Abstract
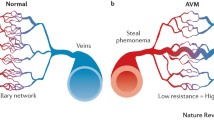
Brain arteriovenous malformation (bAVM) is an important cause of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), particularly in the young population. ICH is the first clinical symptom in about 50 % of bAVM patients. The vessels in bAVM are fragile and prone to rupture, causing bleeding into the brain. About 30 % of unruptured and non-hemorrhagic bAVMs demonstrate microscopic evidence of hemosiderin in the vascular wall. In bAVM mouse models, vascular mural cell coverage is reduced in the AVM lesion, accompanied by vascular leakage and microhemorrhage. In this review, we discuss possible signaling pathways involved in abnormal vascular development in bAVM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleetwood IG, Steinberg GK (2002) Arteriovenous malformations. Lancet 359(9309):863–873
Arteriovenous Malformation Study Group (1999) Arteriovenous malformations of the brain in adults. N Engl J Med 340(23):1812–1818
Guo Y, Saunders T, Su H, Kim H, Akkoc D, Saloner DA, Hetts SW, Hess C, Lawton MT, Bollen AW, Pourmohamad T, McCulloch CE, Tihan T, Young WL (2012) Silent intralesional microhemorrhage as a risk factor for brain arteriovenous malformation rupture. Stroke 43(5):1240–1246
Spetzler RF, Martin NA (1986) A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65(4):476–483
Han PP, Ponce FA, Spetzler RF (2003) Intention-to-treat analysis of Spetzler-Martin grades IV and V arteriovenous malformations: natural history and treatment paradigm. J Neurosurg 98(1):3–7
Stapf C, Mohr JP, Choi JH, Hartmann A, Mast H (2006) Invasive treatment of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations is experimental therapy. Curr Opin Neurol 19(1):63–68
Cockroft KM, Jayaraman MV, Amin-Hanjani S, Derdeyn CP, McDougall CG, Wilson JA (2012) A perfect storm: how a randomized trial of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations’ (ARUBA’s) trial design challenges notions of external validity. Stroke 43(7):1979–1981
Mohr JP, Moskowitz AJ, Stapf C, Hartmann A, Lord K, Marshall SM, Mast H, Moquete E, Moy CS, Parides M, Pile-Spellman J, Al-Shahi Salman R, Weinberg A, Young WL, Estevez A, Kureshi I, Brisman JL (2010) The ARUBA trial: current status, future hopes. Stroke 41(8):e537–e540
Mohr JP, Moskowitz AJ, Parides M, Stapf C, Young WL (2012) Hull down on the horizon: a randomized trial of unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA) trial. Stroke 43(7):1744–1745
Mohr JP, Parides MK, Stapf C, Moquete E, Moy CS, Overbey JR, Salman RA, Vicaut E, Young WL, Houdart E, Cordonnier C, Stefani MA, Hartmann A, von Kummer R, Biondi A, Berkefeld J, Klijn CJ, Harkness K, Libman R, Barreau X, Moskowitz AJ (2014) Medical management with or without interventional therapy for unruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (ARUBA): a multicentre, non-blinded, randomised trial. Lancet 383(9917):614–621
Mansmann U, Meisel J, Brock M, Rodesch G, Alvarez H, Lasjaunias P (2000) Factors associated with intracranial hemorrhage in cases of cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Neurosurgery 46(2):272–279
Stefani MA, Porter PJ, terBrugge KG, Montanera W, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC (2002) Angioarchitectural factors present in brain arteriovenous malformations associated with hemorrhagic presentation. Stroke 33(4):920–924
Stefani MA, Porter PJ, terBrugge KG, Montanera W, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC (2002) Large and deep brain arteriovenous malformations are associated with risk of future hemorrhage. Stroke 33(5):1220–1224
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Bissonette DJ, Kondziolka D (1996) Factors that predict the bleeding risk of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 27(1):1–6
Hademenos GJ, Massoud TF (1996) Risk of intracranial arteriovenous malformation rupture due to venous drainage impairment. A theoretical analysis. Stroke 27(6):1072–1083
Stapf C, Mast H, Sciacca RR, Choi JH, Khaw AV, Connolly ES, Pile-Spellman J, Mohr JP (2006) Predictors of hemorrhage in patients with untreated brain arteriovenous malformation. Neurology 66(9):1350–1355
Duong DH, Young WL, Vang MC, Sciacca RR, Mast H, Koennecke HC, Hartmann A, Joshi S, Mohr JP, Pile-Spellman J (1998) Feeding artery pressure and venous drainage pattern are primary determinants of hemorrhage from cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 29(6):1167–1176
Walker EJ, Su H, Shen F, Choi EJ, Oh SP, Chen G, Lawton MT, Kim H, Chen Y, Chen W, Young WL (2011) Arteriovenous malformation in the adult mouse brain resembling the human disease. Ann Neurol 69(6):954–962
Chen W, Guo Y, Walker EJ, Shen F, Jun K, Oh SP, Degos V, Lawton MT, Tihan T, Davalos D, Akassoglou K, Nelson J, Pile-Spellman J, Su H, Young WL (2013) Reduced mural cell coverage and impaired vessel integrity after angiogenic stimulation in the Alk1-deficient brain. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(2):305–310
Chen W, Sun Z, Han Z, Jun K, Camus M, Wankhede M, Mao L, Arnold T, Young WL, Su H (2014) De novo cerebrovascular malformation in the adult mouse after endothelial Alk1 deletion and angiogenic stimulation. Stroke 45(3):900–902
Choi EJ, Chen W, Jun K, Arthur HM, Young WL, Su H (2014) Novel brain arteriovenous malformation mouse models for type 1 hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. PLoS One 9(2), e88511
Braverman IM, Keh A, Jacobson BS (1990) Ultrastructure and three-dimensional organization of the telangiectases of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Invest Dermatol 95(4):422–427
Bharatha A, Faughnan ME, Kim H, Pourmohamad T, Krings T, Bayrak-Toydemir P, Pawlikowska L, McCulloch CE, Lawton MT, Dowd CF, Young WL, Terbrugge KG (2012) Brain arteriovenous malformation multiplicity predicts the diagnosis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: quantitative assessment. Stroke 43(1):72–78
Shovlin CL (2010) Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Blood Rev 24(6):203–219
Chen Y, Zhu W, Bollen AW, Lawton MT, Barbaro NM, Dowd CF, Hashimoto T, Yang GY, Young WL (2008) Evidence of inflammatory cell involvement in brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 62(6):1340–1349
Chen Y, Pawlikowska L, Yao JS, Shen F, Zhai W, Achrol AS, Lawton MT, Kwok PY, Yang GY, Young WL (2006) Interleukin-6 involvement in brain arteriovenous malformations. Ann Neurol 59(1):72–80
Chen Y, Fan Y, Poon KY, Achrol AS, Lawton MT, Zhu Y, McCulloch CE, Hashimoto T, Lee C, Barbaro NM, Bollen AW, Yang GY, Young WL (2006) MMP-9 expression is associated with leukocytic but not endothelial markers in brain arteriovenous malformations. Front Biosci 11:3121–3128
Lebrin F, Srun S, Raymond K, Martin S, van den Brink S, Freitas C, Breant C, Mathivet T, Larrivee B, Thomas JL, Arthur HM, Westermann CJ, Disch F, Mager JJ, Snijder RJ, Eichmann A, Mummery CL (2010) Thalidomide stimulates vessel maturation and reduces epistaxis in individuals with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Nat Med 16(4):420–428
Isoda K, Fukuda H, Takamura N, Hamamoto Y (1981) Arteriovenous malformation of the brain – histological study and micrometric measurement of abnormal vessels. Acta Pathol Jpn 31(5):883–893
Guo Y, Qumu SW, Nacar OA, Yang JY, Du J, Belen D, Pan L, Zhao YL (2013) Human brain arteriovenous malformations are associated with interruptions in elastic fibers and changes in collagen content. Turk Neurosurg 23(1):10–15
Lee RM (1995) Morphology of cerebral arteries. Pharmacol Ther 66(1):149–173
Niu H, Cao Y, Wang X, Xue X, Yu L, Yang M, Wang R (2012) Relationships between hemorrhage, angioarchitectural factors and collagen of arteriovenous malformations. Neurosci Bull 28(5):595–605
Meng JS, Okeda R (2001) Histopathological structure of the pial arteriovenous malformation in adults: observation by reconstruction of serial sections of four surgical specimens. Acta Neuropathol 102(1):63–68
Uranishi R, Baev NI, Kim JH, Awad IA (2001) Vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in human cerebral vascular malformations. Neurosurgery 49(3):671–679
Hoya K, Asai A, Sasaki T, Nagata K, Kimura K, Kirino T (2003) Expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms by smooth muscle cells in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Acta Neuropathol 105(5):455–461
Hoya K, Asai A, Sasaki T, Kimura K, Kirino T (2001) Expression of smooth muscle proteins in cavernous and arteriovenous malformations. Acta Neuropathol 102(3):257–263
Chen W, Guo Y, Walker EJ, Shen F, Jun K, Oh SP, Degos V, Lawton MT, Tihan T, Davalos D, Akassoglou K, Nelson J, Pile-Spellman J, Su H, Young WL (2013). Reduced mural cell coverage and impaired vessel integrity after angiogenic stimulation in the Alk1-deficient brain. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(2):305–310
ZhuGe Q, Zhong M, Zheng W, Yang GY, Mao X, Xie L, Chen G, Chen Y, Lawton MT, Young WL, Greenberg DA, Jin K (2009) Notch1 signaling is activated in brain arteriovenous malformation in humans. Brain 132(Pt 12):3231–3241
Murphy PA, Lu G, Shiah S, Bollen AW, Wang RA (2009) Endothelial Notch signaling is upregulated in human brain arteriovenous malformations and a mouse model of the disease. Lab Invest 89(9):971–982
Gridley T (2010) Notch signaling in the vasculature. Curr Top Dev Biol 92:277–309
Murphy PA, Lam MT, Wu X, Kim TN, Vartanian SM, Bollen AW, Carlson TR, Wang RA (2008) Endothelial Notch4 signaling induces hallmarks of brain arteriovenous malformations in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(31):10901–10906
Murphy PA, Kim TN, Huang L, Nielsen CM, Lawton MT, Adams RH, Schaffer CB, Wang RA (2014) Constitutively active Notch4 receptor elicits brain arteriovenous malformations through enlargement of capillary-like vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(50):18007–18012
Murphy PA, Kim TN, Lu G, Bollen AW, Schaffer CB, Wang RA (2012) Notch4 normalization reduced blood vessel size in arteriovenous malformations. Sci Transl Med 4(117):117ra118
Yao Y, Yao J, Radparvar M, Blazquez-Medela AM, Guihard PJ, Jumabay M, Bostrom KI (2013) Reducing Jagged 1 and 2 levels prevents cerebral arteriovenous malformations in matrix Gla protein deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(47):19071–19076
Phng LK, Potente M, Leslie JD, Babbage J, Nyqvist D, Lobov I, Ondr JK, Rao S, Lang RA, Thurston G, Gerhardt H (2009) Nrarp coordinates endothelial Notch and Wnt signaling to control vessel density in angiogenesis. Dev Cell 16(1):70–82
Benedito R, Roca C, Sorensen I, Adams S, Gossler A, Fruttiger M, Adams RH (2009) The notch ligands Dll4 and Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell 137(6):1124–1135
Kim H, Su H, Weinsheimer S, Pawlikowska L, Young WL (2011) Brain arteriovenous malformation pathogenesis: a response-to-injury paradigm. Acta Neurochir Suppl 111:83–92
Xu B, Wu YQ, Huey M, Arthur HM, Marchuk DA, Hashimoto T, Young WL, Yang GY (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces abnormal microvasculature in the endoglin heterozygous mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(2):237–244
Hao Q, Su H, Marchuk DA, Rola R, Wang Y, Liu W, Young WL, Yang GY (2008) Increased tissue perfusion promotes capillary dysplasia in the ALK1-deficient mouse brain following VEGF stimulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295(6):H2250–H2256
