Abstract
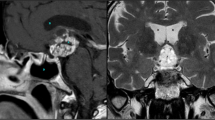
There are several kinds of craniopharyngioma that can be managed via two variations of the endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal procedure: the “standard” approach to the sellar region and the “extended” approach to the suprasellar area. These two variations have different indications.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guiot G, Derome P (1972) Indications for trans-sphenoid approach in neurosurgery. 521 cases. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 123(8):703–712
Weiss MH (1987) The transnasal transsphenoidal approach. In: Apuzzo MLJ (ed) Surgery of the third ventricle. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 476–494
Cavallo LM, de Divitiis O, Aydin S, Messina A, Esposito F, Iaconetta G, Talat K, Cappabianca P, Tschabitscher M (2008) Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the suprasellar area: anatomic considerations – part 1. Neurosurgery 62(6 Suppl 3):1202–1212. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000333786.98596.33
Couldwell WT, Weiss MH, Rabb C, Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI, Fukushima T (2004) Variations on the standard transsphenoidal approach to the sellar region, with emphasis on the extended approaches and parasellar approaches: surgical experience in 105 cases. Neurosurgery 55(3):539–550
Dusick JR, Esposito F, Kelly DF, Cohan P, DeSalles A, Becker DP, Martin NA (2005) The extended direct endonasal transsphenoidal approach for nonadenomatous suprasellar tumors. J Neurosurg 102(5):832–841
de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM (2002) Endoscopic transsphenoidal approach: adaptability of the procedure to different sellar lesions. Neurosurgery 51(3):699–705; discussion 705–707
Jho HD (2001) The expanding role of endoscopy in skull-base surgery. Indications and instruments. Clin Neurosurg 48:287–305
Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part I. Crista galli to the sella turcica. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E3
Cavallo LM, Frank G, Cappabianca P, Solari D, Mazzatenta D, Villa A, Zoli M, D’Enza AI, Esposito F, Pasquini E (2014) The endoscopic endonasal approach for the management of craniopharyngiomas: a series of 103 patients. J Neurosurg 121(1):100–113. doi:10.3171/2014.3.JNS131521
Koutourousiou M, Gardner PA, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Tyler-Kabara EC, Wang EW, Snyderman CH (2013) Endoscopic endonasal surgery for craniopharyngiomas: surgical outcome in 64 patients. J Neurosurg 119(5):1194–1207. doi:10.3171/2013.6.JNS122259
Cappabianca P, Frank G, Pasquini E, de Divitiis O, Calbucci F (2003) Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approaches to the suprasellar region, planum sphenoidale & clivus. In: de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P (eds) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Springer, Wien
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, de Divitiis O, Messina A, de Divitiis E (2008) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the midline skull base: the evolving role of transsphenoidal surgery. In: Pickard JD, Akalan N, Di Rocco C et al (eds) Advances and technical standards in neurosurgery. Springer, Wien/New York, pp 152–199
Jane JA Jr, Kiehna E, Payne SC, Early SV, Laws ER Jr (2010) Early outcomes of endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for adult craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurg Focus 28(4):E9. doi:10.3171/2010.1.FOCUS09319
Kassam AB, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Mintz AH, Prevedello DM (2008) Expanded endonasal approach, a fully endoscopic transnasal approach for the resection of midline suprasellar craniopharyngiomas: a new classification based on the infundibulum. J Neurosurg 108(4):715–728. doi:10.3171/JNS/2008/108/4/0715
Cavallo LM, Prevedello DM, Solari D, Gardner PA, Esposito F, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Kassam AB, Cappabianca P (2009) Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for residual or recurrent craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 111(3):578–589. doi:10.3171/2009.2.JNS081026
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM (2012) The evolving role of the transsphenoidal route in the management of craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg 77(2):273–274
Samii M, Samii A (2000) Surgical management of craniopharyngiomas. In: Schmidek HH (ed) Schmidek & Sweet operative neurosurgical techniques, vol 1, Indications, methods and results. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 489–502
Yasargil MG, Abdulrauf SI (2008) Surgery of intraventricular tumors. Neurosurgery 62(6 Suppl 3):1029–1040. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000333768.12951.9a, 00006123-200806001-00010 [pii]; discussion 1040–1021
Yasargil MG, Curcic M, Kis M, Siegenthaler G, Teddy PJ, Roth P (1990) Total removal of craniopharyngiomas. Approaches and long-term results in 144 patients. J Neurosurg 73(1):3–11
Fatemi N, Dusick JR, de Paiva Neto MA, Malkasian D, Kelly DF (2009) Endonasal versus supraorbital keyhole removal of craniopharyngiomas and tuberculum sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery 64(5 Suppl 2):269–284. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000327857.22221.53; discussion 284–266
Gerganov V, Metwali H, Samii A, Fahlbusch R, Samii M (2014) Microsurgical resection of extensive craniopharyngiomas using a frontolateral approach: operative technique and outcome. J Neurosurg 120(2):559–570. doi:10.3171/2013.9.JNS122133
Rhoton AL Jr (2002) The sellar region. Neurosurgery 51(4 Suppl):S335–S374
Bouthillier A, van Loveren HR, Keller JT (1996) Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification. Neurosurgery 38(3):425–432; discussion 432–423
de Notaris M, Solari D, Cavallo LM, D’Enza AI, Ensenat J, Berenguer J, Ferrer E, Prats-Galino A, Cappabianca P (2012) The “suprasellar notch,” or the tuberculum sellae as seen from below: definition, features, and clinical implications from an endoscopic endonasal perspective. J Neurosurg 116(3):622–629. doi:10.3171/2011.11.JNS111162
Cavallo LM, Di Somma A, de Notaris M, Prats-Galino A, Aydin S, Catapano G, Solari D, de Divitiis O, Somma T, Cappabianca P (2015) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the third ventricle. Multimodal anatomical study with surgical implications. World Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2015.03.007
Spaziante R, De Divitiis E, Irace C, Cappabianca P, Caputi F (1989) Management of primary or recurring grossly cystic craniopharyngiomas by means of draining systems. Topic review and 6 case reports. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 97(3–4):95–106
de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, de Divitiis O, Messina A (2007) Extended endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for extrasellar craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 61(5 Suppl 2):219–227. doi:10.1227/01.neu.0000303220.55393.73, 00006123-200711001-00006 [pii]; discussion 228
Frank G, Pasquini E, Doglietto F, Mazzatenta D, Sciaretta V, Farneti G, Calbucci F (2006) The endoscopic extended transsphenoidal approach for craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 59(Suppl 1):ONS75–ONS83
Hadad G, Bassagasteguy L, Carrau RL, Mataza JC, Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A (2006) A novel reconstructive technique after endoscopic expanded endonasal approaches: vascular pedicle nasoseptal flap. Laryngoscope 116(10):1882–1886
Conger AR, Lucas J, Zada G, Schwartz TH, Cohen-Gadol AA (2014) Endoscopic extended transsphenoidal resection of craniopharyngiomas: nuances of neurosurgical technique. Neurosurg Focus 37(4):E10. doi:10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14364
Kassam A, Snyderman CH, Mintz A, Gardner P, Carrau RL (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: the rostrocaudal axis. Part I. Crista galli to the sella turcica. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E3:1–12
Cavallo LM, Solari D, Esposito F, Cappabianca P (2013) The endoscopic endonasal approach for the management of craniopharyngiomas involving the third ventricle. Neurosurg Rev 36(1):27–37. doi:10.1007/s10143-012-0403-4; discussion 38
Snyderman CH, Kassam AB, Carrau R, Mintz A (2007) Endoscopic reconstruction of cranial base defects following endonasal skull base surgery. Skull Base 17(1):73–78. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959337
Ditzel Filho LFS, Prevedello DM, Kerr EE, Jamshidi AO, Ottoy BA, Carrau RL (2015) Endonasal resection of craniopharyngiomas: post-operative management. In: Evans JJ, Kenning TJ (eds) Craniopharyngiomas: comprehensive diagnosis, treatment and outcome. Elsevier, Inc. USA, pp 271–280
Banu MA, Szentirmai O, Mascarenhas L, Salek AA, Anand VK, Schwartz TH (2014) Pneumocephalus patterns following endonasal endoscopic skull base surgery as predictors of postoperative CSF leaks. J Neurosurg 121(4):961–975. doi:10.3171/2014.5.JNS132028
Cavallo LM, Solari D, Somma T, Savic D, Cappabianca P (2014) The awake endoscope-guided sealant technique with fibrin glue in the treatment of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak after extended transsphenoidal surgery: technical note. World Neurosurg 82(3–4):e479–e485. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2013.01.017
Acknowledgment
The editors wish to thank Doctor Carmela Chiaramonte for the original drawings prepared for this chapter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cavallo, L.M. et al. (2016). Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Approach. In: Cappabianca, P., Cavallo, L., de Divitiis, O., Esposito, F. (eds) Midline Skull Base Surgery. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21533-4_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21533-4_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-21532-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-21533-4
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)