Abstract
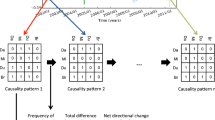
The inference of network representations that capture causal relations in time series is a challenging problem. In this paper, we explore the use of information theoretic tools for characterising information flow between time series, and how to infer networks representing time series data. We explore two different approaches. The first uses transfer entropy as a means of characterising information flow and measures network similarity using Jensen-Shannon divergence. The second uses time series correlation and used Kullback-Leibler divergence to compare the distribution of correlations across edges for different networks. We explore how both weighted and unweighted representations derived from these two characterisations perform on real-world time series data. Experiments on time series data for the New York Stock Exchange show that transfer entropy results in better localisation of temporal anomalies in graph time series. Moreover, the method leads to embeddings of network time series that better preserve their temporal order.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Razak, F., Jensen, H.J.: Quantifying ‘causality’ in complex systems: understanding transfer entropy. PLoS ONE 9(6), 1–14 (2014)
Bai, L., Hancock, E.R., Ren, P.: Jensen-Shannon graph kernel using information functionals. In: Proceedings - International Conference on Pattern Recognition ICPR, pp. 2877–2880 (2012)
Bai, L., Hancock, E.R.: Graph kernels from the jensen-shannon divergence. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 47(1–2), 60–69 (2013)
Caglar, I., Hancock, E.R.: Graph time series analysis using transfer entropy. In: Bai, X., Hancock, E.R., Ho, T.K., Wilson, R.C., Biggio, B., Robles-Kelly, A. (eds.) S+SSPR 2018. LNCS, vol. 11004, pp. 217–226. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97785-0_21
Cover, T.M., Thomas, J.A.: Entropy, Relative Entropy, and Mutual Information. In: Elements of Information Theory, pp. 13–55. Wiley, New York (2005)
Frenzel, S., Pompe, B.: Partial mutual information for coupling analysis of multivariate time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(20), 1–4 (2007)
Granger, C.W.J.: Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37(3), 424 (1969)
Han, L., Escolano, F., Hancock, E.R., Wilson, R.C.: Graph characterizations from von Neumann entropy. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 33(15), 1958–1967 (2012)
Hlavackovaschindler, K., Palus, M., Vejmelka, M., Bhattacharya, J.: @AssociationMeasure@Causality detection based on information-theoretic approaches in time series analysis. Phys. Rep. 441(1), 1–46 (2007)
Kraskov, A., Stögbauer, H., Grassberger, P.: Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E - Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 69, 66138 (2004)
Kwon, O., Yang, J.S.: Information flow between stock indices. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 82(6), 68003 (2008)
Lee, J., Nemati, S., Silva, I., Edwards, B.A., Butler, J.P., Malhotra, A.: Transfer entropy estimation and directional coupling change detection in biomedical time series. Biomed. Eng. Online 11(1), 19 (2012)
Passerini, F., Severini, S.: The von Neumann entropy of networks. In: Developments in Intelligent Agent Technologies and Multi-Agent Systems, pp. 66–76, December 2008
Ross, B.C.: Mutual information between discrete and continuous data sets. PLoS ONE 9(2), 1–5 (2014)
Schreiber, T.: Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 461–464 (2000)
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(3), 379–423 (1948)
Silva, F.N., et al.: Modular Dynamics of Financial Market Networks. arXiv e-prints arXiv:1501.05040, January 2015
Ye, C., Torsello, A., Wilson, R.C., Hancock, E.R.: Thermodynamics of time evolving networks. In: Liu, C.-L., Luo, B., Kropatsch, W.G., Cheng, J. (eds.) GbRPR 2015. LNCS, vol. 9069, pp. 315–324. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-18224-7_31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Caglar, I., Hancock, E.R. (2019). Network Time Series Analysis Using Transfer Entropy. In: Conte, D., Ramel, JY., Foggia, P. (eds) Graph-Based Representations in Pattern Recognition. GbRPR 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11510. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20081-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20081-7_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-20080-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-20081-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)