Summary
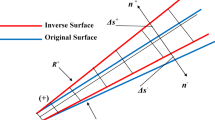
Iterative inverse design methods for compressor and turbine blades, with prescribed Mach number or pressure distribution, are presented. It is explained how the permeable wall concept can be used to define the blade modifications required to obtain the target performances with a small number of iterations. It is shown how the method can be combined with potential flow methods, Euler and Navier Stokes solvers. Each method is illustrated with examples. Advantages and problems are discussed and practical solutions to the existancy problem and mechanical constraints are proposed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer F., Garabedian, P., and Korn, D.: Supercritical Wing Sections, Vol. I, Springer-Verlag, New York, (1972).
Cantrell, H.N. and Fowler, J.E.: The aerodynamic design of two dimensional turbine cascades for incompressible flows with high speed computer, ASME paper 58-A-141, (1958).
Sanz J.M.: Automated design of controlled diffusion blades, ASME Journal of Turbomachinery, Vol. 110, No 4, pp 540–544, (1988).
Stanitz, J.D.: Design of two dimensional channels with prescribed velocity distributions along the channel walls, NACA TR 1115, (1953).
Schmidt, E.: Computation of supercritical compressor and turbine cascades with a design method for transonic flows, ASME Journal of Engineering for Power, Vol. 102, pp 68–74, (1980).
Varonos, A., Chaviaropoulos, P. and Papailiou K.: A design method for stator cascades with streamsur-faces of revolution using natural coordinates, Inverse Problems in Engineering, Vol. 2, pp.119–139, (1995).
Lighthill, J.M.: A new method of two dimensional aerodynamic design, ARC R&M 2112, (1945).
Volpe, G.: Transonic shock free wing design, Inverse Methods for Airfoil Design for Aeronautical and Turbomachinery Applications, AGARD R 780, Paper 5, (1990).
Papailiou, K.D.: Blade optimization based on boundary layer concepts, von Karman Institute CN 60, (1967).
Vanderplaats, G.N.: Approximation concepts for numerical airfoils optimization, NASA TP-1370, (1979).
Eyi, S. and Lee, D.: High-lift design optimization using the Navier-Stokes equations, AIAA paper 95–0477, (1995).
Thibert, J.J.: One point and multi-point design optimization for airplane and helicopter application, Inverse methods for Airfoil Design for Aeronautical and Turbomachinery Applications, AGARD-R-780, (1990).
Gunzburger, M.D.: Introduction to the mathematical aspects of flow control and optimization, Inverse design and optimization, von Karman Institute LS 1997–05, (1997).
Ta’asan S.: Introduction to shape design and control, Inverse design and optimization, von Karman Institute LS 1997–5, (1997).
Van den Braembussche, R.A., Léonard, O., Nekmouche, L.: Subsonic and transonic blade design by means of analysis codes, Computational Methods for Aerodynamic Design (Inverse) and Optimization, AGARD CP 463, Paper 9, (1989).
Murugesan, K. and Railly, J.W.: Pure design method for aerofoils in cascade, J. Mechanical Engineering Science, Vol. 11, No 5, pp. 454–464, (1969).
Sata, A., Ubaldi, M. and Zunino, P.: Design of axial turbines for mini hydro plants, Fourth International Symposium on Hydro Power Fluid Machinery, ASME FED-Vol. 43, pp. 29–36, (1984).
Van den Braembussche, R.A.: The application of the singularity method to blade-to-blade calculations, Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics of Turbomachinery, NATO Advanced Sciences Institute Series, series E: Applied Sciences, No 97A, eds. A.S. Ucer, P. Stow and Ch. Hirsch, pp. 167–191, (1984).
Arts, T.: Workshop on two- and three dimensional calculations in turbine bladings, Numerical Methods for Flows in Turbomachinery Bladings, von Karman Institute LS 1982–05, (1982).
Sanger, N.L. and Shreeve R.P.: Comparison of calculated and experimental cascade performance for controlled diffusion compressor stator blading, ASME Journal of Turbomachinery, Vol. 108, pp. 43–50, (1986).
Bogers P., Breugelmans F.A. and Van den Braembussche R.A.: Design and experimental verification of an optimized compressor blade, paper submitted for presentation at the ASME Gas Turbine conference, (1998).
Léonard, O.: Subsonic and transonic cascade design, Inverse methods for Airfoil Design for Aeronautical and Turbomachinery Applications, AGARD-R-780, paper 7, (1990).
Léonard, O.: Conception et développement d’une méthode inverse de type Euler et application à la génération de grilles d’aubes transsoniques, Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté Polytechnique de Mons & von Karman Institute, (1992).
Léonard, O. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: Design method for subsonic and transonic cascade with prescribed Mach number distribution, ASME Journal of Turbomachinery, Vol. 114, No 3, pp. 553–560, (1993).
