Abstract
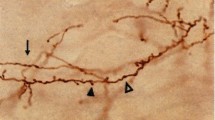
Synaptic connections are established with a high degree of specificity. They are specific with respect to the cell they contact but also often with respect to particular parts of that cell, e.g., a particular zone on a dendritic field. Such laminar specificity is particularly well illustrated in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation where nearly all inputs terminate within defined laminar boundaries (Fig. 1).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Das GD (1965) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124: 319–336
Altman J, Das GD (1966) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 126: 337–390
Cotman CW (1971) Specificity of synaptic growth in brain: Remodeling induced by kainic acid lesions. In: Akert K, Baumgartner G, Bloom F, Kreutzberg G, Cuenod M (eds) Development and chemical specificity of neurons, progress in brain research, vol 51. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 203–215
Cotman CW, Nadler JV (1978) Reactive synaptogenesis in the hippocampus. In: Cotman CW (ed) Neuronal plasticity. Raven Press, New York, pp 227–271
Cotman CW, Matthews DA, Taylor D, Lynch G (1973) Synaptic rearrangement in the dentate gyrus: Histochemical evidence of adjustments after lesions in immature and adult rats. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 70: 343–347
Curtis ASG (1978a) Cell-cell recognition: psoitioning and patterning systems. Soc Exp Biol Symposium 32. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 51–82
Curtis ASG (1978b) Cell Positioning. In: Garrod DR (ed) Receptors and recognition, specificity of embriological interactions, Series B, vol 4. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 157–195
Curtis ASG, van de Vyver (1971) The control of cell adhesion in a morphogenetic system. J Embryol Exp Morphol 26: 295–312
Dunn EG (1916–1917) Primary and secondary findings in a series of attempts to transplant cerebral cortex in the albino rat. J Comp Neurol 27: 565–582
Fonnum F (1970) Topographical and subcellular localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat hippocampal region. J Neurochem 17: 1029–1037
Fraser SE, Hunt RK (1980) Retinotectal specificity: models and experiments in search of a mapping function. Ann Rev Neurosci 3: 319–352
Fricke RA, Cowan WM (1977) An autoradiographic study of the development of the entorhinal and hippocampal afferents to the dentate gyrus of the rat. J Comp Neur 173: 231–250
Jacobsen M (1978) Developmental neurobiology, 2nd ed. Plenum Press, New York
Le Gros Clark WE (1940) Neuronal Differentiation in implanted fetal cortical tissue. J Neur Psych-iatr 3: 263–272
Lewis ER, Cotman CW (1980) Mechanisms of septal lamination in the developing hippocampus revealed by outgrowth of fibers from septal implants: I. Positional and temporal factors. Brain Res 196: 307–330
Lewis ER, Kelly P, Cotman CW (1980a) Absence of degenerative debri guidance in the specific growth of septal tissue grafts implanted into neonatal hosts. Abstr Soc Neurosci 6: 161. 6
Lewis ER, Mueller JC Cotman CW (1980b) Neonatal septal implants: Development of afferent lamination in the rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res Bull 5 (3): 217–221
Loy R, Cotman CW, Lynch G (1977) The development of afferent lamination in the fascia dentate of the rat. Brain Res 121: 229–243
Lynch G, Matthews D, Mosko S, Parks T, Cotman CW (1977) Induced acetylcholinesterase-rich layer in rat dentate gyrus following entorhinal lesions. Brain Res 42: 311–318
Matthews DA, Nadler JV, Lynch GS, Cotman CW (1974) Development of cholinergie innervation in the hippocampal formation of the rat. I. Histochemical demonstration of acetylcholinesterase activity. Dev Biol 36: 130–141
Nadler JV, Matthews DA, Cotman CW, Lynch GS (1974) Development of cholinergic innervation in the hippocampal formation of the rat. II. Quantitative changes in choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Dev Biol 36: 142–154
Nadler JV, Cotman CW, Lynch G (1977a) Histochemical evidence of altered development of cholinergic fibers in the rat dentate gyrus following lesions. I. Time course after complete unilateral entorhinal lesion at various ages. J Comp Neurol 171: 589–604
Nadler JV, Paoletti C, Cotman CW, Lynch G (1977b) Histochemical evidence of altered development of cholinergic fibers in the rat dentate gyrus following lesions. II. Effects of partial entorhinal and simultaneous multiple lesions. J Comp Neurol 171: 589–604
Nadler JV, Shelton DL, Cotman CW (1979) Lesion-induced plasticity of high affinity choline in the developing rat fascia dentata. Brain Res 164: 207–216
Nadler JV, Perry BW, Cotman CW (1980) Interaction with CA4-derived fibers accounts for distribution of septohippocampal fibers in rat fascia dentata after entorhinal lesion. Exp Neurol 68: 185–194
Scheff SW, Bernardo LS, Cotman CW (1980) Decline in reactive fiber growth in the dentate gyrus of aged rats compared to young rats following entorhinal cortex removal. Brain Res 199: 2138
Shelton DL, Nadler JV, Cotman CW (1979) Development of high affinity choline uptake and associated acetylcholine synthesis in the rat fascia dentata. Brain Res 163: 263–275
Stanfield BB, Caviness VS, Cowan WM (1979) The organization of certain afferents to the hippo-campus and dentate gyrus in normal and reeler mice. J Comp Neurol 185: 461–484
Stenevi U, Bjorkland A, Svengaard N-A (1976) Transplantation of central and peripheral monoamine neurons to the adult rat brain: techniques and conditions for survival. Brain Res 114: 1–20
Storm-Mathisen J (1970) Quantitative histochemistry of acetylcholinesterase in rat hippocampal region correlated to histochemical staining. J Neurochem 17: 739–750
Storm-Mathisen J (1974) Choline acetyltransferase in fascia dentata following lesion of the entorhinal afferents. Brain Res 80: 181–197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1981 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cotman, C.W., Lewis, E.R., Hand, D. (1981). The Critical Afferent Theory: A Mechanism to Account for Septohippocampal Development and Plasticity. In: Flohr, H., Precht, W. (eds) Lesion-Induced Neuronal Plasticity in Sensorimotor Systems. Proceedings in Life Sciences. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-68074-8_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-68074-8_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-68076-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-68074-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive