Abstract
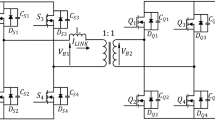
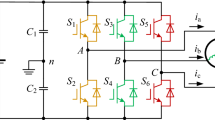
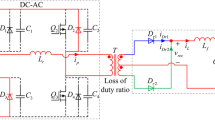
The dead-time effects of an inverter is analyzed, and a no-dead-time control scheme is presented for the Single-Phase bridge inverter. According to current polarity, a phase-leg can be decomposed into two switching cells without dead-time. Using Immune algorithm (IA) to find the optimal no-dead-time control sequence for the Single-Phase inverter. A simulation based on the no-dead-time control is designed based on matlab / Simulink, and the experiment is done with a full-bridge inverter. The simulation and experimental results verify that the output waveform is improved significantly, DC voltage utilization ratio is increased.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Summers, T.J., Betz, R.E.: Dead-time issues in predictive current control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 40(3), 835–844 (2004)
Cichowski, Nieznanski, J.: Self-tuning dead-time compensation method for voltage-source inverters. IEEE Power Electron. Lett. 3(2), 72–75 (2005)
Lai, Y.S., Shyu, F.S.: Optimal common-mode voltage reduction PWM technique for inverter control with consideration of the dead-time effects—Part I: Basic development. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 40(6), 1605–1612 (2004)
Kim, H., Moon, H., Youn, M.: On-line dead-time compensation method using disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 18(6), 1336–1345 (2003)
Urasaki, N., Senjyu, T., Uezatoand, K., Funabashi, T.: Adaptive deadtime compensation strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 22(2), 271–280 (2007)
Lin, J.L.: A New Approach of Dead-time Compensation for PWM Voltage Inverters. IEEE Trans.on Circuits and Systems 49(4), 476–483 (2002)
Choi, J.S., Yoo, J.Y., Lim, S.W., Kim, Y.S.: A novel dead time minimization algorithm of the PWM inverter. In: Conference Record of the IEEE IAS, vol. 4, pp. 2188–2193 (1999)
Attaianese, V., Attaianese, Nardi, V., Tomasso, G.: A novel SVM strategy for VSI dead-time-effect reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 41(6), 1667–1674 (2005)
Chen, L., Peng, F.Z.: Dead-time elimination for voltage source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(2), 574–580 (2008)
Lin, Y.K., Lai, Y.S.: Dead-Time Elimination of PWM-Controlled Inverter/Converter Without Separate Power Sources for Current Polarity Detection Circuit. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 56(6), 2121–2127 (2009)
Zhang, A., Huang, Q., Chen, B.: A novel IGBT gate driver to eliminate the dead-time effect. In: Conference Record of the IAS, vol. 2, pp. 913–917 (2005)
Mehrizi-Sani, A., Filizadeh, S.: An Optimized Space Vector Modulation Sequence for Improved Harmonic Performance. IEEE Trans.Ind. Electron. 56(8), 2894–2903 (2009)
Yuan, J., Su, X., Chen, B., Tian, C., Optimum Vector, P.W.M.: Strategy for Three-Phase Inverter Based on Immune Algorithm. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society 24(9), 114–119 (2009)
Yuan, J., Chen, B., Tian, C., Jia, J.: The research of Inverter’s control based on Immune Algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE 26(5), 110–117 (2006)
Yuan, J., Chen, B., Jia, J.: Gentic Algorithm based approach for invertor control. Automation of Electric PowerSystems (24), 32–35 (2004)
Yuan, J., Chen, B.: Research on Optimum Control Strategy of Three-Level Single-Phase Full-Bridge Inverter. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society 21(3), 42–46 (2006)
Lopez, J., Alvarez, J., Doval-Gandoy, Freijedo, F.D.: Multilevel multiphase space vector PWM algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 55(5), 1933–1942 (2008)
Jiao, L., Wanlei: A novel Genetic algorithm Based on Immunity. IEEE Transactions on System,Man,and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and humans 30(5), 552–561 (2000)
Jiao, L., Wanlei: A novel Genetic algorithm Based on Immunity. IEEE Transactions on System,Man,and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and humans 30(5), 552–561 (2000)
Bowes, S.R., Holliday, D.: Optimal regular-sampled PWM inverter control techniques. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 54(3), 1547–1559 (2007)
Chen, B.-Y., Lai, Y.-S.: Switching Control technique of phase-shift- controlled full-bridge converter to improve efficiency under light-load and stand by conditions without additional auxiliary components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 25(4), 1001–1012 (2009)
Oggier, G.G., García, G.O., Oliva, A.R.: Switching control strategy to minimize dual active bridge converter losses. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 24(7), 1826–1837 (2009)
Mao, X., Ayyanar, R., Krishnamurthy, H.K.: Optimal variable switching frequency scheme for reducing switching loss in single-phase inverters based on time-domain ripple analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 24(4), 991–1001 (2009)
Lai, R., Wang, F.F., Burgos, R., Pei, Y., Boroyevich, D., Wang, B., Lipo, T.A., Immanuel, V.D., Karimi, K.J.: A systematic topology evaluation methodology for high-density Three-phase pwm AC-AC converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 23(6), 2665–2680 (2008)
Maswood, A.I., Wei, S.: Genetic-algorithm-based solution in PWM converter switching. In: IEE Proceedings Electric Power Applications, May 6, vol. 152(3), pp. 473–478 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiaofang, S., Binbin, R., Yongsheng, Z. (2011). Optimal Dead-Time Elimination for Voltage Source Inverters. In: Ma, M. (eds) Communication Systems and Information Technology. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 100. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21762-3_80
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21762-3_80
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-21761-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-21762-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)