Abstract
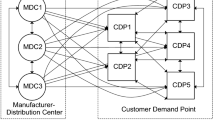
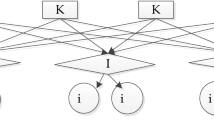
This article is conducting a study on the demand forecast from the x-retailers, y-distribution centers, and z-suppliers supply chain of logistics area. The supply chain will be divided into upstream and downstream levels. Combined with the characteristics of the supply chain and demand characteristics of the regional logistics network, Dijkstra shortest path algorithm is used and its demand forecast model is constructed based on it to obtain the exact demand of each node enterprises. At last, an example is given to prove it.
This work was supported by the Project of the national social science fund (12BJY020) and soft science of hunan province science and technology department.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christopher M (2005) Logistics and supply chain management: creating value-added networks [M]. Pearson education
Ma S, Lin Y (2006) Supply chain management (second edition). Higher Education Press, Beijing
GB/T18354-2006 (2006) The standard logistic terms of People’s Republic of China. China Standard Press, Beijing
Fleischmann M, Bloemhof-Ruwaard JM, Beullens P, Dekker R (2004) Reverse logistics network design. Quantitative approaches to reverse logistics
Zhen-Hua Y (2008) Demand forecasting safety stock optimization research based on supply chain. Tianjin University
Zill DG (2008) A first course in differential equations: with modeling applications. Brooks/Cole Pub Co
Lutkepohl H (2005) New introduction to multiple time series analysis. Springer
Ju-Long D (2002) Grey theory basis. Huazhong University of Science Technology Press, Wuhan
Ripley BD (2008) Pattern recognition and neural networks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Li Y, Chen Y (2004) Research on UML-based ASP business processes modeling. Comput Integr Manuf Syst 10:25–29
Zhu DL, Xu Q, Ye YH (2006) Operations research. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Chen JC (2003) Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm. J Formalized Math
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zou, AQ., Huang, RC. (2015). The Inventory Demand Forecasting Model of the Regional Logistics Network in Supply Chain. In: Proceedings of China Modern Logistics Engineering. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 286. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44674-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44674-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-44673-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-44674-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)