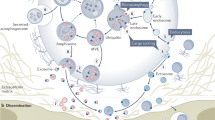
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are increasingly being recognised as players in intercellular communication within the human body. EVs are nano-sized vesicles that are secreted by virtually all cells, primarily arising from either the plasma membrane or the endocytic system. They contain a wide range of proteins and nucleic acids in their lumen, as well as cell surface proteins on their exterior. The proteins and nucleic acids within are the ‘cargo’ that EVs deliver into the cytosol of recipient cells to elicit a response or phenotypic change. For delivery to occur, the cargo needs to cross two lipid bilayers; one that makes up the vesicle itself, and the other of the recipient cell. Exactly how this process works is a topic that is poorly understood, despite being pivotal for their function. Furthermore, extracellular vesicles have therapeutic potential as drug delivery vehicles. Therefore, understanding their delivery mechanism and harnessing its action for drug delivery is of great importance. This chapter will focus on the proposed mechanisms for cargo delivery and discuss existing evidence for cargo delivery from EVs into the cytosol of recipient cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand S, Foot N, Ang CS, Gembus KM, Keerthikumar S, Adda CG, Mathivanan S, Kumar S (2018) Arrestin-domain containing protein 1 (Arrdc1) regulates the protein cargo and release of extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 18(17):e1800266. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201800266
Baietti MF, Zhang Z, Mortier E, Melchior A, Degeest G, Geeraerts A, Ivarsson Y, Depoortere F, Coomans C, Vermeiren E, Zimmermann P, David G (2012) Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol 14(7):677–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2502
Bayraktar R, Van Roosbroeck K, Calin GA (2017) Cell-to-cell communication: microRNAs as hormones. Mol Oncol 11(12):1673–1686. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12144
Boomgarden AC, Sheehan C, D’Souza-Schorey C (2020) Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: various implications in tumor progression. Adv Exp Med Biol 1259:155–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-43093-1_9
Brock CK, Wallin ST, Ruiz OE, Samms KM, Mandal A, Sumner EA, Eisenhoffer GT (2019) Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance. Nat Commun 10(1):1044. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09010-6
Buca D, Bologna G, D’Amico A, Cugini S, Musca F, Febbo M, D’Arcangelo D, Buca D, Simeone P, Liberati M, Vitacolonna E, Miscia S, D’Antonio F, Lanuti P (2020) Extracellular vesicles in Feto-maternal crosstalk and pregnancy disorders. Int J Mol Sci 21(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062120
Buzas EI, Toth EA, Sodar BW, Szabo-Taylor KE (2018) Molecular interactions at the surface of extracellular vesicles. Semin Immunopathol 40(5):453–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-018-0682-0
Chevillet JR, Kang Q, Ruf IK, Briggs HA, Vojtech LN, Hughes SM, Cheng HH, Arroyo JD, Meredith EK, Gallichotte EN, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Morrissey C, Stirewalt DL, Hladik F, Yu EY, Higano CS, Tewari M (2014) Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(41):14888–14893. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408301111
Christianson HC, Svensson KJ, van Kuppevelt TH, Li JP, Belting M (2013) Cancer cell exosomes depend on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for their internalization and functional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(43):17380–17385. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304266110
Christoforidis S, McBride HM, Burgoyne RD, Zerial M (1999) The Rab5 effector EEA1 is a core component of endosome docking. Nature 397(6720):621–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/17618
Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2014) Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:255–289. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326
Cossetti C, Iraci N, Mercer TR, Leonardi T, Alpi E, Drago D, Alfaro-Cervello C, Saini HK, Davis MP, Schaeffer J, Vega B, Stefanini M, Zhao C, Muller W, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Mathivanan S, Bachi A, Enright AJ, Mattick JS, Pluchino S (2014) Extracellular vesicles from neural stem cells transfer IFN-gamma via Ifngr1 to activate Stat1 signaling in target cells. Mol Cell 56(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.020
Costa Verdera H, Gitz-Francois JJ, Schiffelers RM, Vader P (2017) Cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles is mediated by clathrin-independent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. J Control Release 266:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.09.019
Crewe C, Joffin N, Rutkowski JM, Kim M, Zhang F, Towler DA, Gordillo R, Scherer PE (2018) An endothelial-to-adipocyte extracellular vesicle Axis governed by metabolic state. Cell 175(3):695–708. e613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.005
Dale GL, Remenyi G, Friese P (2009) Tetraspanin CD9 is required for microparticle release from coated-platelets. Platelets 20(6):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537100903096692
de Jong OG, Murphy DE, Mager I, Willms E, Garcia-Guerra A, Gitz-Francois JJ, Lefferts J, Gupta D, Steenbeek SC, van Rheenen J, El Andaloussi S, Schiffelers RM, Wood MJA, Vader P (2020) A CRISPR-Cas9-based reporter system for single-cell detection of extracellular vesicle-mediated functional transfer of RNA. Nat Commun 11(1):1113. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14977-8
Del Conde I, Shrimpton CN, Thiagarajan P, Lopez JA (2005) Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 106(5):1604–1611. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-1095
Dermine JF, Duclos S, Garin J, St-Louis F, Rea S, Parton RG, Desjardins M (2001) Flotillin-1-enriched lipid raft domains accumulate on maturing phagosomes. J Biol Chem 276(21):18507–18512. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101113200
Dores MR, Chen B, Lin H, Soh UJ, Paing MM, Montagne WA, Meerloo T, Trejo J (2012) ALIX binds a YPX(3)L motif of the GPCR PAR1 and mediates ubiquitin-independent ESCRT-III/MVB sorting. J Cell Biol 197(3):407–419. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201110031
Feng D, Zhao WL, Ye YY, Bai XC, Liu RQ, Chang LF, Zhou Q, Sui SF (2010) Cellular internalization of exosomes occurs through phagocytosis. Traffic 11(5):675–687. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01041.x
French KC, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA (2017) Extracellular vesicle docking at the cellular port: extracellular vesicle binding and uptake. Semin Cell Dev Biol 67:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.01.002
Fujii T, Sakata A, Nishimura S, Eto K, Nagata S (2015) TMEM16F is required for phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle release in activated mouse platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(41):12800–12805. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1516594112
Gauthier SA, Perez-Gonzalez R, Sharma A, Huang FK, Alldred MJ, Pawlik M, Kaur G, Ginsberg SD, Neubert TA, Levy E (2017) Enhanced exosome secretion in down syndrome brain–a protective mechanism to alleviate neuronal endosomal abnormalities. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5(1):65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0466-0
Ghossoub R, Lembo F, Rubio A, Gaillard CB, Bouchet J, Vitale N, Slavik J, Machala M, Zimmermann P (2014) Syntenin-ALIX exosome biogenesis and budding into multivesicular bodies are controlled by ARF6 and PLD2. Nat Commun 5:3477. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4477
Godoy PM, Bhakta NR, Barczak AJ, Cakmak H, Fisher S, MacKenzie TC, Patel T, Price RW, Smith JF, Woodruff PG, Erle DJ (2018) Large differences in small RNA composition between human biofluids. Cell Rep 25(5):1346–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.014
Griffiths G (1989) The structure and function of a mannose 6-phosphate receptor-enriched, pre-lysosomal compartment in animal cells. J Cell Sci (Suppl 11):139–147. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.11
Guo H, Chitiprolu M, Roncevic L, Javalet C, Hemming FJ, Trung MT, Meng L, Latreille E, Tanese de Souza C, McCulloch D, Baldwin RM, Auer R, Cote J, Russell RC, Sadoul R, Gibbings D (2017) Atg5 disassociates the V1V0-ATPase to promote exosome production and tumor metastasis independent of canonical macroautophagy. Dev Cell 43(6):716–730. e717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.11.018
Gyorgy B, Szabo TG, Pasztoi M, Pal Z, Misjak P, Aradi B, Laszlo V, Pallinger E, Pap E, Kittel A, Nagy G, Falus A, Buzas EI (2011) Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(16):2667–2688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0689-3
He D, Wang H, Ho SL, Chan HN, Hai L, He X, Wang K, Li HW (2019) Total internal reflection-based single-vesicle in situ quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of tumor-derived exosomal microRNAs for diagnosis and treatment monitoring. Theranostics 9(15):4494–4507. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.33683
Heath N, Osteikoetxea X, de Oliveria TM, Lazaro-Ibanez E, Shatnyeva O, Schindler C, Tigue N, Mayr LM, Dekker N, Overman R, Davies R (2019) Endosomal escape enhancing compounds facilitate functional delivery of extracellular vesicle cargo. Nanomedicine (Lond) 14(21):2799–2814. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2019-0061
Hessvik NP, Llorente A (2018) Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(2):193–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2595-9
Heusermann W, Hean J, Trojer D, Steib E, von Bueren S, Graff-Meyer A, Genoud C, Martin K, Pizzato N, Voshol J, Morrissey DV, Andaloussi SE, Wood MJ, Meisner-Kober NC (2016) Exosomes surf on filopodia to enter cells at endocytic hot spots, traffic within endosomes, and are targeted to the ER. J Cell Biol 213(2):173–184. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201506084
Hill AF (2019) Extracellular vesicles and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurosci 39(47):9269–9273. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0147-18.2019
Hyenne V, Labouesse M, Goetz JG (2018) The small GTPase Ral orchestrates MVB biogenesis and exosome secretion. Small GTPases 9(6):445–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/21541248.2016.1251378
Jackson CE, Scruggs BS, Schaffer JE, Hanson PI (2017) Effects of inhibiting VPS4 support a general role for ESCRTs in extracellular vesicle biogenesis. Biophys J 113(6):1342–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.05.032
Jadli AS, Ballasy N, Edalat P, Patel VB (2020) Inside(sight) of tiny communicator: exosome biogenesis, secretion, and uptake. Mol Cell Biochem 467(1–2):77–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03703-z
Jenjaroenpun P, Kremenska Y, Nair VM, Kremenskoy M, Joseph B, Kurochkin IV (2013) Characterization of RNA in exosomes secreted by human breast cancer cell lines using next-generation sequencing. PeerJ 1:e201. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.201
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C (1987) Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem 262(19):9412–9420
Joshi BS, de Beer MA, Giepmans BNG, Zuhorn IS (2020) Endocytosis of extracellular vesicles and release of their cargo from endosomes. ACS Nano 14(4):4444–4455. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b10033
Jovic M, Sharma M, Rahajeng J, Caplan S (2010) The early endosome: a busy sorting station for proteins at the crossroads. Histol Histopathol 25(1):99–112. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-25.99
Kastelowitz N, Yin H (2014) Exosomes and microvesicles: identification and targeting by particle size and lipid chemical probes. Chembiochem 15(7):923–928. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201400043
Kobayashi T, Beuchat MH, Chevallier J, Makino A, Mayran N, Escola JM, Lebrand C, Cosson P, Kobayashi T, Gruenberg J (2002) Separation and characterization of late endosomal membrane domains. J Biol Chem 277(35):32157–32164. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202838200
Kobayashi T, Vischer UM, Rosnoblet C, Lebrand C, Lindsay M, Parton RG, Kruithof EK, Gruenberg J (2000) The tetraspanin CD63/lamp3 cycles between endocytic and secretory compartments in human endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 11(5):1829–1843. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.11.5.1829
Lai CP, Kim EY, Badr CE, Weissleder R, Mempel TR, Tannous BA, Breakefield XO (2015) Visualization and tracking of tumour extracellular vesicle delivery and RNA translation using multiplexed reporters. Nat Commun 6:7029. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8029
Larios J, Mercier V, Roux A, Gruenberg J (2020) ALIX- and ESCRT-III-dependent sorting of tetraspanins to exosomes. J Cell Biol 219(3). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201904113
Liu H, Liu S, Qiu X, Yang X, Bao L, Pu F, Liu X, Li C, Xuan K, Zhou J, Deng Z, Liu S, Jin Y (2020) Donor MSCs release apoptotic bodies to improve myocardial infarction via autophagy regulation in recipient cells. Autophagy:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1717128
Lozach PY, Huotari J, Helenius A (2011) Late-penetrating viruses. Curr Opin Virol 1(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2011.05.004
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G, Thery C (2019) Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol 21(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0250-9
Matusek T, Wendler F, Poles S, Pizette S, D’Angelo G, Furthauer M, Therond PP (2014) The ESCRT machinery regulates the secretion and long-range activity of hedgehog. Nature 516(7529):99–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13847
Menck K, Sonmezer C, Worst TS, Schulz M, Dihazi GH, Streit F, Erdmann G, Kling S, Boutros M, Binder C, Gross JC (2017) Neutral sphingomyelinases control extracellular vesicles budding from the plasma membrane. J Extracell Vesicles 6(1):1378056. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2017.1378056
Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan ML, Karlsson JM, Baty CJ, Gibson GA, Erdos G, Wang Z, Milosevic J, Tkacheva OA, Divito SJ, Jordan R, Lyons-Weiler J, Watkins SC, Morelli AE (2012) Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood 119(3):756–766. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-02-338004
Moreno-Gonzalo O, Fernandez-Delgado I, Sanchez-Madrid F (2018) Post-translational add-ons mark the path in exosomal protein sorting. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2690-y
Mulcahy LA, Pink RC, Carter DR (2014) Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles 3. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.24641
Muralidharan-Chari V, Clancy J, Plou C, Romao M, Chavrier P, Raposo G, D’Souza-Schorey C (2009) ARF6-regulated shedding of tumor cell-derived plasma membrane microvesicles. Curr Biol 19(22):1875–1885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.09.059
Murphy RF, Powers S, Cantor CR (1984) Endosome pH measured in single cells by dual fluorescence flow cytometry: rapid acidification of insulin to pH 6. J Cell Biol 98(5):1757–1762. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.98.5.1757
Nabhan JF, Hu R, Oh RS, Cohen SN, Lu Q (2012) Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(11):4146–4151. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200448109
Naslavsky N, Caplan S (2018) The enigmatic endosome–sorting the ins and outs of endocytic trafficking. J Cell Sci 131(13). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.216499
Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Buermans HP, Waasdorp M, Stoorvogel W, Wauben MH, t Hoen PA (2012) Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res 40(18):9272–9285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks658
O’Brien K, Breyne K, Ughetto S, Laurent LC, Breakefield XO (2020) RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0251-y
Owens AP, 3rd, Mackman N (2011) Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res 108 (10):1284–1297. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.233056
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A, Coscia C, Iessi E, Logozzi M, Molinari A, Colone M, Tatti M, Sargiacomo M, Fais S (2009) Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284(49):34211–34222. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.041152
Piper RC, Katzmann DJ (2007) Biogenesis and function of multivesicular bodies. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:519–547. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123319
Pollet H, Conrard L, Cloos AS, Tyteca D (2018) Plasma membrane lipid domains as platforms for vesicle biogenesis and shedding? Biomol Ther 8(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8030094
Popa SJ, Stewart SE, Moreau K (2018) Unconventional secretion of annexins and galectins. Semin Cell Dev Biol 83:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.02.022
Purushothaman A, Bandari SK, Liu J, Mobley JA, Brown EE, Sanderson RD (2016) Fibronectin on the surface of myeloma cell-derived Exosomes mediates exosome-cell interactions. J Biol Chem 291(4):1652–1663. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.686295
Rabia M, Leuzy V, Soulage C, Durand A, Fourmaux B, Errazuriz-Cerda E, Koffel R, Draeger A, Colosetti P, Jalabert A, Di Filippo M, Villard-Garon A, Bergerot C, Luquain-Costaz C, Moulin P, Rome S, Delton I, Hullin-Matsuda F (2020) Bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate, a new lipid signature of endosome-derived extracellular vesicles. Biochimie doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2020.07.005
Rabouille C (2017) Pathways of unconventional protein secretion. Trends Cell Biol 27(3):230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.11.007
Ridder K, Keller S, Dams M, Rupp AK, Schlaudraff J, Del Turco D, Starmann J, Macas J, Karpova D, Devraj K, Depboylu C, Landfried B, Arnold B, Plate KH, Hoglinger G, Sultmann H, Altevogt P, Momma S (2014) Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of genetic information between the hematopoietic system and the brain in response to inflammation. PLoS Biol 12(6):e1001874. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001874
Ridder K, Sevko A, Heide J, Dams M, Rupp AK, Macas J, Starmann J, Tjwa M, Plate KH, Sultmann H, Altevogt P, Umansky V, Momma S (2015) Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of functional RNA in the tumor microenvironment. Onco Targets Ther 4(6):e1008371. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2015.1008371
Roberts-Dalton HD, Cocks A, Falcon-Perez JM, Sayers EJ, Webber JP, Watson P, Clayton A, Jones AT (2017) Fluorescence labelling of extracellular vesicles using a novel thiol-based strategy for quantitative analysis of cellular delivery and intracellular traffic. Nanoscale 9(36):13693–13706. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr04128d
Scott CC, Vacca F, Gruenberg J (2014) Endosome maturation, transport and functions. Semin Cell Dev Biol 31:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.034
Segura E, Amigorena S, Thery C (2005) Mature dendritic cells secrete exosomes with strong ability to induce antigen-specific effector immune responses. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35(2):89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2005.05.003
Shimoda M (2019) Extracellular vesicle-associated MMPs: a modulator of the tissue microenvironment. Adv Clin Chem 88:35–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2018.10.006
Silvie O, Charrin S, Billard M, Franetich JF, Clark KL, van Gemert GJ, Sauerwein RW, Dautry F, Boucheix C, Mazier D, Rubinstein E (2006) Cholesterol contributes to the organization of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains and to CD81-dependent infection by malaria sporozoites. J Cell Sci 119 (Pt 10):1992–2002. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02911
Sitia R, Rubartelli A (2018) The unconventional secretion of IL-1beta: handling a dangerous weapon to optimize inflammatory responses. Semin Cell Dev Biol 83:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.03.011
Skotland T, Sagini K, Sandvig K, Llorente A (2020) An emerging focus on lipids in extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.03.002
Skotland T, Sandvig K, Llorente A (2017) Lipids in exosomes: current knowledge and the way forward. Prog Lipid Res 66:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2017.03.001
Somiya M (2020) Where does the cargo go?: solutions to provide experimental support for the "extracellular vesicle cargo transfer hypothesis". J Cell Commun Signal 14(2):135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-020-00552-9
Steringer JP, Nickel W (2018) A direct gateway into the extracellular space: unconventional secretion of FGF2 through self-sustained plasma membrane pores. Semin Cell Dev Biol 83:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.02.010
Sterzenbach U, Putz U, Low LH, Silke J, Tan SS, Howitt J (2017) Engineered Exosomes as vehicles for biologically active proteins. Mol Ther 25(6):1269–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.030
Stewart SE, Ashkenazi A, Williamson A, Rubinsztein DC, Moreau K (2018) Transbilayer phospholipid movement facilitates the translocation of annexin across membranes. J Cell Sci 131(14). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.217034
Stewart S, Gessler F, Pluchino S, Moreau K (2016) Inside-out: unpredicted Annexin A2 localisation on the surface of extracellular vesicles. ScienceMatters 1(1)
Taylor J, Jaiswal R, Bebawy M (2017) Calcium-calpain dependent pathways regulate Vesiculation in malignant breast cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 17(5):486–494. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009616666161026165736
Thery C, Duban L, Segura E, Veron P, Lantz O, Amigorena S (2002) Indirect activation of naive CD4+ T cells by dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Immunol 3(12):1156–1162. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni854
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK, Ayre DC, Bach JM, Bachurski D, Baharvand H, Balaj L, Baldacchino S, Bauer NN, Baxter AA, Bebawy M, Beckham C, Bedina Zavec A, Benmoussa A, Berardi AC, Bergese P, Bielska E, Blenkiron C, Bobis-Wozowicz S, Boilard E, Boireau W, Bongiovanni A, Borras FE, Bosch S, Boulanger CM, Breakefield X, Breglio AM, Brennan MA, Brigstock DR, Brisson A, Broekman ML, Bromberg JF, Bryl-Gorecka P, Buch S, Buck AH, Burger D, Busatto S, Buschmann D, Bussolati B, Buzas EI, Byrd JB, Camussi G, Carter DR, Caruso S, Chamley LW, Chang YT, Chen C, Chen S, Cheng L, Chin AR, Clayton A, Clerici SP, Cocks A, Cocucci E, Coffey RJ, Cordeiro-da-Silva A, Couch Y, Coumans FA, Coyle B, Crescitelli R, Criado MF, D’Souza-Schorey C, Das S, Datta Chaudhuri A, de Candia P, De Santana EF, De Wever O, Del Portillo HA, Demaret T, Deville S, Devitt A, Dhondt B, Di Vizio D, Dieterich LC, Dolo V, Dominguez Rubio AP, Dominici M, Dourado MR, Driedonks TA, Duarte FV, Duncan HM, Eichenberger RM, Ekstrom K, El Andaloussi S, Elie-Caille C, Erdbrugger U, Falcon-Perez JM, Fatima F, Fish JE, Flores-Bellver M, Forsonits A, Frelet-Barrand A, Fricke F, Fuhrmann G, Gabrielsson S, Gamez-Valero A, Gardiner C, Gartner K, Gaudin R, Gho YS, Giebel B, Gilbert C, Gimona M, Giusti I, Goberdhan DC, Gorgens A, Gorski SM, Greening DW, Gross JC, Gualerzi A, Gupta GN, Gustafson D, Handberg A, Haraszti RA, Harrison P, Hegyesi H, Hendrix A, Hill AF, Hochberg FH, Hoffmann KF, Holder B, Holthofer H, Hosseinkhani B, Hu G, Huang Y, Huber V, Hunt S, Ibrahim AG, Ikezu T, Inal JM, Isin M, Ivanova A, Jackson HK, Jacobsen S, Jay SM, Jayachandran M, Jenster G, Jiang L, Johnson SM, Jones JC, Jong A, Jovanovic-Talisman T, Jung S, Kalluri R, Kano SI, Kaur S, Kawamura Y, Keller ET, Khamari D, Khomyakova E, Khvorova A, Kierulf P, Kim KP, Kislinger T, Klingeborn M, Klinke DJ, 2nd, Kornek M, Kosanovic MM, Kovacs AF, Kramer-Albers EM, Krasemann S, Krause M, Kurochkin IV, Kusuma GD, Kuypers S, Laitinen S, Langevin SM, Languino LR, Lannigan J, Lasser C, Laurent LC, Lavieu G, Lazaro-Ibanez E, Le Lay S, Lee MS, Lee YXF, Lemos DS, Lenassi M, Leszczynska A, Li IT, Liao K, Libregts SF, Ligeti E, Lim R, Lim SK, Line A, Linnemannstons K, Llorente A, Lombard CA, Lorenowicz MJ, Lorincz AM, Lotvall J, Lovett J, Lowry MC, Loyer X, Lu Q, Lukomska B, Lunavat TR, Maas SL, Malhi H, Marcilla A, Mariani J, Mariscal J, Martens-Uzunova ES, Martin-Jaular L, Martinez MC, Martins VR, Mathieu M, Mathivanan S, Maugeri M, McGinnis LK, McVey MJ, Meckes DG, Jr., Meehan KL, Mertens I, Minciacchi VR, Moller A, Moller Jorgensen M, Morales-Kastresana A, Morhayim J, Mullier F, Muraca M, Musante L, Mussack V, Muth DC, Myburgh KH, Najrana T, Nawaz M, Nazarenko I, Nejsum P, Neri C, Neri T, Nieuwland R, Nimrichter L, Nolan JP, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, Noren Hooten N, O'Driscoll L, O'Grady T, O'Loghlen A, Ochiya T, Olivier M, Ortiz A, Ortiz LA, Osteikoetxea X, Ostergaard O, Ostrowski M, Park J, Pegtel DM, Peinado H, Perut F, Pfaffl MW, Phinney DG, Pieters BC, Pink RC, Pisetsky DS, Pogge von Strandmann E, Polakovicova I, Poon IK, Powell BH, Prada I, Pulliam L, Quesenberry P, Radeghieri A, Raffai RL, Raimondo S, Rak J, Ramirez MI, Raposo G, Rayyan MS, Regev-Rudzki N, Ricklefs FL, Robbins PD, Roberts DD, Rodrigues SC, Rohde E, Rome S, Rouschop KM, Rughetti A, Russell AE, Saa P, Sahoo S, Salas-Huenuleo E, Sanchez C, Saugstad JA, Saul MJ, Schiffelers RM, Schneider R, Schoyen TH, Scott A, Shahaj E, Sharma S, Shatnyeva O, Shekari F, Shelke GV, Shetty AK, Shiba K, Siljander PR, Silva AM, Skowronek A, Snyder OL, 2nd, Soares RP, Sodar BW, Soekmadji C, Sotillo J, Stahl PD, Stoorvogel W, Stott SL, Strasser EF, Swift S, Tahara H, Tewari M, Timms K, Tiwari S, Tixeira R, Tkach M, Toh WS, Tomasini R, Torrecilhas AC, Tosar JP, Toxavidis V, Urbanelli L, Vader P, van Balkom BW, van der Grein SG, Van Deun J, van Herwijnen MJ, Van Keuren-Jensen K, van Niel G, van Royen ME, van Wijnen AJ, Vasconcelos MH, Vechetti IJ, Jr., Veit TD, Vella LJ, Velot E, Verweij FJ, Vestad B, Vinas JL, Visnovitz T, Vukman KV, Wahlgren J, Watson DC, Wauben MH, Weaver A, Webber JP, Weber V, Wehman AM, Weiss DJ, Welsh JA, Wendt S, Wheelock AM, Wiener Z, Witte L, Wolfram J, Xagorari A, Xander P, Xu J, Yan X, Yanez-Mo M, Yin H, Yuana Y, Zappulli V, Zarubova J, Zekas V, Zhang JY, Zhao Z, Zheng L, Zheutlin AR, Zickler AM, Zimmermann P, Zivkovic AM, Zocco D, Zuba-Surma EK (2018) Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 7 (1):1535750. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
Tian T, Zhu YL, Hu FH, Wang YY, Huang NP, Xiao ZD (2013) Dynamics of exosome internalization and trafficking. J Cell Physiol 228(7):1487–1495. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24304
Tian T, Zhu YL, Zhou YY, Liang GF, Wang YY, Hu FH, Xiao ZD (2014) Exosome uptake through clathrin-mediated endocytosis and macropinocytosis and mediating miR-21 delivery. J Biol Chem 289(32):22258–22267. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.588046
Trajkovic K, Hsu C, Chiantia S, Rajendran L, Wenzel D, Wieland F, Schwille P, Brugger B, Simons M (2008) Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319(5867):1244–1247. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1153124
Tu C, Ahmad G, Mohapatra B, Bhattacharyya S, Ortega-Cava CF, Chung BM, Wagner KU, Raja SM, Naramura M, Band V, Band H (2011) ESCRT proteins: double-edged regulators of cellular signaling. BioArchitecture 1(1):45–48. https://doi.org/10.4161/bioa.1.1.15173
Usman WM, Pham TC, Kwok YY, Vu LT, Ma V, Peng B, Chan YS, Wei L, Chin SM, Azad A, He AB, Leung AYH, Yang M, Shyh-Chang N, Cho WC, Shi J, Le MTN (2018) Efficient RNA drug delivery using red blood cell extracellular vesicles. Nat Commun 9(1):2359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04791-8
Valadi H, Ekstrom K, Bossios A, Sjostrand M, Lee JJ, Lotvall JO (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9(6):654–659. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1596
van der Goot FG, Gruenberg J (2006) Intra-endosomal membrane traffic. Trends Cell Biol 16(10):514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2006.08.003
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G (2018) Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(4):213–228. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.125
Vanlandingham PA, Ceresa BP (2009) Rab7 regulates late endocytic trafficking downstream of multivesicular body biogenesis and cargo sequestration. J Biol Chem 284(18):12110–12124. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809277200
Veerman RE, Gucluler Akpinar G, Eldh M, Gabrielsson S (2019) Immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles–functions and therapeutic applications. Trends Mol Med 25(5):382–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2019.02.003
Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM, Shamburek RD, Remaley AT (2011) MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol 13(4):423–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2210
Vietri M, Radulovic M, Stenmark H (2020) The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(1):25–42. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0177-4
Villarroya-Beltri C, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Sanchez-Cabo F, Perez-Hernandez D, Vazquez J, Martin-Cofreces N, Martinez-Herrera DJ, Pascual-Montano A, Mittelbrunn M, Sanchez-Madrid F (2013) Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat Commun 4:2980. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3980
Wang Q, Lu Q (2017) Plasma membrane-derived extracellular microvesicles mediate non-canonical intercellular NOTCH signaling. Nat Commun 8(1):709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00767-2
Wang Q, Yu J, Kadungure T, Beyene J, Zhang H, Lu Q (2018) ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules. Nat Commun 9(1):960. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03390-x
Willms E, Johansson HJ, Mager I, Lee Y, Blomberg KE, Sadik M, Alaarg A, Smith CI, Lehtio J, El Andaloussi S, Wood MJ, Vader P (2016) Cells release subpopulations of exosomes with distinct molecular and biological properties. Sci Rep 6:22519. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22519
Xu B, Fu Y, Liu Y, Agvanian S, Wirka RC, Baum R, Zhou K, Shaw RM, Hong T (2017) The ESCRT-III pathway facilitates cardiomyocyte release of cBIN1-containing microparticles. PLoS Biol 15(8):e2002354. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2002354
Yao Z, Qiao Y, Li X, Chen J, Ding J, Bai L, Shen F, Shi B, Liu J, Peng L, Li J, Yuan Z (2018) Exosomes exploit the virus entry machinery and pathway to transmit alpha interferon-induced antiviral activity. J Virol 92(24). https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01578-18
Zakharova L, Svetlova M, Fomina AF (2007) T cell exosomes induce cholesterol accumulation in human monocytes via phosphatidylserine receptor. J Cell Physiol 212(1):174–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21013
Zweemer AJM, French CB, Mesfin J, Gordonov S, Meyer AS, Lauffenburger DA (2017) Apoptotic bodies elicit Gas6-mediated migration of AXL-expressing tumor cells. Mol Cancer Res 15(12):1656–1666. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0012
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Michael E. D’Angelo for intellectual discussion and proof reading.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Funding
This work was supported by a Wellcome Trust PhD studentship for S.J.P. and a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council Future Leader Fellowship (BB/P010911/1) for S. E. S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Popa, S.J., Stewart, S.E. (2021). Socially Distanced Intercellular Communication: Mechanisms for Extracellular Vesicle Cargo Delivery. In: Mathivanan, S., Fonseka, P., Nedeva, C., Atukorala, I. (eds) New Frontiers: Extracellular Vesicles. Subcellular Biochemistry, vol 97. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67170-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67171-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)