Abstract
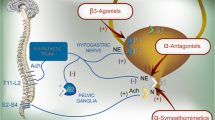
Urinary continence is the result of correct bladder storage and emptying. This mechanism is under the control of the peripheral and central nervous systems. In particular, urethral closure comes from innervations of the pudendal nerves, which determine a good functioning of the urethral rhabdosphincter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Sugaya K, Nishjima S, Miyazato M, Ogawa Y (2005) Central nervous control of micturition and urine storage. J Smooth Muscle Res 41(3):117–132
Norton PA, Zinner NR, Yalcin I, Bump RC, for the duloxetine Incontinence Study Group (2002) Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:40–48
Millard RJ, Moore K, Rencken R, Yalcin I, Bump RC, for the Duloxetine Incontinence Study Group (2004) Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: a four-continent randomized clinical trial. BJU Int 93:311–318
Schlenker B, Gratzke C, Reich O, Schorsch I, Seitz M, Stief CG (2006) Preliminary results on the off-label use of duloxetine for the treatment of stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy or cystectomy. Eur Urol 49:1075–1078
Zahariou A, Papaioannou P, Kalogirou G (2006) Is HCl duloxetine effective in the management of urinary stress incontinence after radical prostatectomy? Urol Int 77:9–12
Filocamo MT, Li Marzi V, Del Popolo G et al (2007) Pharmacologic treatment in postprostatectomy stress urinary incontinence. Eur Urol 51:1559–1564
Fink KG, Huber J, Wurnschimmel E, Schmeller NT (2008) The use of duloxetine in the treatment of male stress urinary incontinence. Wien Med Wochenschr 158:116–118
Collado Serra A, Rubio-Briones J, Puyol Payàs M et al (2011) Post- prostatectomy established SUI treated with duloxetine. Urology 78:261–266
Cornu JN, Merlet B, Ciofu C et al (2011) Duloxetine for mild to mo- derate postprostatectomy incontinence: preliminary results of a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol 59:148–154
Neff D, Guise A, Guralnick ML, Langenstroer P, See WA, Jacobsohn KM, O’Connor RC (2013) Duloxetine for the treatment of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence. Can Urol Assoc J 7(5–6):E260–E262
Collazos F, Ramos M, Qureshi A, Eiroa-Orosa FJ, Rodriguez A, Castells X, Ribases M, Valero S, Casas M (2013) Effectiveness and tolerability of duloxetine in 2 different ethnic samples: a prospective observational cohort study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 33(2):254–256
Kitta T, Miyazato M, Chancellor MB et al (2010) α2-Adrenergic receptor blockade potentiates the effects of duloxetine, a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, on sneeze-induced urethral continence reflex in rats. J Urol 164:762–768
Furuta A, Asano K, Egawa S et al (2009) Role of α2-adrenoceptors and glutamate mechanisms in external urethral sphincter continence reflex in rats. J Urol 18:19–25
Alberti C (2013) Coadministration of low-dose serotonin/noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) duloxetine with α2-adrenoceptor blockers to treat both female and male mild-to-moderate stress urinary incontinence (SUI). G Chir 34:189–194
Lai HH, Boone TB (2011) Implantation of artificial urinary sphincter in patients with post-prostatectomy incontinence, and preoperative overactive bladder and mixed symptoms. J Urol 185(6):2254–2259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Filocamo, M.T. (2015). Pharmacologic Therapy. In: Del Popolo, G., Pistolesi, D., Li Marzi, V. (eds) Male Stress Urinary Incontinence. Urodynamics, Neurourology and Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19252-9_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19252-9_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-19251-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-19252-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)