Abstract
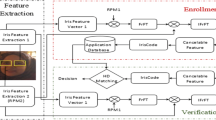
In a cancelable iris recognition technique, all enrollment patterns are masked using a transformation function, and the invertibility for obtaining the original data should not be possible. This paper presents an approach for mixing multi-biometric features based on Double Random Phase Encryption (DRPE) to obtain a single protected IrisCode from different IrisCodes based on the Fractional Fourier Transform (FrFT). For the IrisCode generation, two encryption keys (RPM1 and RPM2) are utilized. The RPM2 is suggested to be the right iris feature vector of the same user. As a result, this feature level mixing of two different templates highly increases privacy and slightly enhances performance compared to its original counterpart. This proposed system achieves a high success rate in identification due to the fact that the iris authentication issue has been transformed to a key authentication process.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daugman, J.: High confidence visual recognition of persons by a test of statistical independence. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 15(11), 1148–1161 (1993)
Daugman, J.: How iris recognition works. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 14(1), 21–30 (2004)
Venugopalan, S., Savvides, M.: How to generate spoofed irises from an iris code template. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 6(2), 385–395 (2011)
Rathgeb, C., Uhl, A.: A survey on biometric cryptosystems and cancelable biometrics. EURASIP. Inf. Secur. 2011, 3 (2011)
Nagar, A., Nandakumar, K., Jain, A.: Multibiometric cryptosystems based on feature-level fusion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(1), 255–268 (2012)
Rathgeb, C., Busch, C.: Multibiometric template protection: issues and challenges. In: New Trends and Developments in Biometrics, pp. 173–190. InTech (2012)
Nandakumar, K., Jain, A.K.: Biometric template protection: bridging the performance gap between theory and practice. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 32(5), 88–100 (2015)
Patel, V.M., Ratha, N.K., Chellappa, R.: Cancelable biometrics: a review. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. Spec. Issue Biom. Secur. Priv. 32(5), 54–65 (2015)
Punithavathi, P., Subbiah, G.: Can cancellable biometrics preserve privacy? Biometr. Technol. Today 2017(7), 8–11 (2017)
Ratha, N.K., Chikkerur, S., Connell, J.H., Bolle, R.M.: Generating cancelable fingerprint templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. 29(4), 561–572 (2007)
Harjoko, A., Hartati, S., Dwiyasa, H.: A method for iris recognition based on 1D Coiflet wavelet. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 56, 126–129 (2009)
Zuo, J., Ratha, N.K., Connel, J.H.: Cancelable iris biometric. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Florida, USA, pp. 1–4 (2008)
Teoh, A.B.J., Ngo, D.C.L., Goh, A.: Biohashing: two factor authentication featuring fingerprint data and tokenised random number. Pattern Recogn. 37(11), 2245–2255 (2004)
Rathgeb, C., Breitinger, F., Baier, H., Busch, C.: Towards bloom filter-based indexing of iris biometric data. In 15th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics, pp. 422–429 (2015)
Rathgeb, C., Breitinger, F., Busch, C., Baier, H.: On the application of bloom filters to iris biometrics. IET J. Biom. 3(4), 207–218 (2014)
Ouda, O., Tsumura, N., Nakaguchi, T.: On the security of bioencoding based cancelable biometrics. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 94-D(9), 1768–1777 (2011)
Ouda, O., Tsumura, N., Nakaguchi, T.: A reliable tokenless cancelable biometrics scheme for protecting iriscodes. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E93-D(7), 1878–1888 (2010)
Lacharme, P.: Analysis of the iriscodes bioencoding scheme. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 6(5), 315–321 (2012)
Hammerle-Uhl, J., Pschernig, E., Uhl, A.: Cancelable iris biometrics using block re-mapping and image warping. In: International Conference on Information Security, Italy, pp. 135–142 (2009)
Jenisch, S., Uhl, A.: Security analysis of a cancelable iris recognition system based on block remapping. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Belgium, pp. 3274–3277 (2011)
Tarek, M., Ouda, O., Hamza, T.: Robust cancelable biometrics scheme based on neural networks. IET J. Biom. 5(3), 220–228 (2016)
Tarek, M., Ouda, O., Hamza, T.: Pre-image resistant cancelable biometrics scheme using bidirectional memory model. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 19(4), 498–506 (2017)
Refregier, P., Javidi, B.: Optical image encryption based on input plane and fourier plane random encoding. Opt. Lett. 20, 767–769 (1995)
Joshi, M., Shakher, C., Singh, K.: Color image encryption and decryption for twin images in fractional Fourier domain. Opt. Commun. 281(23), 5713–5720 (2008)
Ozaktas, H.M.: Fractional Fourier domains. Signal Process. 46, 119–124 (1995)
Soliman, N.F., Mohamed, E., Magdi, F., Abd El-Samie, F.E., AbdElnaby, M.: Efficient iris localization and recognition. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 140, 469–475 (2017)
CASIA-IrisV3 Database. http://www.cbsr.ia.ac.cn/english/IrisDatabase.asp. Accessed Dec 2017
Masek, L.: Recognition of human iris patterns for biometric identification. M.Sc. Thesis, The University of Western Australia (2003)
Jain, A.K., Li, S.Z.: Handbook of Face Recognition. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Kumar, A., Passi, A.: Comparison and combination of iris matchers for reliable personal authentication. Pattern Recogn. 43, 1016–1026 (2010)
Rahulkar, A.D., Holambe, R.S.: Half-iris feature extraction and recognition using a new class of biorthogonal triplet half-band filter bank and flexible k-out-of-n. A post classifier. IEEE Trans. IFS 7, 230–240 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Soliman, R.F., Amin, M., Abd El-Samie, F.E. (2019). On Mixing Iris-Codes. In: Hassanien, A., Tolba, M., Shaalan, K., Azar, A. (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2018. AISI 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 845. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99010-1_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99010-1_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-99009-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-99010-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)