Abstract
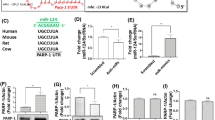
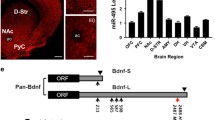
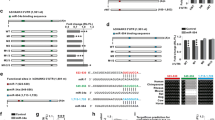
Midbrain dopamine neurons (mDNs) play a central role in complex behaviors such as reward and addiction, and these cells are lost in Parkinson's disease (PD). A number of transcription factors have been implicated in the regulation of mDNs. However, the role of post-transcriptional mechanisms in mDNs, or in other post-mitotic neuron types, is relatively uncharacterized. Here we investigate the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in mDN regulation in relation to previously described transcriptional control mechanisms. miRNAs are evolutionarily conserved, 18-25 nucleotide, non-protein coding transcripts that play an important function in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression during development. In preliminary studies and a recent manuscript, we identified eight miRNA enriched in the midbrain, and one -- miR-133b -- as a mDN-enriched miRNA that appears to function within a feedback circuit with the homeodomain transcription factor Pitx3.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2003) MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113:673–676
Andersson E, Tryggvason U, Deng Q, Friling S, Alekseenko Z, Robert B, Perlmann T, Ericson J (2006) Identification of intrinsic determinants of midbrain dopamine neurons. Cell 124:393–405
Barberi T, Klivenyi P, Calingasan NY, Lee H, Kawamata H, Loonam K, Perrier AL, Bruses J, Rubio ME, Topf N, Tabar V, Harrison NL, Beal MF, Moore MA, Studer L (2003) Neural subtype specification of fertilization and nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells and application in parkinsonian mice. Nature Biotechnol 21:1200–1207
Ben-Hur T, Idelson M, Khaner H, Pera M, Reinhartz E, Itzik A, Reubinoff BE (2004) Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors improves behavioral deficit in Parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells 22:1246–1255
Chang S, Johnston RJ Jr., Frokjaer-Jensen C, Lockery S, Hobert O (2004) MicroRNAs act sequentially and asymmetrically to control chemosensory laterality in the nematode. Nature 430:785–789
Chung S, Hedlund E, Hwang M, Kim DW, Shin BS, Hwang DY, Jung Kang U, Isacson O, Kim KS (2005) The homeodomain transcription factor Pitx3 facilitates differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into AHD2-expressing dopaminergic neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 28:241–252
Davidson TJ, Harel S, Arboleda VA, Prunell GF, Shelanski ML, Greene LA, Troy CM (2004) Highly efficient small interfering RNA delivery to primary mammalian neurons induces MicroRNA-like effects before mRNA degradation. J Neurosci 24:10040–10046
Giraldez AJ, Cinalli RM, Glasner ME, Enright AJ, Thomson JM, Baskerville S, Hammond SM, Bartel DP, Schier AF (2005) MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. Science 308:833–838
Giraldez AJ, Mishima Y, Rihel J, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Inoue K, Enright AJ, Schier AF (2006) Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 312:75–79
Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, Li N, Parrish S, Ha I, Baillie DL, Fire A, Ruvkun G, Mello CC (2001) Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell 106:23–34
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nature Rev Genet 5:522–531
Hwang DY, Ardayfio P, Kang UJ, Semina EV, Kim KS (2003) Selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of Pitx3-deficient aphakia mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 114:123–131
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS (2004) Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2z; e363
Johnston RJ, Hobert O (2003) A microRNA controlling left/right neuronal asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 426:845–849
Kawasaki H, Mizuseki K, Nishikawa S, Kaneko S, Kuwana Y, Nakanishi S, Nishikawa SI, Sasai Y (2000) Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons from ES cells by stromal cell-derived inducing activity. Neuron 28:31–40
Kim JH, Auerbach JM, Rodriguez-Gomez JA, Velasco I, Gavin D, Lumelsky N, Lee SH, Nguyen J, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Bankiewicz K, McKay R (2002) Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 418:50–56
Kosik KS, Krichevsky AM (2005) The elegance of the microRNAs: a neuronal perspective. Neuron 47:779–782
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K, Kosik KS (2003) A microRNA array reveals extensive regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA 9:1274–1281
Krichevsky AM, Sonntag KC, Isacson O, Kosik KS (2006) Specific microRNAs modulate embryonic stem cell-derived neurogenesis. Stem Cells 24:857–864
Lee SH, Lumelsky N, Studer L, Auerbach JM, McKay RD (2000) Efficient generation of midbrain and hindbrain neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnol 18:675–679
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J, Lee J, Provost P, Rådmark O, Kim S, Kim VN (2003) The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425:415–419
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115:787–798
Martinat C, Bacci JJ, Leete T, Kim J, Vanti WB, Newman AH, Cha JH, Gether U, Wang H, Abeliovich A (2006) Cooperative transcription activation by Nurr1 and Pitx3 induces embryonic stem cell maturation to the midbrain dopamine neuron phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2874–2879
Meister G, Tuschl T (2004) Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 431:343–349
Murchison EP, Partridge JF, Tam, OH, Cheloufi S, Hannon GJ (2005) Characterization of Dicer-deficient murine embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12135–12140
Nunes I, Tovmasian LT, Silva RM, Burke RE, Goff SP (2003) Pitx3 is required for development of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4245–4250
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439:283–289
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Burbach JP (2004) Homeobox gene Pitx3 and its role in the development of dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra. Cell Tissue Res 318:35–43
Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Kim KS, Isacson O (2004) Temporally induced Nurr1 can induce a non-neuronal dopaminergic cell type in embryonic stem cell differentiation. Eur J Neurosci 19:1141–1152
van den Munckhof P, Luk KC, Ste-Marie L, Montgomery J, Blanchet PJ, Sadikot AF, Drouin J (2003) Pitx3 is required for motor activity and for survival of a subset of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Development 130:2535–2542
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Abeliovich, A. (2010). A microRNA Feedback Circuit in Midbrain Dopamine Neurons. In: De Strooper, B., Christen, Y. (eds) Macro Roles for MicroRNAs in the Life and Death of Neurons. Research and Perspectives in Neurosciences. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04298-0_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04298-0_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04297-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04298-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)