Hao Q, Zhu Y, Su H, Shen F, Yang GY, Kim H, Young WL (2010) VEGF induces more severe cerebrovascular dysplasia in Endoglin+/− than in Alk1+/− mice. Transl Stroke Res 1(3):197–201
Walker EJ, Su H, Shen F, Degos V, Amend G, Jun K, Young WL (2012) Bevacizumab attenuates VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular malformations in the adult mouse brain. Stroke 43(7):1925–1930
Benedito R, Trindade A, Hirashima M, Henrique D, da Costa LL, Rossant J, Gill PS, Duarte A (2008) Loss of Notch signalling induced by Dll4 causes arterial calibre reduction by increasing endothelial cell response to angiogenic stimuli. BMC Dev Biol 8:117
Djokovic D, Trindade A, Gigante J, Badenes M, Silva L, Liu R, Li X, Gong M, Krasnoperov V, Gill PS, Duarte A (2010) Combination of Dll4/Notch and Ephrin-B2/EphB4 targeted therapy is highly effective in disrupting tumor angiogenesis. BMC Cancer 10(1):641
Trindade A, Djokovic D, Gigante J, Badenes M, Pedrosa AR, Fernandes AC, Lopes-da-Costa L, Krasnoperov V, Liu R, Gill PS, Duarte A (2012) Low-dosage inhibition of Dll4 signaling promotes wound healing by inducing functional neo-angiogenesis. PLoS One 7(1), e29863
Gridley T (2007) Notch signaling in vascular development and physiology. Development 134(15):2709–2718
Herbert SP, Huisken J, Kim TN, Feldman ME, Houseman BT, Wang RA, Shokat KM, Stainier DY (2009) Arterial-venous segregation by selective cell sprouting: an alternative mode of blood vessel formation. Science 326(5950):294–298
Li F, Lan Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang G, Meng F, Han H, Meng A, Wang Y, Yang X (2011) Endothelial Smad4 maintains cerebrovascular integrity by activating N-cadherin through cooperation with Notch. Dev Cell 20(3):291–302
Hofmann JJ, Iruela-Arispe ML (2007) Notch signaling in blood vessels: who is talking to whom about what? Circ Res 100(11):1556–1568
Larrivee B, Prahst C, Gordon E, Del Toro R, Mathivet T, Duarte A, Simons M, Eichmann A (2012) ALK1 signaling inhibits angiogenesis by cooperating with the Notch pathway. Dev Cell 22(3):489–500
Outtz HH, Tattersall IW, Kofler NM, Steinbach N, Kitajewski J (2011) Notch1 controls macrophage recruitment and Notch signaling is activated at sites of endothelial cell anastomosis during retinal angiogenesis in mice. Blood 118(12):3436–3439
Outtz HH, Wu JK, Wang X, Kitajewski J (2010) Notch1 deficiency results in decreased inflammation during wound healing and regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages. J Immunol 185(7):4363–4373
Moya IM, Umans L, Maas E, Pereira PN, Beets K, Francis A, Sents W, Robertson EJ, Mummery CL, Huylebroeck D, Zwijsen A (2012) Stalk cell phenotype depends on integration of notch and smad1/5 signaling cascades. Dev Cell 22(3):501–514
Kim JH, Peacock MR, George SC, Hughes CC (2012) BMP9 induces EphrinB2 expression in endothelial cells through an Alk1-BMPRII/ActRII-ID1/ID3-dependent pathway: implications for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type II. Angiogenesis 15(3):497–509
Heldin CH, Westermark B (1999) Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol Rev 79(4):1283–1316
Betsholtz C, Keller A (2014) PDGF, pericytes and the pathogenesis of idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC). Brain Pathol 24(4):387–395
Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X (2010) Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(25):11307–11312
Yao H, Duan M, Hu G, Buch S (2011) Platelet-derived growth factor B chain is a novel target gene of cocaine-mediated Notch1 signaling: implications for HIV-associated neurological disorders. J Neurosci Meth 31(35):12449–12454
Lindahl P, Johansson BR, Leveen P, Betsholtz C (1997) Pericyte loss and microaneurysm formation in PDGF-B-deficient mice. Science 277(5323):242–245
