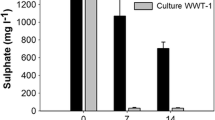
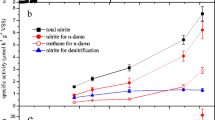
Sulfate reduction can be used in a large number of environmental technologies. Methanogenic bioreactors treating organic wastewater containing sulfate can be negatively affected by the sulfide produced; however, it is possible to combine methanogenesis and sulfate reduction when adequate measures are applied. For the treatment of inorganic wastewaters containing sulfate, organic substrates or H2/CO2 are added as electron donors. Alternatively synthesis gas or methane can be used; however, the sulfate reduction rates with methane are still extremely low. Heavy metals such as Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni and Fe can be removed from waste streams by precipitation with biogenic sulfide. Because of differences in solubility products the metals can be selectively precipitated. The insoluble metal sulfides formed can be recovered in order to be reused.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton CD, Karathanasis AD (1999) Renovation of a failed constructed wetland treating acid mine drainage. Environ Geol 39:39–50.
Benner SG, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Mayer KU (2002) Rates of sulphate reduction and metal sulfide precipitation in a permeable reactive barrier. Appl Geochem 17:301–320.
Brown TL, Lemay HE, Bursten BE (1997) Chemistry: the central science, 7th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Chen BY, Utgikar VP, Harmon SM, Tabak HH, Bishop DF, Govind R (2000) Studies on biosorption of zinc(II) and copper (II) on Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 46:11–18.
Colleran E, Finnegan S, Lens P (1995) Anaerobic treatment of sulphate-containing waste streams. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 67:29–46.
De Smul A, Verstraete W (1999) The phenomenology and the mathematical modelling of the silicone-supported chemical oxidation of aqueous sulfide to elemental sulfur with ferric sulfate. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:456–466.
Esposito G, Veeken A, Weijma J, Lens PNL (2006) Effect of the use of biogenic sulphide on ZnS precipitation under different process conditions. Sep Purif Technol 51:31–39.
Fedorovich V, Greben M, Kalyuzhnyi S, Lens P, Hulshoff Pol L, Lettinga G (2000) Use of membranes for hydrogen supply in a sulfate reducing reactor. Biodegradation 11:295–303.
Gibert O, de Pablo J, Cortina JL, Ayora C (2004) Chemical characterisation of natural organic substrates for biological mitigation of acid mine drainage. Water Res 38:4186–4196.
König J, Keesman KJ, Veeken A, Lens PNL (2006) Dynamic modelling and process control of ZnS precipitation. Sep Sci Technol 41:1025–1042.
Krüger M, Treude T, Wolters H, Nauhaus K, Boetius A (2005) Microbial methane turnover in different marine habitats. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 227:6–17.
Kim BM, Amodeo PA (1983) Calcium sulfide process for treatment of metal-containing wastes. Environ Prog 2:175–180.
Lens P, Visser A, Janssen A, Hulshoff Pol L, Lettinga G (1998a) Biotechnological treatment of sulfate rich wastewaters. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 28:41–88.
Lens P, van den Bosch M, Hulshoff Pol L, Lettinga G (1998b) Effect of staging on volatile fatty acid degradation in a sulfidogenic granular sludge reactor. Water Res 32:1178–1192.
Lens P, Gastesi R, Hulshoff Pol L, Lettinga G (2003) Use of sulphate reducing cell suspension bioreactors for the treatment of SO2 rich flue gases. Biodegradation 14:229–240.
Lens PNL, Korthout D, van Lier JB, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (2001) Effect of upflow velocity on thermofilic sulfate reduction under acidifying conditions. Environ Technol 22:183–193.
Lens PNL, Klijn R, van Lier JB, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (2002) Effect of specific gas loading rate on thermofilic sulfate reduction under acidifying conditions. Water Res 37:1033–1047.
Markewitz K, Cabral AR, Panarotto CT, Lefebvre G (2004) Anaerobic biodegradation of an organic by-products leachate by interaction with different mine tailings. J Hazard Mater 110:93–104.
Omil F, Lens P, Visser A, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (1998) Long term competition between sulfate reducing and methanogenic bacteria in UASB reactors treating volatile fatty acids. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:676–685.
Parshina SN, Sipma J, Nakashimada Y, Henstra HM, Smidt H, Lysenko AM, Lens PNL, Lettinga G, Stams AJM (2005) Desulfotomaculum carboxydivorans sp. nov., a novel sulfate reducing bacterium capable of growth at 100% CO. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2159–2165.
Paulo P, Kleerebezem R, Lettinga G, Lens PNL (2005) Cultivation of high-rate sulphate reducing sludge by pH-based electron donor dosage. J Biotechnol 118:107–116.
Peters RW, Ku Y, Battacharyya D (1984) Evaluation of recent treatment techniques for removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters. Paper presented at AIChE meeting, Philadelphia, pp 19–22.
Reis MAM, Lemos PC, Carrondo MJT (1995) Biological sulfate removal of industrial effluents using the anaerobic digestion. Med Fac Landbouwwet Univ Gent 60:2701–2707.
Rose PD, Boshoff GA, van Hille RP, Wallace LC, Dunn KM, Duncan JR (1998) An integrated algal sulphate reducing high rate ponding process for the treatment of acid mine drainage wastewaters. Biodegradation 9:247–257.
Sipma J, Lens PNL, Vieira A, Miron Y, van Lier JB, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (2000) Thermofilic sulfate reduction in UASB reactors under acidifying conditions. Process Biochem 35:509–522.
Sipma J, Meulepas RJW, Parshina SN, Stams AJM, Lettinga G, Lens PNL (2004) Effect of carbon monoxide, hydrogen and sulfate on thermophilic (55°C) hydrogenogenic carbon monoxide conversion in two anaerobic bioreactor sludges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:421–428.
Sipma J, Lettinga G, Stams AJM, Lens PNL (2006) Hydrogenogenic CO conversion in a moderately thermophilic (55°C) sulfate-fed gas lift reactor: competition for CO-derived H2. Biotechnol Progr 22:1327–1334.
Smith RM, Martell AE (1976) Critical stability constants, vol. 4. Inorganic ligands. Plenum, New York.
Tabak HH, Scharp R, Burckle J, Kawahara FK, Govind R (2003) Advances in biotreatment of acid mine drainage and biorecovery of metals: 1. Metal precipitation for recovery and recycle. Biodegradation 14:423–436.
Vallero MVG, Lens PNL, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (2003) Effect of NaCl on thermophilic (55°C) methanol degradation in sulfate reducing reactors. Water Res 37:2269–2280.
Vallero MVG, Camarero E, Lettinga G, Lens PNL (2007) Hyperthermophilic sulfate reduction in methanol and formate fed UASB reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol (in press).
van Houten RT, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (1994) Biological sulphate reduction using gas-lift reactors fed with hydrogen and carbon dioxide as energy and carbon source. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:586–594.
van Houten RT, Oude Elferink SJWH, van Hamel SE, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lettinga G (1995) Sulphate reduction by aggregates of sulphate-reducing bacteria and homo-acetogenic bacteria in a lab-scale gas-lift reactor. Bioresour Technol 54:73–79.
van Houten RT, Yun SY, Lettinga G (1997) Thermophilic sulphate and sulfite reduction in lab-scale gas-lift reactors using H2 and CO2 as energy and carbon source. Biotechnol Bioeng 55:807–814.
Veeken AHM, de Vries S, van der Mark A, Rulkens WH (2003) Selective precipitation of heavy metals as controlled by a sulfide-selective electrode. Sep Sci Technol 38:1–19.
Verstraete W, de Beer D, Pena M, Lettinga G, Lens P (1996) Anaerobic bioprocessing of waste. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:221–238.
Waybrant KR, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ (1998) Selection of reactive mixtures for use in permeable reactive walls for treatment of acid mine drainage. Environ Sci Technol 32:1972–1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lens, P.N.L., Meulepas, R.J.W., Sampaio, R., Vallero, M., Esposito, G. (2008). Bioprocess Engineering of Sulfate Reduction for Environmental Technology. In: Dahl, C., Friedrich, C.G. (eds) Microbial Sulfur Metabolism. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72682-1_22
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-72682-1_22
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-72679-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-72682-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)