Léonard, O. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: Inverse design of compressor and turbine blades at transonic flow conditions, ASME Paper 92-GT-430, (1993).
Demeulenaere, A. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: Inverse design of transonic blades taking into account radius change, von Karman Institute PR 1993–31, (1993).
Van den Braembussche, R.A., Demeulenaere, A. and Borges, J.: Inverse design of radial flow impellers with prescribed velocity distribution, Technology Requirements for Small Gas Turbines, AGARD-CP-537, paper 18, (1993).
Van den Braembussche R.A.: Inverse design methods for axial and radial turbomachines, Numerical methods for flow calculation in turbomachinery, von Karman Institute LS-1994–06, (1994).
Demeulenaere, A. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: Three-dimensional inverse method for turbomachinery blading design, ASME paper 96-GT-39, (1996).
Demeulenaere, A. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: Three-dimensional inverse design method for turbine and compressor blades, 3rd. International Symposium on Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows, Beijing, September (1996).
Meauzé, G.: An inverse time marching method for the definition of cascade geometry, ASME Journal of Engineering for Power, Vol. 104, pp. 650–656, (1982).
Zannetti L. and Larocca F.: Inverse Method for 3D Internal Flows, Inverse Methods for Airfoil Design for Aeronautical and Turbomachinery Applications, AGARD-R-780, paper 8, (1990).
Demeulenaere, A. and Van den Braembussche, R.A.: A new compressor and turbine blade design method based on three-dimensional Euler computations with moving boundaries, VKI preprint 1997–56, (1997).
Demeulenaere, A.: PhD thesis, University of Liege & von Karman Institute, (1997).
Demeulenaere, A.: An Euler and Navier Stokes inverse method for compressor and turbine blade design, Inverse design and optimization, von Karman Institute LS 1997–5, (1997).
Demeulenaere, A. and Van den Braembussche, R.: Application of a three-dimensional inverse method to the design of a centrifugal compressor impeller, 4th National Congress on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Leuven, pp. 353–356, (1997).
Demirdzic, I. and Peric, M.: Space conservation law in finite volume calculations of fluid flow, International Journal for Numerical methods in Fluids, Vol. 8, pp. 1037–1050, (1988).
Demirdzic, I. and Peric, M.: Finite volume method for prediction of fluid flow in arbitrarily shaped domains with moving boundaries, International Journal for Numerical methods in Fluids, Vol. 10, pp. 771–790, (1990).
van Leer, B.: Flux vector splitting for the Euler equations, ICASE, Report No 82–30, (1982).
Giles, M.: Non reflecting boundary conditions for Euler equations calculations, AIAA Journal, Vol. 108, No 12, pp 2050–2058, (1989).
Arts, T., Lambert de Rouvroy, M. and Sieverding, C.H.: Highly loaded transonic linear turbine guide vane cascade LS89, in: Numerical Methods for flows in turbomachinery, von Karman Institute LS 1989–06, May 22–26, (1989).
Han, W., Tan, C., Shi, H., Zhou, M. and Wang, Z.: Effects of leaning and curving of blades with high turning angles on the aerodynamic characteristics of turbine rectangular cascades, ASME Paper 93-GT-296, (1993).
Léonard, O., Rogiest, P. and Delaneye M.: Blade analysis and design using an implicit flow solver, 2nd. European Conference on Turbomachinery-Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Antwerpen, March 5–7, pp. 331–338, (1997).
Léonard, O. and Demeulenaere, A.: A Navier Stokes inverse method based on moving wall strategy, ASME paper 97-GT-416, (1997).
Demeulenaere, A., Léonard, O. and Van den Braembussche R.: A two-dimensional Navier-Stokes inverse solver for compressor and turbine design, 2nd. European Conference on Turbomachinery-Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Antwerpen, March 5–7, pp. 339–346, (1997).
Denton, J., Hodson, H.P. and Dominy R.G.: Subsonic turbine cascade LA, in: AGARD-AR-275, (1990).
Deplaen, D. and Van den Braembussche R.A.: Ontwerp van transsone vleugelprofielen bij middel van een inverse Euler methode, von Karman Institute & Luru, afstudeerwerk, (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Braunschweig/Wiesbaden
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Van den Braembussche, R.A. (1999). Inverse Blade Design Based on Permeable Wall Concept. In: Fujii, K., Dulikravich, G.S. (eds) Recent Development of Aerodynamic Design Methodologies. Notes on Numerical Fluid Mechanics (NNFM), vol 65. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-322-89952-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-322-89952-1_7
Publisher Name: Vieweg+Teubner Verlag
Print ISBN: 978-3-322-89954-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-322-89952-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive