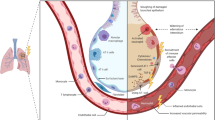
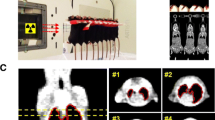
Abstract
The lung is one of the most important dose-limiting organs in radiotherapy. Substantial research efforts have been undertaken over the past decades to understand the radiobiology and radiopathology of lung tissue, to define mechanisms of radiation responses in the lung, and to transfer experimental results into clinical trials and practice.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson IYR, Bowden DH (1983) Endothelial injury and repair in radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 112:224–230
Adamson IYR, Bowden DH, Wyatt JP (1970) A pathway to pulmonary fibrosis: an ultrastructural study of mouse and rat following radiation to the whole body and hemithorax. Am J Pathol 58:481–487
Anscher MS, Kong FM, Andrews K, Clough R, Marks LB, Bentel G, Jirtle RL (1998) Plasma transforming growth factor beta1 as a predictor of radiation pneumonitis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 41:1029–1035
Antoniades HN, Bravo MA, Avila RE, Galanopoulos T, Neville-Golden J, Maxwell M, Selman M (1990) Platelet-derived growth factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 86:1055–1064
Basset F, Ferrans VJ, Soler P, Takemura T, Fukuda Y, Crystal RG (1986) Intraluminal fibrosis in interstitial lung disorders. Am J Pathol 122:443–461
Bennett DE, Million RR, Ackerman IV (1969) Bilateral radiation pneumonitis. A complication of the radiotherapy of bronchogenic carcinoma. Cancer 23:1001–1018
Burger A, Loffler H, Bamberg M, Rodemann HP (1998) Molecular and cellular basis of radiation fibrosis. Int J Radiat Biol 73:401–408
Dörr W, Herrmann T (2002) Akute Strahlenveränderungen der Gewebe. In: Bamberg M, Molls M, Sack H (eds) Radio-Onkologie, 5th edn. Zuckschwerdt, Munich
Dörr W, Baumann M, Herrmann T (2000) Radiation-induced lung damage: a challenge for radiation biology, experimental and clinical radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol 76:443–446
Donnelly SC, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Walz A, Robertson CR, Carter DC, Grant IS, Pollok AJ, Haslett C (1993) Interleukin-8 and development of adult respiratory distress syndrome in at-risk patient groups. Lancet 341:643–647
Epperly MW, Bray JA, Krager S, Berry LM, Gooding W, Engelhardt JF, Zwacka R, Travis EL, Greenberger JS (1998) Intratracheal injection of adenovirus containing the human MnSOD transgene protects athymic nude mice from irradiation-induced organizing alveolitis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1999 43:169–181
Epperly MW, Travis EL, Sikora C, Greenberger JS (1999) Manganese (correction of Magnesium) superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) plasmid/liposome pulmonary radioprotective gene therapy: modulation of irradiation-induced mRNA for IL-I, TNF-alpha, and TGF-βeta correlates with delay of organizing alveolitis/fibrosis. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl 5:204–214
Evans ML, Graham MM, Mahler PA, Rasey JS (1986) Changes in vascular permeability following thorax irradiation in the rat. Radiat Res 107:262–271
Fajardo LFL-G, Berthrong M, Andrson RE (2001) Radiation pathology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 198–208
Fehrenbach H, Kasper M, Haase M, Schuh D, Müller M (1999) Differential immunolocalization of VEGF in rat and human adult lung, and in experimental rat lung fibrosis: light, fluorescence, and electron microscopy. Anat Rec 254:61–73
Fries KM, Felch ME, Phipps RP (1994) Interleukin-6 is an autocrine growth factor for murine lung fibroblast subsets. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11:552–560
Fukuda Y, Ishizaki M, Masuda Y, Kimura G, Kawanami O, Masugi Y (1987) The role of intraalveolar fibrosis in the process of pulmonary structural remodeling in patients with diffuse alveolar damage. Am J Pathol 126:171–182
Gross NJ (1977) Pulmonary effects of radiation therapy. Ann Intern Med 129:81–92
Hakenjos L, Bamberg M, Rodemann HP (2000) TGF-beta1-mediated alterations of rat lung fibroblast differentiation resulting in the radiation-induced fibrotic phenotype. Int J Radiat Biol 76:503–509
Hallahan DE, Geng L, Shyr Y (2002) Effects of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) null mutation on radiationinduced pulmonary fibrosis and respiratory insufficiency in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:733–741
Henke C, Marineili W, Jessurun J, Fox J, Harms D, Peterson M, Chiang L, Doran P (1993) Macrophage production of basic fibroblast growth factor in the fibroproliferative disorder of alveolar fibrosis after lung injury. Am J Pathol 143: 1189–1199
Herrmann T, Knorr A (1995) Radiogenic lung reactions. Pathogenesis-prevention-therapy. Strahlenther Onkol 171: 490–498
Hopewell JW, Rezvani M, Moustafa HF (2000) The pig as a model for the study of radiation effects on the lung. Int J Radiat Biol 76:447–452
Jiang Y, Beller DI, Frendl G, Graves DT (1992) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates adhesion molecule expression and cytokine production in human monocytes. J Immunol 148:2423–2428
Iyonaga K, Takeya M, Saita N, Sakamoto O, Yoshimura T, Ando M, Takahashi K (1994) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial lung diseases. Hum Pathol 25:455–463
Kodama N, Yamaguchi E, Hizawa N, Furuya K, Kojima J, Oguri M, Takahashi T, Kawakami Y (1998) Expression of RANTES by bronchoalveolar lavage cells in nonsmoking patients with interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 18:526–531
Kuwano K, Hagimoto N, Hara N (2001) Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis and current treatment. Curr Mol Med 1:551–573
Madtes DK, Busby HK, Strandjord TP, Clark JG (1994) Expression of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor is increased following bleomycin-induced lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 11: 540–551
Martin M, Lefaix J-L, Delanian S (2000) TGF-β1 and radiation fibrosis: a master switch and a specific therapeutic target? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:277–290
McDonald S, Rubin P, Phillips TL, Marks LB (1995) Injury to the lung from cancer therapy: clinical syndromes, measurable endpoints and potential scoring systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1187–1203
Movsas B, Raffin TA, Epstein AH, Link CJ Jr (1997) Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis and current treatment. Chest 111:1061–1076
Pesci A, Bertorelli G, Gabrielli M, Olivieri D (1993) Mast cells in fibrotic lung disorders. Chest 103:989–996
Philips TL (1966) An ultrastructural study of the development of radiation injury in the lung. Radiol 87:49–54
Piguet PF, Vesin C (1994) Treatment by human recombinant soluble TNF receptor of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin or silica in mice. Eur Respir J 7:515–518
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Kapanci Y, Vassalli PJ (1989) Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin plays a key role in bleomycin-induced pneumopathy and fibrosis. J Exp Med 170: 655–663
Piguet PF, Rosen H, Vesin C, Grau GE (1993a) Effective treatment of the pulmonary fibrosis elicited in mice by bleomycin or silica with anti-CD-11 antibodies. Am Rev Respir Dis 147:435–441
Piguet PF, Ribaux C, Karpuz V, Grau GE, Kapanci Y (1993b) Expression and localization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its mRNA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 143:651–655
Raghow R, Irish P, Kang AH (1989) Coordinate regulation of transforming growth factor beta gene expression and cell proliferation in hamster lungs undergoing bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 84:1836–1842
Raines EW, Dower SK, Ross R (1989) Interleukin-1 mitogenic activity for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells is due to PDGF-AA. Science 243:393–396
Rodemann HP, Bamberg M (1995) Cellular basis of radiation-induced fibrosis. Radiother Oncol 35:83–90
Rom WN, Basset P, Fells GA, Nukiwa T, Trapnell BC, Crysal RG (1988) Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J Clin Invest 82:1685–1693
Rubin P, Johnston CJ, Williams JP, McDonald S, Finkelstein JN (1995) A perpetual cascade of cytokines postirradiation leads to pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 33:99–109
Smith DR, Kunkel SL, Standiford TJ, Rolfe MW, Lynch JP III, Arenberg DA, Wilke CA, Burdick MD, Martinez FJ, Hampton JN, Whyte RI, Orringer MB, Strieter RM (1995) Increased interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A compartmental analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:1965–1973
Smith RE, Strieter RM, Phan SH, Lukacs NW, Huffnagle GB, Wilke CA, Burdick MD, Lincoln P, Evanoff H, Kunkel SL (1994) Production and function of murine macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in bleomycin-induced lung injury. J Immunol 153:4704–4712
Spencer H (1968) Pathology of the lung, 2nd edn. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 472–478
Standiford TJ, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, Greenberger MJ, Danforth JM, Kunkel RG, Strieter RM (1995) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha mediates lung leukocyte recruitment, lung capillary leak, and early mortality in murine endotoxemia. J Immunol 155:1515–1524
Thrall RS, Scalise PJ (1995) Bleomycin. In: Phan SH, Thrall RS (eds) Pulmonary fibrosis. Dekker, New York
Toomey D, Condron C, Wu QD, Kay E, Harmey J, Broe P, Kelly C, Bouchier-Hayes D (2001) TFG-beta1 is elevated in breast cancer tissue and regulates nitric oxide production from a number of cellular sources during hypoxia re-oxygenation injury. Br J Biomed Sci 58:177–183
Ts’ao CH, Ward WF, Port CD (1983a) Radiation injury in the rat lung. I. Prostacyclin (PGI2) production, arterial perfusion and ultrastructure. Radiat Res 96:284–293
Ts’ao CH, Ward WF, Port CD (1983b) Radiation injury in the rat lung. III. Plasminogen activator and fibrinolytic inhibitor activities. Radiat Res 96:301–308
Wallace WA, Ramage EA, Lamb D, Howie SE (1995) A type 2 (Th2-like) pattern of immune response predominates in the pulmonary interstitium of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA). Clin Exp Immunol 101: 436–441
Ward WF, Solliday NH, Molteni A, Port CD (1983) Radiation injury in the rat lung. II. Angiotensin converting enzyme activity. Radiat Res 96:294–300
Zwacka RM, Dudus L, Epperly MW, Greenberger JS, Engelhardt JF (1998) Redox gene therapy protects human IB-3 lung epithelial cells against ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis. Hum Gene Ther 9:1381–1386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dörr, W., Herrmann, T. (2003). Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Lung Fibrosis. In: Nieder, C., Milas, L., Ang, K.K. (eds) Modification of Radiation Response. Medical Radiology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55613-5_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55613-5_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-62670-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-55613-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive