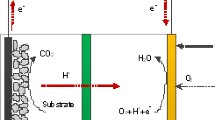
Abstract
Water and energy securities are emerging as increasingly important and vital issues for today’s world. Therefore, the field of wastewater management and alternative energy is one of the most unexplored fields of Biotechnology and Science. Microbial fuel cell (MFC) is emerging as a modern wastewater treatment technology which converts chemical energy stored in the bonds of organic matter present in wastewater directly into electricity using electrogenic bacteria as a catalyst, without causing environmental pollution. In this chapter, the technical know-how of MFC and biocatalyst has been depicted. A thorough understanding of the fundamental principles of microbial fuel cells would help to perceive new aspects of bioenergy conversions and how such systems could be integrated with the present energy generation systems to maximize the energy recovery. In this respect, MFCs show promise to treat wastewater with simultaneous production of renewable energy. In this chapter, the theories underlying the electron transfer mechanisms, the biochemistry and the microbiology involved, and the material characteristics of anode, cathode, and the separator have been clearly described. This chapter highlights the major factors involved toward the improvement bioelectricity production processes. Advance in the design of MFC Technology and the economy of the process are also included.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Pham HT, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:3388–3394. doi:10.1021/es0525511
Babauta J, Renslow R, Lewandowski Z, Beyenal H (2012) Electrochemically active biofilms: facts and fiction. A review. Biofouling 28:789–812. doi:10.1080/08927014.2012.710324
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Bond DR, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity production by geobacter sulfurreducens attached to electrodes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1548–1555. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.3.1548-1555.2003
Chandrasekhar K, Venkata Mohan S (2012) Bio-electrochemical remediation of real field petroleum sludge as an electron donor with simultaneous power generation facilitates biotransformation of PAH: effect of substrate concentration. Bioresour Technol 110:517–525. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.128
Chandrasekhar K, Venkata Mohan S (2014a) Bio-electrohydrolysis as a pretreatment strategy to catabolize complex food waste in closed circuitry: Function of electron flux to enhance acidogenic biohydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:11411–11422. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.05.035
Chandrasekhar K, Venkata Mohan S (2014b) Induced catabolic bio-electrohydrolysis of complex food waste by regulating external resistance for enhancing acidogenic biohydrogen production. Bioresour Technol 165:372–382. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.02.073
Chandrasekhar K, Lee YJ, Lee DW (2015a) Biohydrogen production: strategies to improve process efficiency through microbial routes. Int J Mol Sci 16:8266–8293. doi:10.3390/ijms16048266
Chandrasekhar K, Amulya K, Venkata Mohan S (2015b) Solid phase bio-electrofermentation of food waste to harvest value-added products associated with waste remediation. Waste Manage 45:57–65. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.001
Chaudhuri SK, Lovley DR (2003) Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediatorless microbial fuel cells. Nat Biotechnol 21:1229–1232. doi:10.1038/nbt867
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006a) Increased performance of single-chamber microbial fuel cells using an improved cathode structure. Electrochem Commun 8:489–494. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2006.01.010
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006b) Increased power generation in a continuous flow MFC with advective flow through the porous anode and reduced electrode spacing. Environ Sci Technol 40:2426–2432. doi:10.1021/es051652w
Deval AS, Parikh HA, Kadier A, Chandrasekhar K, Bhagwat AM, Dikshit AK (2016) Sequential microbial activities mediated bioelectricity production from distillery wastewater using bio-electrochemical system with simultaneous waste remediation. Int J Hydrogen Energy. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.114
Du Z, Li H, Gu T (2007) A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: a promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol Adv 25:464–482. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.05.004
Erable B, Duţeanu NM, Ghangrekar MM, Dumas C, Scott K (2010) Application of electro-active biofilms. Biofouling 26:57–71. doi:10.1080/08927010903161281
Evelyn Li Y, Marshall A, Gostomski PA (2014) Gaseous pollutant treatment and electricity generation in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) utilising redox mediators. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 13:35–51. doi:10.1007/s11157-013-9322-2
Fricke K, Harnisch F, Schröder U (2008) On the use of cyclic voltammetry for the study of anodic electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 1:144–147. doi:10.1039/B802363H
Ghasemi M, Daud WRW, Hassan SHA, Oh S-E, Ismail M, Rahimnejad M, Jahim JM (2013) Nano-structured carbon as electrode material in microbial fuel cells: a comprehensive review. J Alloys Compd 580:245–255. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.094
Gil G-C, Chang I-S, Kim BH, Kim M, Jang J-K, Park HS, Kim HJ (2003) Operational parameters affecting the performance of a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 18:327–334. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00110-0
