Summary
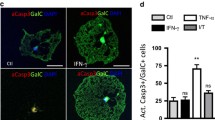
Oligodendrocytes are myelin forming cells in mammalian central nervous system. About 50% of oligodendrocytes (OLGs) undergo cell death in normal development. In addition, OLG cell deaths have been observed in demyelinating diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS). Clinical observations and in vitro cell culture studies have suggested that cytokines mediate OLG cell damage in multiple sclerosis (MS). Among the cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is thought to be one of the mediators responsible for the damage of OLGs in MS. The administration of TNF-α to primary cultures of OLGs induced DNA fragmentation, and significantly decreased the number of live OLGs. Chemical inhibitors Ac-YVAD-CHO (a specific inhibitor of caspase-1 (ICE)-like proteases) enhanced the survival of TNF-α treated OLGs better than Ac-DEVD-CHO (a specific inhibitor of caspase-3 (CPP32)-like proteases). These results indicate that caspase-1-mediated celldeath pathway are activated in TNF-induced OLG cell death. Caspase-11 is involved in activation of caspase-1. Oligodendrocytes from caspase-11-deficient mice are partially resistant to TNF-induced OLG cell death. Our results suggest that the inhibition of caspase-1 sufamily may be a novel therapeutic approach to treat MS.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alnemri E.S., Livingston D.J., Nicholson D.W., Salvesen G, Thornberry N.A., Wong W.W., Yuan J (1996) Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 87: 171
Boldin M.P., Mett I.L., Varfolomeev E.E., Chumakov I, Shemer-Avni Y, Camonis J.H., Wallach D (1995) Self-association of the “death domains” of the p55 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor and Fas/APOI prompts signaling for TNF and Fas/APOI effects. J Biol Chem 270: 387–391
Boldin M.P., Goncharov T.M., Goltsev Y.V., Wallach D (1996) Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptorinduced cell death. Cell 85: 803–815
Chinnaiyan A.M., Tepper C.G., Seldin M.F., O’Rourke K, Kischkel F.C., Hellbardt S, Krammer P.H., Peter M.E., Dixit V.M. (1996) FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 271: 4961–4965
Dolle R.E., Hoyer D, Prasad C.V., Schmidt S.J., Helaszek C.T., Miller R.E., Ator M.A. (1994) P1 aspartate-based peptide a-((2,6-dichlorobenzoyl)oxy)methyl ketones as potent time-dependent inhibitors of interleukin-1β-converting enzyme. J Med Chem 37:563–564
Dopp J.M., Makenzie-Graham A, Otero G.C., Merrill J.E. (1997) Differential expression, cytokine modulation, and specific functions of type-1 and type-2 tumor necrosis factor receptors in rat glia. J Neuroimmnol 75: 104–112
Dowling P, Husar W, Menonna J, Donnenfeld H, Cook S, Sidhu M (1997) Cell death and birth in multiple sclerosis brain. J Neurol Sci 149: 1–11
D’Souza S, Alinauskas K, McCrea E, Goodyer C, Antel J.P. (1995) Differential susceptibility of human CNS-derived cell populations to TNF-dependent and independent immune-mediated injury. J Neurosci 15: 7293–7300
Genain C.P., Roberts T, Davis R.L., Nguyen M.H., Uccelli A, Faulds D, Li Y, Hedgpeth J, Hauser S.L. (1995) Prevention of autoimmune demyelination in non-human primates by a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3601–3605
Hisahara S, Shoji S, Okano H, Miura M (1997) ICE/CED-3 family executes oligodendrocyte apoptosis by tumor necrosis factor. J Neurochem 69: 10–20
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel D.V. (1995) The TNF receptor I-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-KB activation. Cell 81: 495–504
Hsu H, Shu H.B., Pan M.G., Goeddel D.V. (1996) TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 84: 299–308
Itoh N, Nagata S (1993) A novel protein domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human Fas antigen. J Biol Chem 268: 10932–10937
Medema J.P., Scaffidi C, Kischkel F.C., Shevchenko A, Mann M, Krammer P.H., Peter M.E. (1997) FLICE is activated by association with the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). EMBO J 16: 2794–2804
Miura M, Zhu H, Rotello R (1993) Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1βconverting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell 75: 653–660
Miura M, Friedlander R.M., Yuan J (1995) Tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is mediated by a CrmA-sensitive cell death pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 8318–8322
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan A.M., Kischkel F.C., O’Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Ni J, Scaffidi C, Bretz J.D., Zhang M, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer P.H., Peter M.E., Dixit V.M. (1996) Flice, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell 85: 817–827
Pender M.P., Nguyen K.B., McCombe P.A., Kerr J.F.R. (1991) Apoptosis in the nervous system in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurol Sci 104: 81–87
Power M, Mitchell D, Lederman J, Buckmeier J, Zamvil S, Graham M, Ruddle N, Steinman L (1990) Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by myelin basic protein-specific T cell clones correlates with encephalitogenicity. Int Immunol 2: 539–544
Probert L, Akassoglou K, Pasparakis M, Kontogeordos G, Kollias G (1995) Spontaneous inflammatory demyelinating disease in transgenic mice showing central nervous system-specific expression of tumor necrosis factor alfha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11294–11298
Ray C.A., Black R.A., Kronheim S.R., Greenstreet T.A., Sleath P.R., Salvesen G.S., Pickup D.J. (1992) Viral inhibition of inflammation: cowpox virus encodes an inhibitor of the interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Cell 69: 597–604
Ruddle N, Bergman C, McGrath K, Lingenheld E, Grunnet M, Padula S, Clark R (1990) An antibody tolymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor prevents transfer to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med 172: 1193–1200
Selmaj K.W., Raine C.S. (1988) Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol 23: 339–346
Selmaj K, Raine C, Canella B, Brosnan C (1991a) Identification of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Clin Inv 87: 949–954
Selmaj K, Raine C, Cross A (1991b) Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy abrogates autoimmune demyelination. Ann Neurol 30: 694–700
Tartaglia L.A., Ayres T.M., Wong G.H., Goeddel D.V. (1993) A novel domain within the 55kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell 74: 845–853
Tewari M, Dixit V.M. (1995) Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem 270: 3255–3260
Thornberry N.A., Rano T.A., Peterson E.P., Rasper D.M., Timkey T, Garcia-Calvo M, Houtzager V.M., Nordstrom P.A., Roy S, Vaillancourt J.P., Chapman K.T., Nicholson D.W. (1997) A combinatorial approach defines specificities of members of the caspase family and granzyme B functional relationships established for key mediators of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272: 17907–17911
Wang S, Miura M, Jung Y.K., Zhu H, Gagliardini V, Shi L, Greenberg A.H., Yuan J (1996) Identification and characterization of Ich-3, a member of the interleukin-1β converting enzyme (ICE)/Ced-3 family and an upstream regulator of ICE. J Biol Chem 271:20580–20587
Wang S, Miura M, Jung Y-K, Zhu H, Li E, Yuan J (1998) Murine caspase-11, an ICE-interacting protease, is essential for the activation of ICE. Cell 92: 501–509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hisahara, S., Takano, R., Shoji, S., Okano, H., Miura, M. (2000). Role of caspase-1 subfamily in cytotoxic cytokine-induced oligodendrocyte cell death. In: Mizuno, Y., Calne, D.B., Horowski, R., Poewe, W., Riederer, P., Youdim, M.B.H. (eds) Advances in Research on Neurodegeneration. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6284-2_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6284-2_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7246-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6284-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive