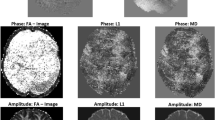
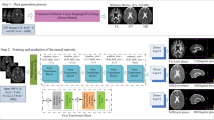
Abstract
In clinical settings, diffusion MRI can be used for extracting biomarkers such as fractional anisotropy or for revealing brain connectivity based on fiber tractography. Both are impacted by the free-water partial volume effect that arises at the border of cerebrospinal fluid or in presence of vasogenic edema. Hence, in order to robustly track white matter fibers close to cerebrospinal fluid and in presence of edema, or to extract consistent biomarkers in these cases, the diffusion MRI signal needs to be corrected for partial volume effects. We present a novel method that reproducibly infers plausible free-water volumes across different diffusion MRI acquisition schemes. Based on simulated data closely following the individual characteristics of each measurement, a neural network is trained on synthetic groundtruth data. According to our evaluation, this methodology produces more consistent and more plausible results than previous approaches.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, B., Klose, U.: Cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid volume measurements in the human brain at 3t with epi. Magn. Reson. Med. 61(4), 834–841 (2009)
Collier, Q., Veraart, J., Jeurissen, B., Vanhevel, F., Pullens, P., Parizel, P.M., den Dekker, A.J., Sijbers, J.: Diffusion kurtosis imaging with free water elimination: a bayesian estimation approach. Magn. Reson. Med. 80(2), 802–813 (2018)
Dhollander, T., Raffelt, D., Connelly, A.: Unsupervised 3-tissue response function estimation from single-shell or multi-shell diffusion mr data without a co-registered t1 image (2016)
Garyfallidis, Eleftherios., Brett, Matthew., et al.: Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Frontiers Neuroinform. 8, 8 (2014)
Ernst, T., Kreis, R., Ross, B.: Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. i. compartments and water. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 102(1), 1 – 8 (1993)
Essen, D.C.V., Smith, S.M., Barch, D.M., Behrens, T.E., Yacoub, E., Ugurbil, K.: The wu-minn human connectome project: an overview. NeuroImage 80, 62 – 79 (2013). Mapping the Connectome
Fick, R.H., Wassermann, D., Deriche, R.: Mipy: An open-source framework to improve reproducibility in brain microstructure imaging. In: OHBM 2018—Human Brain Mapping, pp. 1–4. Singapore, Singapore (2018)
Hoy, A.R., Koay, C.G., Kecskemeti, S.R., Alexander, A.L.: Optimization of a free water elimination two-compartment model for diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage 103, 323–333 (2014)
Jeurissen, B., Tournier, J.D., Dhollander, T., Connelly, A., Sijbers, J.: Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion mri data. NeuroImage 103, 411–426 (2014)
Molina-Romero, M., Wiestler, B., Gómez, P., Menzel, M.I., Menze, B.H.: Deep learning with synthetic diffusion MRI data for free-water elimination in glioblastoma cases. MICCAI (2018)
Pasternak, O., Sochen, N., Gur, Y., Intrator, N., Assaf, Y.: Free water elimination and mapping from diffusion MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 62(3), 717–730 (2009)
Scherrer, B., Schwartzman, A., Taquet, M., Sahin, M., Prabhu, S.P., Warfield, S.K.: Characterizing brain tissue by assessment of the distribution of anisotropic microstructural environments in diffusion-compartment imaging (diamond). Magn. Reson. Med. 76(3), 963–977 (2016)
Schultz, T.: Learning a reliable estimate of the number of fiber directions in diffusion MRI. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI, pp. 493–500 (2012)
Smith, S.M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M.W., Beckmann, C.F., Behrens, T.E., Johansen-Berg, H., Bannister, P.R., Luca, M.D., Drobnjak, I., Flitney, D.E., Niazy, R.K., Saunders, J., Vickers, J., Zhang, Y., Stefano, N.D., Brady, J.M., Matthews, P.M.: Advances in functional and structural mr image analysis and implementation as fsl. NeuroImage 23, S208 – S219 (2004). Mathematics in Brain Imaging
Tournier, J.D., Calamante, F., Connelly, A.: Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion mri: Non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. NeuroImage 35(4), 1459–1472 (2007)
Zhang, Y., Brady, M., Smith, S.: Segmentation of brain mr images through a hidden markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20(1), 45–57 (2001)
Acknowledgments
Data were provided in part by the Human Connectome Project, WU-Minn Consortium (Principal Investigators: David Van Essen and Kamil Ugurbil; 1U54MH091657) funded by the 16 NIH Institutes and Centers that support the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research; and by the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience at Washington University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Weninger, L., Koppers, S., Na, CH., Juetten, K., Merhof, D. (2020). Free-Water Correction in Diffusion MRI: A Reliable and Robust Learning Approach. In: Bonet-Carne, E., Hutter, J., Palombo, M., Pizzolato, M., Sepehrband, F., Zhang, F. (eds) Computational Diffusion MRI. Mathematics and Visualization. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52893-5_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52893-5_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-52892-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-52893-5
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)