He Z, Wagner N, Minteer SD, Angenent LT (2006) An upflow microbial fuel cell with an interior cathode: assessment of the internal resistance by impedance spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 40:5212–5217. doi:10.1021/es060394f
Jadhav GS, Ghangrekar MM (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cell subjected to variation in pH, temperature, external load and substrate concentration. Bioresour Technol 100:717–723. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.041
Jong BC, Kim BH, Chang IS, Liew PWY, Choo YF, Kang GS (2006) Enrichment, performance, and microbial diversity of a thermophilic mediatorless microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 40:6449–6454. doi:10.1021/es0613512
Kadier A, Simayi Y, Abdeshahian P, Azman NF, Chandrasekhar K, Kalil MS (2015a) A comprehensive review of microbial electrolysis cells (MEC) reactor designs and configurations for sustainable hydrogen gas production. Alex Eng J. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2015.10.008
Kadier A, Simayi Y, Chandrasekhar K, Ismail M, Kalil MS (2015b) Hydrogen gas production with an electroformed Ni mesh cathode catalysts in a single-chamber microbial electrolysis cell (MEC). Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:14095–14103. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.08.095
Khilari S, Pandit S, Ghangrekar MM, Pradhan D, Das D (2013) Graphene oxide-impregnated PVA–STA composite polymer electrolyte membrane separator for power generation in a single-chambered microbial fuel cell. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:11597–11606. doi:10.1021/ie4016045
Khilari S, Pandit S, Varanasi JL, Das D, Pradhan D (2015) Bifunctional manganese ferrite/polyaniline hybrid as electrode material for enhanced energy recovery in microbial fuel cell. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20657–20666. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b05273
Kim Y, Logan BE (2013) Microbial desalination cells for energy production and desalination. Desalination 308:122–130. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2012.07.022
Kiran Kumar A, Venkateswar Reddy M, Chandrasekhar K, Srikanth S, Venkata Mohan S (2012) Endocrine disruptive estrogens role in electron transfer: bio-electrochemical remediation with microbial mediated electrogenesis. Bioresour Technol 104:547–556. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.037
Leong JX, Daud WRW, Ghasemi M, Liew KB, Ismail M (2013) Ion exchange membranes as separators in microbial fuel cells for bioenergy conversion: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 28:575–587. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.052
Logan BE (2008) Microbial fuel cells, 1st edn. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Logan BE (2012) Essential data and techniques for conducting microbial fuel cell and other types of bioelectrochemical system experiments. ChemSusChem 5:988–994. doi:10.1002/cssc.201100604
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schröder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192. doi:10.1021/es0605016
Lu M, Li SFY (2012) Cathode reactions and applications in microbial fuel cells: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:2504–2525. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.592744
Mo Y, Liang P, Huang X, Wang H, Cao X (2009) Enhancing the stability of power generation of single-chamber microbial fuel cells using an anion exchange membrane. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:1767–1772. doi:10.1002/jctb.2242
Mook WT, Aroua MKT, Chakrabarti MH, Noor IM, Irfan MF, Low CTJ (2013) A review on the effect of bio-electrodes on denitrification and organic matter removal processes in bio-electrochemical systems. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2012.07.004
Moon H, Chang IS, Kim BH (2006) Continuous electricity production from artificial wastewater using a mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 97:621–627. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.03.027
Pandit S, Sengupta A, Kale S, Das D (2011) Performance of electron acceptors in catholyte of a two-chambered microbial fuel cell using anion exchange membrane. Bioresour Technol 102:2736–2744
Pandit S, Ghosh S, Ghangrekar MM, Das D (2012a) Performance of an anion exchange membrane in association with cathodic parameters in a dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:9383–9392. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.03.011
Pandit S, Nayak BK, Das D (2012b) Microbial carbon capture cell using cyanobacteria for simultaneous power generation, carbon dioxide sequestration and wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 107:97–102. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.067
Pandit S, Khilari S, Bera K, Pradhan D, Das D (2014a) Application of PVA–PDDA polymer electrolyte composite anion exchange membrane separator for improved bioelectricity production in a single chambered microbial fuel cell. Chem Eng J 257:38–147. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.077
Pandit S, Khilari S, Roy S, Pradhan D, Das D (2014b) Improvement of power generation using Shewanella putrefaciens mediated bioanode in a single chambered microbial fuel cell: Effect of different anodic operating conditions. Bioresour Technol 166:451–457. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.075
Pandit S, Khilari S, Roy S, Ghangrekar MM, Pradhan D, Das D (2015) Reduction of start-up time through bioaugmentation process in microbial fuel cells using an isolate from dark fermentative spent media fed anode. Water Sci Technol 72:106–115. doi:10.2166/wst.2015.174
