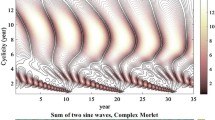
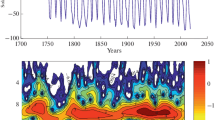
Summary
When compared with classical Fourier or spectral analysis there are several remarkable advantages of the wavelet analysis. In particular, it allows the time localisation of an unstable quasiharmonic signal within a given data set. This paper concentrates on seasonal variations and on the short-period, i.e. subseasonal fluctuations of Earth rotation. The analysis of length of day (lod) series yields in the high frequency range periods of 28 days, 14 days down to 5.6 days caused by the lunisolar tides and irregular periodic variations between 40 and 150 days. These are mainly excited by global zonal winds. For the semi-annual variations of lod a correlation with El Niño events and with the antarctic circumpolar current can be seen. The main seasonal components of polar motion are the prograde annual and semi-annual variations. Both get maximal amplitudes one to two years after strong El Niño events. Additionally, variable periods in polar motion with periods between two and five months and even down to periods of 8–10 days can be seen in the wavelet spectrum of the short-period range.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, R.T.H, R. Hide, A.A. White, and C.A. Wilson: Atmospheric angular momentum fluctuations, length-of-day changes and polar motion, Proc. R. London, Vol. A387, 31–73, 1983
Baudin, F., A. Gabriel, D. Gilbert, P.L. Pallé, and C. Régulo: Temporal characteristics of solar P-modes, Astron. Astrophys., Vol. 311, 1024–1032, 1996
Brzeziński, A.: Statistical investigations on atmospheric angular momentum functions and their effects on polar motion, Manuscripta Geodaetica, Vol. 12, 268–281, 1987
Chao, B.F., and I. Naito: Wavelet analysis provides a new tool for studying Earth’s rotation, EOS, Trans. AGU, Vol. 76, 161–165, 1995
Chao, B.F., R.D. Ray, and G.D. Egbert: Diurnal/semidiurnal oceanic tidal angular momentum: Topex/Poseidon models in comparison with Earth’s rotation rate, Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol. 22, 1993–1996, 1995
Chao, B.F., R.D. Ray, J.M. Gipson, G.D. Egbert, and C. Ma: Diurnal/semidiurnal polar motion excited by oceanic tidal angular momentum, J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 101, 20151–20163, 1996
Chao, B.F., and Y-H. Zhou: Meteorological excitation of interannual polar motion by the North Atlantic Oscillation, Journ. of Geodynamics, Vol. 27, 61–73, 1999
Dehant, V. et al.: Considerations concerning the non-rigid Earth nutation theory, accept. by Celest. Mech., 1999
Dickey, J.O. et al.: The oceanic contribution to the Earth’s seasonal angular momentum budget, Geophys. Res. Lett., Vol. 20, No. 24, 2953–2956, 1993
Eubanks, T.M., J.A. Steppe, J.O. Dickey, R.D. Rosen, and D.A. Salstein: Causes of rapid motions of the Earth’s pole, Nature, Vol. 334, 115–119, 1988
Eubanks, T.M.: Variations in the orientation of the Earth, In: Contributions of Space Geodesy to Geodynamics: Earth Dynamics, Geodynamics Series, AGU, Vol. 24, 1–54, 1993
Furuya, M, and Y. Hamano: Effect of the Pacific Ocean on the Earth’s seasonal wobble inferred from National Center for Environmental Prediction ocean analysis data, Journ. of Geophys. Res., Vol. 103, No. B5, 10131–10140, 1998
Gambis, D.: Wavelet transform analysis of the length of the day and the El Niño/Southern Oscillation variations at intraseasonal and interannual time scales, Ann. Geophysicae, Vol. 10, 429–437, 1992
Gibert, D., M. Holschneider, and J.L. Le Mouël: Wavelet Analysis of the Chandler Wobble, Journ. Geophys. Res., Vol. 103, No. B11, 27069–27089, 1998
Grossmann, A., and J. Morlet: Decomposition of Hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape, SIAM J. Math Anal., Vol. 15(4), 723–736, 1984
Kolaczek, B.: Short Period Variations of Earth Rotation, Proc. Journées 1995 Systèmes de Référence SpatioTemporels, Warsaw, Poland, 18–20, publ. by the Space Res. Centre, PAS, Poland, 147–154, 1995
Kosek, W., J. Nastula, and B. Kolaczek: Variability of polar motion oscillations with periods from 20 to 150 days in 1979–1991, Bull. Géodés., Vol. 69, 308–319, 1995
Kosek, W.: Time Variable Band Pass Filter Spectra of Real and Complex-Valued Polar Motion Series, Artificial Satellites, Planetary Geodesy No 24, Vol. 30, No 1, publ. by the Space Research Centre, Warsaw, 27–43, 1995
Kosek, W., and L. Kolaczek: Semi-Chandler and semiannual oscillation of polar motion, Geophys. Res. Letters, Vol. 24, No. 17, 2235–2238, Sept. 1997
Kuehne, J., S. Johnson, and C.R. Wilson: Atmospheric excitation of nonseasonal polar motion, J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 98, 19973–19978, 1993
Nastula, J.: Short periodic variations in the Earth’s rotation in the period 1984–1990, Ann. Geophysicae, 10, 441–448, 1992
Nastula, J.: The regional atmospheric contribution to the polar motion and EAAM excitation functions, Proceedings of the Int. Symp. on Gravity, Geoid and Marine Geodesy, 1996, Tokyo, 1997
Nastula, J., W. Kosek, and B. Kolaczek: Analysis of zonal atmospheric excitation functions and their correlation with polar motion excitation functions, Space Res. Centre, PAS, Warsaw, Poland, 1997
Popinski, W., and W. Kosek: Wavelet Transform and its Application for Short Period Earth Rotation Analysis, Planetary Geodesy, 22, Vol. 29, 2, 75–86, 1994
Praveen, K.: Wavelet Analysis for Geophysical Applications, Reviews of Geophysics, Vol. 35/4, 385–412, 1997
Rosen, R.D.: The Axial Momentum Balance of Earth and its Fluid Envelope, Surveys in Geophysics, Vol. 14, 1–29, 1993
Schmidt, M.: Moderne Methoden der Signalanalyse, Zeitschrift für Vermessungswesen, ZfV, Vol. 121, 315–325, 1996
Schmidt, M., and H. Schuh: Wavelet-Analyse der mit VLBI beobachteten Nutationsreihen, Zeitschrift für Vermessungswesen, ZfV, Vol. 124, 25–30, 1999
Schmidt, M.: Grundprinzipien der Wavelet-Analyse und Anwendungen in der Geodäsie, habilitation thesis (preprint), München, 1999
Schmitz-Hübsch, H.: Wavelet Analysis of Earth Rotation, Proc. of the III. Venezuelian Congress of Geodesy, 23.–27.02.1998, Maracaibo, in press, 1999
Schuh, H., and O. Titov: Short-period variations of the Earth rotation parameters as seen by VLBI, Proc. of the 13th Working Meeting on European VLBI for Geodesy and Astrometry, Viechtach, Feb. 1999, ed. by W. Schlüter and H. Hase, 172–177, 1999
Torrence, C., and G.P. Compo: A practical guide to wavelet analysis, Bull. of the American Meteorological Society, Vol. 79(1), 61–78, 1998
Whitcher, B.: Assessing Nonstationary Time Series Using Wavelets, Ph. D. thesis, Univ. of Washington, 1998
Yoder, C.E., J.G. Williams, and M.E. Parke: Tidal variations of Earth rotation, J. Geophys. Res., Vol. 86, 881–891, 1981
Zatman, S., and J. Bloxham: The phase difference between length of day and atmospheric angular momentum at subannual frequencies and the possible role of coremantle coupling, Geophys. Res. Letters, Vol. 24, No. 14, 1799–1802, 1997
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Schmitz-Hübsch, H., Schuh, H. (2003). Seasonal and Short-Period Fluctuations of Earth Rotation Investigated by Wavelet Analysis. In: Grafarend, E.W., Krumm, F.W., Schwarze, V.S. (eds) Geodesy-The Challenge of the 3rd Millennium. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05296-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05296-9_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-07733-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-05296-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive