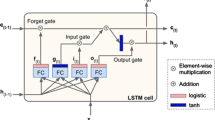
Abstract
In social media and microblogging platforms, it is very popular to share news about sport activities from all around the world. This makes it important to extract information about sports out of text crawled from such platforms. In the scope of this paper, a binary classification is presented to identify tweets containing any information of sports in Turkish. To do so, firstly a dataset, composed of two categories (namely, sport and non-sport), is collected from eleven different Twitter news accounts. Afterwards, a preprocess phase takes place to remove the punctuation marks, the extra spaces, and the numeric characters. In the classification phase, accuracy values of four deep-learning architectures (namely, convolutional neural network, recurrent neural network, gated recurrent unit, and long short-term memory) are calculated to show the classification performances of each architecture. At last, the deep learning classification accuracy values are compared to the most commonly used supervised learning algorithms (namely, Naïve Bayes algorithm, Support Vector Machines, Random Forest, Dense Artificial Neural Network and Decision Tree).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pak, A., Paroubek, P.: Twitter as a corpus for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Malta, pp. 1320–1326 (2010)
Lin, Y.R., Margolin, D., Keegan, B., Lazer, D.: Voices of victory: a computational focus group framework for tracking opinion shift in real time. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, pp. 737–748. ACM (2013)
Nichols, J., Mahmud, J., Drews, C.: Summarizing sporting events using twitter. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Lisbon, pp. 189–198. ACM (2012)
Becker, H., Iter, D., Naaman, M., Gravano, L.: Identifying content for planned events across social media sites. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, New York, pp. 533–542. ACM (2012)
Sriram, B., Fuhry, D., Demir, E., Ferhatosmanoglu, H., Demirbas, M.: Short text classification in twitter to improve information filtering. In: Proceeding of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Geneva, pp. 841–842. ACM (2010)
Genc, Y., Sakamoto, Y., Nickerson J.V.: Discovering context: classifying tweets through a semantic transform based on Wikipedia. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Foundations of Augmented Cognition, Orlando, FL, pp. 484–492. Springer (2011)
Yerva, S.R., Miklos, Z., Aberer, K.: What have fruits to do with technology? The case of orange, blackberry and apple. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics, Sogndal, Norway, pp. 1–10. ACM (2011)
Khan, I., Naqvi, S.K., Alam, M., Rizvi, S.N.A.: An efficient framework for real-time tweet classification. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 9(2), 215–221 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-017-0015-x
Duwairi, R.M., Qarqaz, I.: Arabic sentiment analysis using supervised classification. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, Barcelona, pp. 579–583. IEEE (2014)
Lee, K., Palsetia, D., Narayanan, R., Patwary, M.A., Agrawal, A., Choudhary, A.: Twitter trending topic classification. In: Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Vancouver, BC, pp. 251–258. IEEE (2011)
Roesslein, J.: Tweepy Documentation. http://docs.tweepy.org/en/latest/. Accessed 14 Apr 2020
Porter, M.F.: Snowball: a language for stemming algorithms. http://snowball.tartarus.org/texts/introduction.html. Accessed 14 Feb 2020
Can, F., Kocberber, S., Balcik, E., Kaynak, C., Ocalan, H.C., Vursavas, O.M.: Information retrieval on Turkish texts. J. Am. Soc. Inform. Sci. Technol. 59(3), 407–421 (2008)
Zhang, H.: The optimality of Naive Bayes. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, Florida, pp. 562–567. AAAI Press (2004)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Quinlan, J.R.: Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1, 81–106 (1986)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001)
Caudill, M., Butler, C.: Understanding Neural Networks: Computer Explorations. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Nevada, pp. 1097–1105. Curran Associates, Inc. (2012)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Sailunaz, K., Alhajj, R.: Emotion and sentiment analysis from Twitter text. J. Comput. Sci. 36, 101003 (2019)
Cho, K., Merrienboer, B.V., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., Bengio, Y.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078, Qatar (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Toçoğlu, M.A., Onan, A. (2021). Identification of Sport News in Turkish Tweets Using Deep Learning Architectures. In: Allahviranloo, T., Salahshour, S., Arica, N. (eds) Progress in Intelligent Decision Science. IDS 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1301. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66501-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66501-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66500-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66501-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)