Pant D, Van Bogaert G, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2010) A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour Technol 101:1533–1543. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.017
Pant D, Singh A, Van Bogaert G, Irving Olsen S, Singh Nigam P, Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2012) Bioelectrochemical systems (BES) for sustainable energy production and product recovery from organic wastes and industrial wastewaters. RSC Adv 2:1248–1263. doi:10.1039/C1RA00839K
Prasad D, Sivaram TK, Berchmans S, Yegnaraman V (2006) Microbial fuel cell constructed with a micro-organism isolated from sugar industry effluent. J Power Sources 160:991–996. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.02.051
Qiao Y, Bao S-J, Li CM (2010) Electrocatalysis in microbial fuel cells—from electrode material to direct electrochemistry. Energy Environ Sci 3:544. doi:10.1039/b923503e
Rabaey K, Keller J (2008) Microbial fuel cell cathodes: from bottleneck to prime opportunity? Water Sci Technol 57:655. doi:10.2166/wst.2008.103
Rabaey K, Angenent L, Schroder U (2009) Bioelectrochemical systems: from extracellular electron transfer to biotechnological application. IWA Publishing, London
Rahimnejad M, Bakeri G, Najafpour G, Ghasemi M, Oh S-E (2014) A review on the effect of proton exchange membranes in microbial fuel cells. Biofuel Res J 1:7–15. doi:10.18331/BRJ2015.1.1.4
Rimboud M, Pocaznoi D, Erable B, Bergel A (2014) Electroanalysis of microbial anodes for bioelectrochemical systems: basics, progress and perspectives. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:16349. doi:10.1039/C4CP01698J
Ringeisen BR, Henderson E, Wu PK, Pietron J, Ray R, Little B, Biffinger JC, Jones-Meehan JM (2006) High power density from a miniature microbial fuel cell using shewanella oneidensis DSP10. Environ Sci Technol 40:2629–2634. doi:10.1021/es052254w
Rismani-Yazdi H, Carver SM, Christy AD, Tuovinen OH (2008) Cathodic limitations in microbial fuel cells: an overview. J Power Sources 180:683–694. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.02.074
Schröder U (2008) From wastewater to hydrogen: biorefineries based on microbial fuel-cell technology. ChemSusChem 1:281–282. doi:10.1002/cssc.200800041
Stams AJM, de Bok FAM, Plugge CM, van Eekert MHA, Dolfing J, Schraa G (2006) Exocellular electron transfer in anaerobic microbial communities. Environ Microbiol 8:371–382. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.00989.x
Strik DPBTB, Timmers RA, Helder M, Steinbusch KJJ, Hamelers HVM, Buisman CJN (2011) Microbial solar cells: applying photosynthetic and electrochemically active organisms. Trends Biotechnol 29:41–49. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.10.001
Venkata Mohan S, Chandrasekhar K (2011a) Self-induced bio-potential and graphite electron accepting conditions enhances petroleum sludge degradation in bio-electrochemical system with simultaneous power generation. Bioresour Technol 102:9532–9541. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.038
Venkata Mohan S, Chandrasekhar K (2011b) Solid phase microbial fuel cell (SMFC) for harnessing bioelectricity from composite food waste fermentation: influence of electrode assembly and buffering capacity. Bioresour Technol 102:7077–7085. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.039
Venkata Mohan S, Velvizhi G, Annie Modestra J, Srikanth S (2014) Microbial fuel cell: Critical factors regulating bio-catalyzed electrochemical process and recent advancements. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 40:779–797. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.109
Wang H, Ren ZJ (2013) A comprehensive review of microbial electrochemical systems as a platform technology. Biotechnol Adv 31:1796–1807. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.10.001
Wang L, Zhou X, Zhong S, Zhou N (2010) Novel materials and technologies of microbial fuel cell in environmental engineering. ECS Trans 25:311–333. doi:10.1149/1.3414027
You S, Zhao Q, Zhang J, Jiang J, Zhao S (2006a) A microbial fuel cell using permanganate as the cathodic electron acceptor. J Power Sources 162:1409–1415. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.07.063
You SJ, Zhao QL, Jiang JQ, Zhang JN, Zhao SQ (2006b) Sustainable approach for leachate treatment: electricity generation in microbial fuel cell. J Environ Sci Health Part A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:2721–2734. doi:10.1080/10934520600966284
Zhang T, Cui C, Chen S, Ai X, Yang H, Shen P, Peng Z (2006) A novel mediatorless microbial fuel cell based on direct biocatalysis of Escherichia coli. Chem Commun Camb Engl 2257–2259. doi:10.1039/b600876c
Zhao F, Slade RCT, Varcoe JR (2009) Techniques for the study and development of microbial fuel cells: an electrochemical perspective. Chem Soc Rev 38:1926–1939. doi:10.1039/b819866g
Zhou M, Chi M, Luo J, He H, Jin T (2011) An overview of electrode materials in microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 196:4427–4435. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.01.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pandit, S., Chandrasekhar, K., Kakarla, R., Kadier, A., Jeevitha, V. (2017). Basic Principles of Microbial Fuel Cell: Technical Challenges and Economic Feasibility. In: Kalia, V., Kumar, P. (eds) Microbial Applications Vol.1. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52666-9_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52666-9_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-52665-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-52666-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)