Hellstrom M, Gerhardt H, Kalen M, Li X, Eriksson U, Wolburg H, Betsholtz C (2001) Lack of pericytes leads to endothelial hyperplasia and abnormal vascular morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 153(3):543–553
Crosby JR, Seifert RA, Soriano P, Bowen-Pope DF (1998) Chimaeric analysis reveals role of Pdgf receptors in all muscle lineages. Nat Genet 18(4):385–388
Bell RD, Winkler EA, Sagare AP, Singh I, LaRue B, Deane R, Zlokovic BV (2010) Pericytes control key neurovascular functions and neuronal phenotype in the adult brain and during brain aging. Neuron 68(3):409–427
Armulik A, Genove G, Mae M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, Johansson BR, Betsholtz C (2010) Pericytes regulate the blood–brain barrier. Nature 468(7323):557–561
Hashimoto T, Wu Y, Lawton MT, Yang GY, Barbaro NM, Young WL (2005) Co-expression of angiogenic factors in brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 56(5):1058–1065
Yildirim O, Bicer A, Ozkan A, Kurtkaya O, Cirakoglu B, Kilic T (2010) Expression of platelet-derived growth factor ligand and receptor in cerebral arteriovenous and cavernous malformations. J Clin Neurosci 17(12):1557–1562
Sasahara M, Sato H, Iihara K, Wang J, Chue CH, Takayama S, Hayase Y, Hazama F (1995) Expression of platelet-derived growth factor B-chain in the mature rat brain and pituitary gland. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 32(1):63–74
Hashimoto T, Lam T, Boudreau NJ, Bollen AW, Lawton MT, Young WL (2001) Abnormal balance in the angiopoietin-tie2 system in human brain arteriovenous malformations. Circ Res 89(2):111–113
Hashimoto T, Wen G, Lawton MT, Boudreau NJ, Bollen AW, Yang GY, Barbaro NM, Higashida RT, Dowd CF, Halbach VV, Young WL (2003) Abnormal expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 34(4):925–931
Hao Q, Liu J, Pappu R, Su H, Rola R, Gabriel RA, Lee CZ, Young WL, Yang GY (2008) Contribution of bone marrow-derived cells associated with brain angiogenesis is primarily through leucocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(12):2151–2157
Hao Q, Chen Y, Zhu Y, Fan Y, Palmer D, Su H, Young WL, Yang GY (2007) Neutrophil depletion decreases VEGF-induced focal angiogenesis in the mature mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(11):1853–1860
Ota R, Kurihara C, Tsou TL, Young WL, Yeghiazarians Y, Chang M, Mobashery S, Sakamoto A, Hashimoto T (2009) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in flow-induced outward vascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(9):1547–1558
Nuki Y, Matsumoto MM, Tsang E, Young WL, van Rooijen N, Kurihara C, Hashimoto T (2009) Roles of macrophages in flow-induced outward vascular remodeling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29(3):495–503
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the UCSF BAVM Study Project (http://avm.ucsf.edu) for their support, and Voltaire Gungab for assistance with manuscript preparation. This study was supported by grants to Hua Su from the National Institutes of Health (R01 NS027713, R01 HL122774, and 1R21NS083788) and from the Michael Ryan Zodda Foundation and UCSF Research Evaluation and Allocation Committee (REAC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhang, R., Zhu, W., Su, H. (2016). Vascular Integrity in the Pathogenesis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformation. In: Applegate, R., Chen, G., Feng, H., Zhang, J. (eds) Brain Edema XVI. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, vol 121. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18497-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18497-5_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-18496-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-18497-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)