Abstract
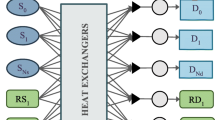
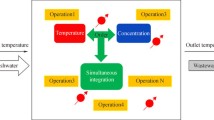
This chapter presents the use of process integration as a useful tool for intensifying processes. Particularly, mass and heat integration through the synthesis of mass and heat exchanger networks represent powerful tools that can be used for reducing the need of external agents such as fresh water and hot and cold utilities. Two optimization formulations are presented for mass and heat integration and the application to two case studies shows significant savings of external utilities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stankiewicz A, Moulijn J (eds) (2004) Process intensification: history, philosophy, principles. Marcel Dekker, New York
Ponce-Ortega JM, Al-Thubaiti MM, El-Halwagi MM (2012) Process intensification: new understanding and systematic approach. Chem Eng ProcessProcess Intensif 53(3):63–75
Lutze P, Gani R, Woodley JM (2010) Process intensification: a perspective on process synthesis. Chem Eng ProcessProcess Intensif 49(6):57–558
El-Halwagi MM (2012) Sustainable design through process integration: fundamentals and applications to industrial pollution prevention, resource conservation and profitability enhancement. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford
Gopalakrishnan M, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2012) A systems approach for process simplification through process integration. Chem Eng Technol 35(7):1262–1272
Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A, Ponce-Ortega JM (2007) Targets for heat exchanger networks synthesis with different heat transfer coefficients and non-uniform exchanger specifications. Chem Eng Res Des 85(A10):1447–1457
Serna-González M, Ponce-Ortega JM (2011) Total cost target for heat exchanger networks considering simultaneously pumping and area effects. Appl Therm Eng 31(11–12):1964–1975
Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2008) Synthesis of multipass heat exchanger networks using genetic algorithms. Comput Chem Eng 32(10):2320–2332
Ponce-Ortega JM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A, Grossmann IE (2008) Optimal synthesis of heat exchanger networks involving isothermal streams. Comput Chem Eng 32(8):1918–1942
Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2010) Synthesis of heat exchanger networks with optimal placement of multiple utilities. Ind Eng Chem Res 49(6):2849–2856
López-Maldonado LA, Ponce-Ortega JM, Segovia-Hernández JG (2011) Mutiobjective synthesis of heat exchanger networks minimizing the total annual cost and the environmental impact. Appl Therm Eng 31(6–7):1099–1113
Lira-Barragán LF, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM (2014) Optimal design of process energy systems integrating sustainable considerations. Energy 76:139–160
Lira-Barragán LF, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM (2014) Sustainable integration of trigeneration systems with heat exchanger networks. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(7):2732–2750
Ponce-Ortega JM, Hortua AC, El-Halwagi MM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2009) A property-based optimization of direct recycle networks and wastewater treatment processes. AIChE J 55(9):2329–2344
Nápoles-Rivera F, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2010) Global optimization of mass and property integration networks with in-plant property interceptors. Chem Eng Sci 65(15):4363–4377
Rojas-Torres MG, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, Nápoles-Rivera F, El-Halwagi MM (2013) Synthesis of water networks involving temperature-based property operators and thermal integration. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(1):442–461
Rubio-Castro E, Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM, Pham V (2013) Global optimization in property-based inter-plant water integration. AIChE J 59(3):813–833
Sotelo-Pichardo C, Ponce-Ortega JM, Nápoles-Rivera F, Serna-González M, El-Halwagi MM, Frausto-Hernández S (2014) Optimal reconfiguration of water networks base on properties. Clean Technol Environ Policy 16(2):303–328
Sotelo-Pichardo C, Bamufleh H, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2014) Optimal synthesis of property-based water networks considering growing demand projections. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(47):18260–18272
Jimenez-Gutierrez A, Lona-Ramírez J, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2014) An MINLP model for the simultaneous integration of energy, mass and properties in water networks. Comput Chem Eng 71:52–66
Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2010) Global optimization of property-based recycle and reuse networks including environmental constraints. Comput Chem Eng 34(3):318–330
Ponce-Ortega JM, Mosqueda-Jiménez FW, Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A, El-Halwagi MM (2011) A property-based approach to the synthesis of material conservation networks with economic an environmental objectives. AIChE J 57(9):2369–2387
López-Villareal F, Lira-Barragán LF, Rico-Ramírez V, Ponce-Ortega JM, El-Halwagi MM (2014) An MFA optimization approach for pollution treading considering the sustainability of the surrounding watershed. Comput Chem Eng 63:140–151
El-Halwagi A, Rosas C, Ponce-Ortega JM, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A, Mannan MS, El-Halwagi MM (2013) Multi-objective optimization of biorefineries with economic and safety objectives. AIChE J 59(7):2427–2434
Yee TF, Grossmann IE (1990) Simultaneous optimization models for heat integration-II. Heat exchanger network synthesis. Comput Chem Eng 14(10):1165–1184
Shenoy UV, Sinha A, Bondyopadhyay S (1998) Multiple utilities targeting for heat exchanger networks. Chem Eng Res Des 76(Part A):259–272
Isafiade AJ, Fraser DM (2008) Interval-based MINLP superstructure synthesis of heat exchange networks. Chem Eng Res Des 86(A3):245–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ponce-Ortega, J.M. (2016). Process Intensification in Heat and Mass Exchanger Networks. In: Segovia-Hernández, J., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A. (eds) Process Intensification in Chemical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28392-0_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28392-0_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-28390-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-28392-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)