Abstract
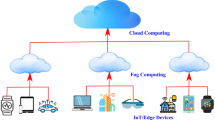
The concept of Edge or Fog Computing is fast emerging as a powerful Computing paradigm for real-time data capture , processing, decision-making and actuation. The accumulation of Edge devices in different forms in multiple environments is the key motivation for the surging popularity of Fog Computing. In this chapter, we concentrate on identifying the important parameter of device performance in Fog Computing environments . This measurement metric helps to analyse the Quality of Service (QoS ) attributes for Fog or Edge applications. The Fog device connectivity guarantees the goal of low latency for fulfilling time-sensitive applications and use cases. However, there are issues with the participating devices and the connectivity between devices and the intermediaries such as the IoT gateway , broker or the middleware. The primary communication happens in wireless mode, and hence, there are several variables that can intermittently go wrong. The purpose of this chapter is to expose the various performance issues being associated with the Fog Computing model and to convey the ways and means of establishing and sustaining the goal of high performance.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tordera EM, Masip X, Garcia Alminana J, Farre J (2016) What is a fog node? a tutorial on current concepts towards a common definition, networking and internet architecture (cs.NI). Cornell University Library, cite as: arXiv:1611.09193v1
Iorga M, Feldman L, Barton R, Martin MJ, Goren N, Mahmoudi C (2017) The NIST definition of Fog Computing, NIST SP 800-191 (DRAFT). www.csrc.nist.gov/csrc/media/publications/sp/800-191/draft/
Bonomi F, Milito R, Zhu J, Addepall S (2012) Fog Computing and its role in the internet of things. In: Proceedings of MCC’12, Helsinki, Finland, pp 13–16, 17 Aug 2012
OpenFog Consortium (2017) OpenFog reference architecture for Fog Computing, While paper published USA OPFRA001.020817, Feb 2017
i-Scoop (2017) The internet of things in 2017: trends, technologies, market data and evolutions. www.i-scoop.eu/internet-of-things-guide/connectivity-networks-Fog-Computing-internet-of-things/. Accessed 22 Dec 2017
García-Pérez CA, Pedro M (2017) Experimental evaluation of Fog Computing techniques to reduce latency in LTE networks. Emerg Telecommun Technol (inpress). http://dx.doi.org/10.2759/54788, http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ett.3201
Mohan N, Kangasharju J (2017) Edge-Fog cloud: a distributed cloud for the internet of things computations. In: IEEE Cloudification of the Internet of Things, arXiv:1702.06335v2
Westbase.io (2016) Fog Computing versus cloud Computing what’s the difference, www.westbaseuk.com/news/Fog-Computing-vs-cloud-Computing-whats-thedifference/. Accessed 30 Nov 2017
Dastjerdi AV, Gupta H, Calheiros RN, Ghosh S, Buyya R (2016) In: Buyya R, Dastjerdi AV (eds) Fog Computing: principles, architectures, and applications, pp 61–75. Morgan Kaufmann, New York. Cite as arXiv:1601.02752
Ai Y, Peng M, Zhang K (2017) Edge cloud Computing technologies for the internet of things: a primer. Digital Commun Netw, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommuniocations. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V, July 2017
Yi S, Hao Z, Qin Z, Li Q (2015) Fog Computing: platform and applications. In: Third IEEE workshop on hot topics in web systems and technologies (HotWeb), pp 73–78
Satyanarayanan M, Bahl P, Caceres R, Davies N (2009) The case for vm-based cloudlets in mobile Computing. IEEE Pervasive Comput 8(4):14–23
Li C, Qin Z, Novak E, Li Q, Senior Member (2017) Securing SDN infrastructure of IoT–fog networks from MitM attacks. In: ICSEA 2017: The twelfth international conference on software engineering advances. ISBN: 978-1-61208-590-6
Jiang Q, Tang R, Liu P, Qiu Y, Xu H (2014) Research on dynamic data fusion algorithm based on context awareness. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE international conference on progress in informatics and computing. IEEE, pp 529–534. https://doi.org/10.1109/pic.2014.6972391
Shah-Mansouri H, Wong VWS (2017) Hierarchical fog-cloud computing for IoT systems: a computation offloading game. Cite as: arXiv:1710.06089v1 [cs.DC] Oct 2017
Hirve R (2017) What is Fog Computing? why Fog Computing trending now? https://www.linkedin.com/today/author/rhirve
Byers CC, Wetterwald P (2015) Fog Computing distributing data and intelligence for resiliency and scale necessary for IoT: the Internet of Things. In: Symposium Ubiquity, pp 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1145/2822875
Peng G (2003) CDN: Content Distribution Network, Technical Report TR-125. Experimental Computer Systems Lab, Department of Computer Science, State University of New York, Stony Brook, NY. http://citeseer.ist.psu.edu/peng03cdn.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pushpa, J., Raj, P. (2018). Performance Enhancement of Fog Computing Using SDN and NFV Technologies. In: Mahmood, Z. (eds) Fog Computing. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-94890-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-94890-4_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-94889-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-94890-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)