebroventricular injections in mice. Some methodolegical refinements. J Pharmacol Methods 16: 355–357
Leyser H.M.O., Lincoln C.A., Timpte C, Lammer D, Turner J, Estelle M (1993) Arabidopsis auxin-resistance gene AXR1 encodes a protein related to ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1. Nature 364: 161–164
Matsumoto A (1994) Altered processing characteristics of amyloid-coataining peptides in cytosol and media of familial Alzheime’s disease cells. Biochem Biophys Acta 1225:304–310
Matsumoto A, Matsumoto R (1994) Familial Alzheimer’s disease cells abnormal abnormally accumulate beta-amyloid harbouring peptides preferentially in cytosol but not in extracellar fluid. Eur J Biochem 225: 1055–1062
McPhie D.L., Lee R.K.K., Eckman C.B., Olstein D.H., Durham S.P., Yager D, Younkin S.G., Wurtman R.J., Neve R.L. (1997) Neuronal expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein Alzheimer mutations causes intracellular accumulation of a C-terminal fragment containing both the amyloid beta and cytoplasmic domains. J Biol Chem 272(40):24743–24746
Nalbantoglu J, Tirado-Santiago G, Lahsaini A, Poirier J, Gonocalves O, Verge G, Momoli F, Weiner S.A., Massicotte G, Jullien J.P., Shapiro M.L. (1997) Impaired learning and LTP in mice expressing the carboxy terminus of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein. Nature 387: 500–505
Palade P, Dettbarn C, Volpe P, Alderson B, Otero A.S. (1989) Direct inhibition of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from brain microsomes by K+ channel blockers. Mol Pharmacol 36(4): 664–672
Pike C.J., Cummings B.J., Cotman C.W. (1995) Early association of reactive astrocytes with senile palques in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 132: 172–179
Podlisny M.B., Stephenson D.T., Frosch M.P., Tolan D.R., Lieberburg I, Clemens JA, Selkoe DJ (1993) Microinjection of synthetic amyloid beta-protein monkey cerebral cortex fails to produce acute neurotoxicity. Am J Pathol 142: 17–24
Potter H (1992) The involvement of astrocytes and an acute phase response in the amyloid deposition of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Brain Res 94: 447–458
Selkoe D.J. (1994) Alzheimer’s disease: a central role for amyloid. J Neuropathol Exp Neurosci 60: 607–619
Selkoe D.J., Podlisny M.B., Joachim C.L., Vickers E.A., Lee G, Friz LC, Oltersdorf T (1988) Beta-amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease occurs as 110- to 135-kilodalton membrane-associated proteins in neuronal and nonneural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7341–7345
Shearman M.S., Hawtin S.R., Tailor V.J. (1995) The intracellular component of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction is specifically inhibited by beta-amyloid peptides. J Neurochem 65(1): 218–227
Song D.K., Won M.H., Jung J.S., Lee J.C., Kang T.C., Suh H.W., Huh S.O., Paek S.H., Kim Y.H., Kim S.H., Suh Y.H. (1998) Behavioral and neuropathologic changes induced by central injection of carboxyl-terminal fragment of beta-amyloid precursor protein in mice. J Neurochem 71(2): 875–878
Sopher B.L., Fukuchi K, Smith A.C., Leppig K.A., Furlong C.E., Martin G.M. (1994) Cytotoxicity mediated by conditional expression of a carboxyl-terminal derivative of the betaamyloid precursor protein. Mol Brain Res 26: 207–217
Stein B.B., Adams K, Yeh M, Sapolsky R (1992) Failure of beta-amyloid protein fragment 25-35 to cause hippocaupal damage in the rat. Neurobiol Aging 13: 577–579
Suh Y.H. (1997) An etiological role of amyloidogenic carbosyl-terminal fragments of the β-amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 68: 1781–1791
Suh Y.H., Chong Y.H., Kim S.H., Choi W, Kim K.S., Jeong S.J., Fraser S.P., Djamgoz M.B.A. (1996) Molecular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein (APP). Ann NY Acad Sci 786: 169–183
Tamaoka A, Kalaria R.N., Lieberburg I, Selkoe D.J. (1992) Identification of a stable fragment of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor contataining the beta-protein in brain microvessels. Proc Natl Sci USA 89: 1345–1349
Tokuda T, Tanaka K, Kametani F, Ikeda S, Yanagisawa N (1995) Seceretory cleavage of beta-amyloid precursor protein in the cerebral white matter produces amyloidogenic carboxyl-terminal fragments. Neurosci Lett 186: 149–152
Wisniewski H.M., Wegiel J (1991) Spatial relationships beween astrocytes and classical plaque components. Neurobiol Aging 12: 593–600
Wolf D, Quon D, Wang Y, Cordell B (1990) Identification and characterzation of C-terminal fragments of the amyloid β/A4 protein precursor produced in cell culture. EMBO J 9: 2079–2084
Yankner B.A., Dawes L.R., Fisher S, Villa Komaroff L, Oster Granite M.L., Neve R.L. (1989) Neurotoxicity of a fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Science 245: 417–420
Yankner B.A., Duffy L.K., Kirschner D.A. (1990) Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250: 279–282
Yoshikawa K, Aizawa T, Hayashi Y (1992) Degeneration in vitro of post-mitotic neurons overexpressing the Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor. Nature 359: 64–67
Young J.D., Peterson C.G., Venge P, Cohn Z.A. (1986) Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by human eosinophil cationic protein. Nature 321: 613–616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Suh, YH. et al. (2000). Roles of Aβ and carboxyl terminal peptide fragments of amyloid precursor protein in Alzheimer disease. In: Mizuno, Y., Calne, D.B., Horowski, R., Poewe, W., Riederer, P., Youdim, M.B.H. (eds) Advances in Research on Neurodegeneration. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6284-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6284-2_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7246-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6284-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive