Abstract
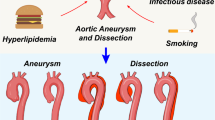
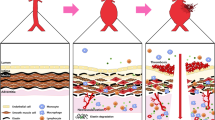
Aortic dissection is a life-threating condition which is caused by sudden separation of the aortic wall. The most common risk factors are elderly age, hypertension, and genetic background. Understanding the normal anatomy, development and physiology of the aorta is important to understand pathogenic mechanisms of aortic dissection, as will be discussed in the first section. There have been substantial advances in the last decades mainly for syndromic aortopathies. In contrast, mechanisms of non-syndromic aortic dissection are still unclear, and the prediction of patients at risk, or prevention of this condition, remains difficult. However, recent studies have started to unveil the triggering mechanism such as novel inflammatory pathways and molecules from new mouse models. In the latter part of this chapter, we will also refer these new insights and potential therapeutic targets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evangelista A, Flachskampf FA, Erbel R, Antonini-Canterin F, Vlachopoulos C, Rocchi G, Sicari R, et al. Echocardiography in aortic diseases: EAE recommendations for clinical practice. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11:645–58.
Hirsch AT, Haskal ZJ, Hertzer NR, Bakal CW, Creager MA, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, et al. American Association for Vascular Surgery/Society for Vascular S, Society for Cardiovascular A, Interventions, Society for Vascular M, Biology, Society of Interventional R, Guidelines AATFoP ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease (lower extremity, renal, mesenteric, and abdominal aortic): a collaborative report from the American Associations for Vascular Surgery/Society for Vascular Surgery, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society for Vascular Medicine and Biology, Society of Interventional Radiology, and the ACC/AHA Task Force on Practice Guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines for the management of patients with peripheral arterial disease)—summary of recommendations. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17:1383–97.
Westerhof N, Lankhaar JW, Westerhof BE. The arterial Windkessel. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47:131–41.
Gasser TC, Ogden RW, Holzapfel GA. Hyperelastic modelling of arterial layers with distributed collagen fibre orientations. J R Soc Interface. 2006;3:15–35.
Mussa FF, Horton JD, Moridzadeh R, Nicholson J, Trimarchi S, Eagle KA. Acute aortic dissection and intramural hematoma: a systematic review. JAMA. 2016;316:754–63.
Kuivaniemi H, Ryer EJ, Elmore JR, Tromp G. Understanding the pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;13:975–87.
Wiegreffe C, Christ B, Huang R, Scaal M. Remodeling of aortic smooth muscle during avian embryonic development. Dev Dyn. 2009;238:624–31.
Ruddy JM, Jones JA, Ikonomidis JS. Pathophysiology of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA): is it not one uniform aorta? Role of embryologic origin. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;56:68–73.
Gadson PF Jr, Dalton ML, Patterson E, Svoboda DD, Hutchinson L, Schram D, Rosenquist TH. Differential response of mesoderm- and neural crest-derived smooth muscle to TGF-beta1: regulation of c-myb and alpha1 (I) procollagen genes. Exp Cell Res. 1997;230:169–80.
Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Hinterseher I, Carey DJ. Novel genetic mechanisms for aortic aneurysms. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2010;12:259–66.
Nienaber CA, Clough RE. Management of acute aortic dissection. Lancet. 2015;385:800–11.
Davies RR, Goldstein LJ, Coady MA, Tittle SL, Rizzo JA, Kopf GS, Elefteriades JA. Yearly rupture or dissection rates for thoracic aortic aneurysms: simple prediction based on size. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73:17–27.
Kim JB, Kim K, Lindsay ME, MacGillivray T, Isselbacher EM, Cambria RP, Sundt TM 3rd. Risk of rupture or dissection in descending thoracic aortic aneurysm. Circulation. 2015;132:1620–9.
Dietz HC, Cutting GR, Pyeritz RE, Maslen CL, Sakai LY, Corson GM, Puffenberger EG, et al. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991;352:337–9.
Loeys BL, Schwarze U, Holm T, Callewaert BL, Thomas GH, Pannu H, De Backer JF, et al. Aneurysm syndromes caused by mutations in the TGF-beta receptor. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:788–98.
Cook JR, Clayton NP, Carta L, Galatioto J, Chiu E, Smaldone S, Nelson CA, Cheng SH, Wentworth BM, Ramirez F. Dimorphic effects of transforming growth factor-beta signaling during aortic aneurysm progression in mice suggest a combinatorial therapy for Marfan syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35:911–7.
Li W, Li Q, Jiao Y, Qin L, Ali R, Zhou J, Ferruzzi J, Kim RW, et al. Tgfbr2 disruption in postnatal smooth muscle impairs aortic wall homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:755–67.
Mallat Z, Ait-Oufella H, Tedgui A. The pathogenic transforming growth factor-beta overdrive hypothesis in aortic aneurysms and dissections: a mirage? Circ Res. 2017;120:1718–20.
Collins JJ. Dissecting aneurysms in turkeys and man. Arch Surg. 1971;102:159–60.
Son BK, Sawaki D, Tomida S, Fujita D, Aizawa K, Aoki H, Akishita M, et al. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor is required for aortic dissection/intramural haematoma. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6994.
Boyle JJ, Weissberg PL, Bennett MR. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes macrophage-induced vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis by direct and autocrine mechanisms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:1553–8.
Tieu BC, Lee C, Sun H, Lejeune W, Recinos A 3rd, Ju X, Spratt H, et al. An adventitial IL-6/MCP1 amplification loop accelerates macrophage-mediated vascular inflammation leading to aortic dissection in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:3637–51.
Ren W, Liu Y, Wang X, Jia L, Piao C, Lan F, Du J. Beta-Aminopropionitrile monofumarate induces thoracic aortic dissection in C57BL/6 mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28149.
Trachet B, Fraga-Silva RA, Piersigilli A, Tedgui A, Sordet-Dessimoz J, Astolfo A, Van der Donckt C, et al. Dissecting abdominal aortic aneurysm in Ang II-infused mice: suprarenal branch ruptures and apparent luminal dilatation. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;105:213–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer-Verlag GmbH Austria, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sawaki, D., Suzuki, T. (2019). Insights into the Pathogenic Mechanisms of Acute Dissection. In: Stanger, O., Pepper, J., Svensson, L. (eds) Surgical Management of Aortic Pathology. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-4874-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-4874-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-4872-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-4874-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)