Abstract
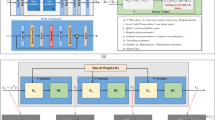
Magnetic-resonance based quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) requires the removal of background magnetic perturbation fields for precise quantification of tissue magnetism within a volume of interest (VOI). Conventional state-of-the-art QSM background removal methods suffer from several limitations in accuracy and performance. To overcome these limitations, a 3D gated convolutional neural network was trained to infer whole brain local tissue magnetic perturbation fields, using total field perturbation measurements and brain region masks as the inputs. The training data for this network are generated from physics simulations seeded from 200 QSM datasets and a set of random background susceptibility distributions. The performance of this neural network was evaluated relative to established background removal methods using 100 in-silico gold standard datasets and clinical susceptibility-weighted imaging datasets. Quantitative and qualitative assessment of the network performance demonstrated the benefits of the trained neural network.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y., Liu, T.: Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM): decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magn. Reson. Med. 73(1), 82–101 (2015)
Schweser, F., Deistung, A., Lehr, B.W., Reichenbach, J.R.: Differentiation between diamagnetic and paramagnetic cerebral lesions based on magnetic susceptibility mapping. Med. Phys. 37(10), 5165–5178 (2010)
Sun, H., Wilman, A.H.: Background field removal using spherical mean value filtering and Tikhonov regularization. Magn. Reson. Med. 71(3), 1151–1157 (2014)
Liu, T., et al.: A novel background field removal method for MRI using projection onto dipole fields. NMR Biomed. 24(9), 1129–1136 (2011)
Zhou, D., Liu, T., Spincemaille, P., Wang, Y.: Background field removal by solving the Laplacian boundary value problem. NMR Biomed. 27(3), 312–319 (2014)
Ashburner, J., Friston, K.J.: Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26(3), 839–851 (2005)
Liu, J., Nencka, A.S., Muftuler, L.T., Swearingen, B., Karr, R., Koch, K.M.: Quantitative susceptibility inversion through parcellated multiresolution neural networks and k-space substitution. arXiv:1903.04961 (2019)
Salomir, R., de Senneville, B.D., Moonen, C.T.: A fast calculation method for magnetic field inhomogeneity due to an arbitrary distribution of bulk susceptibility. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. Educ. J. 19(1), 26–34 (2003)
Marques, J.P., Bowtell, R.: Application of a Fourier-based method for rapid calculation of field inhomogeneity due to spatial variation of magnetic susceptibility. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B 25(1), 65–78 (2005)
Yu, J., Lin, Z., Yang, J., Shen, X., Lu, X., Huang, T.S.: Free-form image in painting with gated convolution. arXiv:1806.03589 (2018)
Liu, J., Koch, K.M.: Non-locally encoder-decoder convolutional network for whole brain QSM inversion. arXiv:1904.05493 (2019)
Wang, Y.: MEDI Toolbox (2019). http://weill.cornell.edu/mri/pages/qsm.html
Bollmann, S., et al.: SHARQnet-Sophisticated harmonic artifact reduction in quantitative susceptibility mapping using a deep convolutional neural network. Zeitschrift für Medizinische Physik 29(2), 139–149 (2019)
Koch, K.M., Papademetris, X., Rothman, D.L., de Graaf, R.: Rapid calculations of susceptibility-induced magnetostatic field perturbations for in vivo magnetic resonance. Phys. Med. Biol. 51(24), 6381–6402 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, J., Koch, K.M. (2019). Deep Gated Convolutional Neural Network for QSM Background Field Removal. In: Shen, D., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2019. MICCAI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11766. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-32247-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-32248-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)