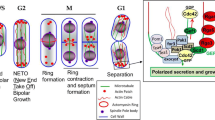
Abstract
Filamentous fungi are highly polarized eukaryotic cells, which continuously elongate their hyphae at the tips. The extension of hyphal tips requires the continuous enlargement of the cell membrane and the extension of the cell wall. Both are achieved through massive vesicle fusion at the tip. Vesicle transport as well as all other dynamic processes related to polar growth, such as organelle duplication and distribution, or the transport of RNA, proteins, or lipids, requires cytoskeletal elements. The establishment and maintenance of cell polarity in fungi—as in higher eukaryotes—requires the interplay between the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons and landmark proteins at the cortex. Here we review recent findings unraveling the mechanism of polarized growth with special emphasis on the roles of the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons, polarity markers linking the two cytoskeletons.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abenza JF, Pantazopoulou A, Rodriguez JM, Galindo A, Penalva MA (2009) Long-distance movement of Aspergillus nidulans early endosomes on microtubule tracks. Traffic 10:57–75
Adams AE, Johnson DI, Longnecker RM, Sloat BF, Pringle JR (1990) CDC42 and CDC43, two additional genes involved in budding and the establishment of cell polarity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 111:131–142
Al-Bassam J, Chang F (2011) Regulation of microtubule dynamics by TOG-domain proteins XMAP215/Dis1 and CLASP. Trends Cell Biol 21:604–614
Al-Bassam J, Larsen NA, Hyman AA, Harrison SC (2007) Crystal structure of a TOG domain: conserved features of XMAP215/Dis1-family TOG domains and implications for tubulin binding. Structure 15:355–362
Al-Bassam J, Kim H, Flor-Parra I, Lal N, Velji H, Chang F (2012) Fission yeast Alp14 is a dose-dependent plus end-tracking microtubule polymerase. Mol Biol Cell 23:2878–2890
Alvarez-Tabares I, Perez-Martin J (2010) Septins from the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis are required for proper morphogenesis but dispensable for virulence. PLoS One 5:e12933
Amberg DC (1998) Three-dimensional imaging of the yeast actin cytoskeleton through the budding cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell 9:3259–3262
Araujo-Bazan L, Penalva MA, Espeso EA (2008) Preferential localization of the endocytic internalization machinery to hyphal tips underlies polarization of the actin cytoskeleton in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 67:891–905
Asakura T, Sasaki T, Nagano F, Satoh A, Obaishi H, Nishioka H, Imamura H, Hotta K, Tanaka K, Nakanishi H, Takai Y (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel actin filament-binding protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Oncogene 16:121–130
Bartnicki-García S, Hergert F, Gierz G (1989) Computer simulation of fungal morphogenesis and the mathematical basis for hyphal tip growth. Protoplasma 153:46–57
Bartnicki-Garcia S, Bartnicki DD, Gierz G, Lopez-Franco R, Bracker CE (1995) Evidence that Spitzenkörper behavior determines the shape of a fungal hypha: a test of the hyphoid model. Exp Mycol 19:153–159
Baumann S, Pohlmann T, Jungbluth M, Brachmann A, Feldbrugge M (2012) Kinesin-3 and dynein mediate microtubule-dependent co-transport of mRNPs and endosomes. J Cell Sci 125:2740–2752
Baumann S, Konig J, Koepke J, Feldbrugge M (2014) Endosomal transport of septin mRNA and protein indicates local translation on endosomes and is required for correct septin filamentation. EMBO Rep 15:94–102
Berepiki A, Read ND (2013) Septins are important for cell polarity, septation and asexual spore formation in Neurospora crassa and show different patterns of localisation at germ tube tips. PLoS One 8:e63843
Berepiki A, Lichius A, Shoji JY, Tilsner J, Read ND (2010) F-actin dynamics in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot Cell 9:547–557
Berepiki A, Lichius A, Read ND (2011) Actin organization and dynamics in filamentous fungi. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:876–887
Bergs A, Ishitsuka Y, Evangelinos M, Nienhaus GU, Takeshita N (2016) Dynamics of actin cables in polarized growth of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Front Microbiol 7:682
Bernards A, Settleman J (2004) GAP control: regulating the regulators of small GTPases. Trends Cell Biol 14:377–385
Bertin A, McMurray MA, Pierson J, Thai L, McDonald KL, Zehr EA, Garcia G 3rd, Peters P, Thorner J, Nogales E (2012) Three-dimensional ultrastructure of the septin filament network in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 23:423–432
Bicho CC, Kelly DA, Snaith HA, Goryachev AB, Sawin KE (2010) A catalytic role for Mod5 in the formation of the Tea1 cell polarity landmark. Curr Biol 20:1752–1757
Bishop AL, Hall A (2000) Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem J 348(Pt 2):241–255
Boyce KJ, Chang H, D’Souza CA, Kronstad JW (2005) An Ustilago maydis septin is required for filamentous growth in culture and for full symptom development on maize. Eukaryot Cell 4:2044–2056
Brent Heath I, Bonham M, Akram A, Gupta GD (2003) The interrelationships of actin and hyphal tip growth in the ascomycete Geotrichum candidum. Fungal Genet Biol 38:85–97
Bridges AA, Gladfelter AS (2014) Fungal pathogens are platforms for discovering novel and conserved septin properties. Curr Opin Microbiol 20:42–48
Brouhard GJ, Stear JH, Noetzel TL, Al-Bassam J, Kinoshita K, Harrison SC, Howard J, Hyman AA (2008) XMAP215 is a processive microtubule polymerase. Cell 132:79–88
Browning H, Hayles J, Mata J, Aveline L, Nurse P, McIntosh JR (2000) Tea2p is a kinesin-like protein required to generate polarized growth in fission yeast. J Cell Biol 151:15–28
Browning H, Hackney DD, Nurse P (2003) Targeted movement of cell end factors in fission yeast. Nat Cell Biol 5:812–818
Chang F, Peter M (2003) Yeasts make their mark. Nat Cell Biol 5:294–299
Dagdas YF, Yoshino K, Dagdas G, Ryder LS, Bielska E, Steinberg G, Talbot NJ (2012) Septin-mediated plant cell invasion by the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae. Science 336:1590–1595
Das M, Drake T, Wiley DJ, Buchwald P, Vavylonis D, Verde F (2012) Oscillatory dynamics of Cdc42 GTPase in the control of polarized growth. Science 337:239–243
Delgado-Alvarez DL, Callejas-Negrete OA, Gomez N, Freitag M, Roberson RW, Smith LG, Mourino-Perez RR (2010) Visualization of F-actin localization and dynamics with live cell markers in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 47:573–586
Delgado-Alvarez DL, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Seiler S, Mourino-Perez RR (2014) Septum development in Neurospora crassa: the septal actomyosin tangle. PLoS One 9:e96744
DeMay BS, Meseroll RA, Occhipinti P, Gladfelter AS (2009) Regulation of distinct septin rings in a single cell by Elm1p and Gin4p kinases. Mol Biol Cell 20:2311–2326
Dodgson J, Chessel A, Yamamoto M, Vaggi F, Cox S, Rosten E, Albrecht D, Geymonat M, Csikasz-Nagy A, Sato M, Carazo-Salas RE (2013) Spatial segregation of polarity factors into distinct cortical clusters is required for cell polarity control. Nat Commun 4:1834
Dominguez R, Holmes KC (2011) Actin structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys 40:169–186
Drummond DR, Cross RA (2000) Dynamics of interphase microtubules in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Biol 10:766–775
Efimov VP, Zhang J, Xiang X (2006) CLIP-170 homologue and NUDE play overlapping roles in NUDF localization in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 17:2021–2034
Egan MJ, McClintock MA, Reck-Peterson SL (2012a) Microtubule-based transport in filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:637–645
Egan MJ, Tan K, Reck-Peterson SL (2012b) Lis1 is an initiation factor for dynein-driven organelle transport. J Cell Biol 197:971–982
Enke C, Zekert N, Veith D, Schaaf C, Konzack S, Fischer R (2007) Aspergillus nidulans Dis1/XMAP215 protein AlpA localizes to spindle pole bodies and microtubule plus ends and contributes to growth directionality. Eukaryot Cell 6:555–562
Evangelista M, Pruyne D, Amberg DC, Boone C, Bretscher A (2002) Formins direct Arp2/3-independent actin filament assembly to polarize cell growth in yeast. Nat Cell Biol 4:260–269
Fajardo-Somera RA, Jöhnk B, Bayram O, Valerius O, Braus GH, Riquelme M (2015) Dissecting the function of the different chitin synthases in vegetative growth and sexual development in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 75:30–45
Feierbach B, Verde F, Chang F (2004) Regulation of a formin complex by the microtubule plus end protein tea1p. J Cell Biol 165:697–707
Fischer R, Zekert N, Takeshita N (2008) Polarized growth in fungi–interplay between the cytoskeleton, positional markers and membrane domains. Mol Microbiol 68:813–826
Garcia-Vidal C, Viasus D, Carratala J (2013) Pathogenesis of invasive fungal infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis 26:270–276
Gladfelter AS (2010) Guides to the final frontier of the cytoskeleton: septins in filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:720–726
Goehring NW, Grill SW (2013) Cell polarity: mechanochemical patterning. Trends Cell Biol 23:72–80
Grove SN, Bracker CE (1970) Protoplasmic organization of hyphal tips among fungi: vesicles and Spitzenkörper. J Bacteriol 104:989–1009
Gunning PW, Schevzov G, Kee AJ, Hardeman EC (2005) Tropomyosin isoforms: divining rods for actin cytoskeleton function. Trends Cell Biol 15:333–341
Haag C, Steuten B, Feldbrügge M (2015) Membrane-coupled mRNA trafficking in fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol 69:265–281
Harris SD (2001) Septum formation in Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:736–739
Harris SD (2006) Cell polarity in filamentous fungi: shaping the mold. Int Rev Cytol 251:41–77
Harris SD (2008) Branching of fungal hyphae: regulation, mechanisms and comparison with other branching systems. Mycologia 100:823–832
Harris SD, Momany M (2004) Polarity in filamentous fungi: moving beyond the yeast paradigm. Fungal Genet Biol 41:391–400
Harris SD, Hofmann AF, Tedford HW, Lee MP (1999) Identification and characterization of genes required for hyphal morphogenesis in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 151:1015–1025
Harris SD, Read ND, Roberson RW, Shaw B, Seiler S, Plamann M, Momany M (2005) Polarisome meets spitzenkörper: microscopy, genetics, and genomics converge. Eukaryot Cell 4:225–229
Helfer H, Gladfelter AS (2006) AgSwe1p regulates mitosis in response to morphogenesis and nutrients in multinucleated Ashbya gossypii cells. Mol Biol Cell 17:4494–4512
Hernandez-Rodriguez Y, Masuo S, Johnson D, Orlando R, Smith A, Couto-Rodriguez M, Momany M (2014) Distinct septin heteropolymers co-exist during multicellular development in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS One 9:e92819
Hervas-Aguilar A, Penalva MA (2010) Endocytic machinery protein SlaB is dispensable for polarity establishment but necessary for polarity maintenance in hyphal tip cells of Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot Cell 9:1504–1518
Higashitsuji Y, Herrero S, Takeshita N, Fischer R (2009) The cell end marker protein TeaC is involved in growth directionality and septation in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot Cell 8:957–967
Higuchi Y, Ashwin P, Roger Y, Steinberg G (2014) Early endosome motility spatially organizes polysome distribution. J Cell Biol 204:343–357
Hill TW, Jackson-Hayes L, Wang X, Hoge BL (2015) A mutation in the converter subdomain of Aspergillus nidulans MyoB blocks constriction of the actomyosin ring in cytokinesis. Fungal Genet Biol 75:72–83
Horio T, Oakley BR (2005) The role of microtubules in rapid hyphal tip growth of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 16:918–926
Ishitsuka Y, Savage N, Li Y, Bergs A, Grün N, Kohler D, Donnelly R, Nienhaus GU, Fischer R, Takeshita N (2015) Super-resolution microscopy reveals a dynamic picture of cell polarity maintenance during directional growth. Sci Adv 1:e1500947
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:247–269
Janmey PA (1994) Phosphoinositides and calcium as regulators of cellular actin assembly and disassembly. Annu Rev Physiol 56:169–191
Johnson JM, Jin M, Lew DJ (2011) Symmetry breaking and the establishment of cell polarity in budding yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21:740–746
Kaksonen M, Toret CP, Drubin DG (2006) Harnessing actin dynamics for clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:404–414
Kim HS, Czymmek KJ, Patel A, Modla S, Nohe A, Duncan R, Gilroy S, Kang S (2012) Expression of the Cameleon calcium biosensor in fungi reveals distinct Ca(2+) signatures associated with polarized growth, development, and pathogenesis. Fungal Genet Biol 49:589–601
Kohli M, Galati V, Boudier K, Roberson RW, Philippsen P (2008) Growth-speed-correlated localization of exocyst and polarisome components in growth zones of Ashbya gossypii hyphal tips. J Cell Sci 121:3878–3889
Konig J, Baumann S, Koepke J, Pohlmann T, Zarnack K, Feldbrugge M (2009) The fungal RNA-binding protein Rrm4 mediates long-distance transport of ubi1 and rho3 mRNAs. EMBO J 28:1855–1866
Konzack S, Rischitor PE, Enke C, Fischer R (2005) The role of the kinesin motor KipA in microtubule organization and polarized growth of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 16:497–506
Kozubowski L, Heitman J (2010) Septins enforce morphogenetic events during sexual reproduction and contribute to virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mol Microbiol 75:658–675
Kroeger J, Geitmann A (2012) The pollen tube paradigm revisited. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:618–624
Lee SC, Schmidtke SN, Dangott LJ, Shaw BD (2008) Aspergillus nidulans ArfB plays a role in endocytosis and polarized growth. Eukaryot Cell 7:1278–1288
Lehmler C, Steinberg G, Snetselaar KM, Schliwa M, Kahmann R, Bolker M (1997) Identification of a motor protein required for filamentous growth in Ustilago maydis. EMBO J 16:3464–3473
Li R, Gundersen GG (2008) Beyond polymer polarity: how the cytoskeleton builds a polarized cell. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:860–873
Lichius A, Goryachev AB, Fricker MD, Obara B, Castro-Longoria E, Read ND (2014) CDC-42 and RAC-1 regulate opposite chemotropisms in Neurospora crassa. J Cell Sci 127:1953–1965
Lindsey R, Momany M (2006) Septin localization across kingdoms: three themes with variations. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:559–565
Lindsey R, Ha Y, Momany M (2010) A septin from the filamentous fungus A. nidulans induces atypical pseudohyphae in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. PLoS One 5:e9858
Lopez-Franco R, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Bracker CE (1994) Pulsed growth of fungal hyphal tips. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:12228–12232
Mahlert M, Leveleki L, Hlubek A, Sandrock B, Bolker M (2006) Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate hyphal growth and cytokinesis in the dimorphic fungus Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 59:567–578
Manck R, Ishitsuka Y, Herrero S, Takeshita N, Nienhaus GU, Fischer R (2015) Genetic evidence for a microtubule-capture mechanism during polarised growth of Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Sci 128:3569–3582
Markina-Inarrairaegui A, Pantazopoulou A, Espeso EA, Penalva MA (2013) The Aspergillus nidulans peripheral ER: disorganization by ER stress and persistence during mitosis. PLoS One 8:e67154
Martin SG, Chang F (2003) Cell polarity: a new mod(e) of anchoring. Curr Biol 13:R711–R713
Mata J, Nurse P (1997) tea1 and the microtubular cytoskeleton are important for generating global spatial order within the fission yeast cell. Cell 89:939–949
Meyer SL, Kaminskyj SG, Heath IB (1988) Nuclear migration in a nud mutant of Aspergillus nidulans is inhibited in the presence of a quantitatively normal population of cytoplasmic microtubules. J Cell Biol 106:773–778
Michelot A, Drubin DG (2011) Building distinct actin filament networks in a common cytoplasm. Curr Biol 21:R560–R569
Miller PJ, Johnson DI (1994) Cdc42p GTPase is involved in controlling polarized cell growth in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol 14:1075–1083
Momany M, Hamer JE (1997) Relationship of actin, microtubules, and crosswall synthesis during septation in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 38:373–384
Momany M, Westfall PJ, Abramowsky G (1999) Aspergillus nidulans swo mutants show defects in polarity establishment, polarity maintenance and hyphal morphogenesis. Genetics 151:557–567
Monshausen GB, Messerli MA, Gilroy S (2008) Imaging of the Yellow Cameleon 3.6 indicator reveals that elevations in cytosolic Ca2+ follow oscillating increases in growth in root hairs of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:1690–1698
Montegi F, Arai R, Mabuchi I (2001) Identification of two type V myosins in fission yeast, one of which functions in polarized cell growth and moves rapidly in the cell. Mol Biol Cell 12:1367–1380
Morris NR, Enos AP (1992) Mitotic gold in a mold: Aspergillus genetics and the biology of mitosis. Trends Genet 8:32–37
Morris NR, Lai MH, Oakley CE (1979) Identification of a gene for alpha-tubulin in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 16:437–442
Mostowy S, Cossart P (2012) Septins: the fourth component of the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:183–194
Mulvihill DP, Edwards SR, Hyams JS (2006) A critical role for the type V myosin, Myo52, in septum deposition and cell fission during cytokinesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 63:149–161
Oakley BR (2004) Tubulins in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 41:420–427
Oakley BR, Morris NR (1980) Nuclear movement is beta--tubulin-dependent in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 19:255–262
Oakley CE, Oakley BR (1989) Identification of gamma-tubulin, a new member of the tubulin superfamily encoded by mipA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Nature 338:662–664
Oakley BR, Oakley CE, Yoon Y, Jung MK (1990) Gamma-tubulin is a component of the spindle pole body that is essential for microtubule function in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 61:1289–1301
Oh Y, Bi E (2011) Septin structure and function in yeast and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 21:141–148
Orr E, Rosenberger RF (1976) Initial characterization of Aspergillus nidulans mutants blocked in the nuclear replication cycle. J Bacteriol 126:895–902
Osmani SA, Mirabito PM (2004) The early impact of genetics on our understanding of cell cycle regulation in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 41:401–410
Pantazopoulou A, Pinar M, Xiang X, Penalva MA (2014) Maturation of late Golgi cisternae into RabE(RAB11) exocytic post-Golgi carriers visualized in vivo. Mol Biol Cell 25:2428–2443
Pearson CL, Xu K, Sharpless KE, Harris SD (2004) MesA, a novel fungal protein required for the stabilization of polarity axes in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 15:3658–3672
Pelham RJ Jr, Chang F (2001) Role of actin polymerization and actin cables in actin-patch movement in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nat Cell Biol 3:235–244
Penalva MA (2010) Endocytosis in filamentous fungi: Cinderella gets her reward. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:684–692
Pinar M, Pantazopoulou A, Arst HN Jr, Penalva MA (2013) Acute inactivation of the Aspergillus nidulans Golgi membrane fusion machinery: correlation of apical extension arrest and tip swelling with cisternal disorganization. Mol Microbiol 89:228–248
Punt PJ, Levasseur A, Visser H, Wery J, Record E (2011) Fungal protein production: design and production of chimeric proteins. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:57–69
Requena N, Alberti-Segui C, Winzenburg E, Horn C, Schliwa M, Philippsen P, Liese R, Fischer R (2001) Genetic evidence for a microtubule-destabilizing effect of conventional kinesin and analysis of its consequences for the control of nuclear distribution in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 42:121–132
Riedl J, Crevenna AH, Kessenbrock K, Yu JH, Neukirchen D, Bista M, Bradke F, Jenne D, Holak TA, Werb Z, Sixt M, Wedlich-Soldner R (2008) Lifeact: a versatile marker to visualize F-actin. Nat Methods 5:605–607
Riquelme M, Sanchez-Leon E (2014) The Spitzenkörper: a choreographer of fungal growth and morphogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 20:27–33
Riquelme M, Reynaga-Pena CG, Gierz G, Bartnicki-Garcia S (1998) What determines growth direction in fungal hyphae? Fungal Genet Biol 24:101–109
Riquelme M, Gierz G, Bartnicki-García S (2000) Dynein and dynactin deficiencies affect the formation and function of the Spitzenkörper and distort hyphal morphogenesis of Neurospora crassa. Microbiology 146:1743–1752
Riquelme M, Bartnicki-García S, González-Prieto JM, Sánchez-León E, Verdín-Ramos JA, Beltrán-Aguilar A, Freitag M (2007) Spitzenkörper localization and intracellular traffic of green fluorescent protein-labeled CHS-3 and CHS-6 chitin synthases in living hyphae of Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot Cell 6:1853–1864
Riquelme M, Yarden O, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Bowman B, Castro-Longoria E, Free SJ, Fleissner A, Freitag M, Lew RR, Mourino-Perez R, Plamann M, Rasmussen C, Richthammer C, Roberson RW, Sanchez-Leon E, Seiler S, Watters MK (2011) Architecture and development of the Neurospora crassa hypha – a model cell for polarized growth. Fungal Biol 115:446–474
Riquelme M, Bredeweg EL, Callejas-Negrete O, Roberson RW, Ludwig S, Beltran-Aguilar A, Seiler S, Novick P, Freitag M (2014) The Neurospora crassa exocyst complex tethers Spitzenkörper vesicles to the apical plasma membrane during polarized growth. Mol Biol Cell 25:1312–1326
Riquelme M, Aguirre J, Bartnicki-García S, Braus GH, Feldbrügge M, Fleig U, Hansberg W, Herrera-Estrella A, Kämper J, Kück U, Mouriño-Pérez RR, Takeshita N, Fischer R (2018) Fungal morphogenesis, from the polarized growth of hyphae to complex reproduction and infection structures. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 82(2)
Sahl SJ, Moerner WE (2013) Super-resolution fluorescence imaging with single molecules. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23:778–787
Sanchez-Leon E, Verdin J, Freitag M, Roberson RW, Bartnicki-Garcia S, Riquelme M (2011) Traffic of chitin synthase 1 (CHS-1) to the Spitzenkörper and developing septa in hyphae of Neurospora crassa: actin dependence and evidence of distinct microvesicle populations. Eukaryot Cell 10:683–695
Saunders DG, Dagdas YF, Talbot NJ (2010) Spatial uncoupling of mitosis and cytokinesis during appressorium-mediated plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell 22:2417–2428
Savage NS, Layton AT, Lew DJ (2012) Mechanistic mathematical model of polarity in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 23:1998–2013
Sawin KE, Tran PT (2006) Cytoplasmic microtubule organization in fission yeast. Yeast 23:1001–1014
Schmidt A, Hall A (2002) Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: turning on the switch. Genes Dev 16:1587–1609
Schneggenburger R, Neher E (2005) Presynaptic calcium and control of vesicle fusion. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:266–274
Schoch CL, Aist JR, Yoder OC, Gillian Turgeon B (2003) A complete inventory of fungal kinesins in representative filamentous ascomycetes. Fungal Genet Biol 39:1–15
Schultzhaus Z, Yan H, Shaw BD (2015) Aspergillus nidulans flippase DnfA is cargo of the endocytic collar and plays complementary roles in growth and phosphatidylserine asymmetry with another flippase, DnfB. Mol Microbiol 97:18–32
Schuster M, Treitschke S, Kilaru S, Molloy J, Harmer NJ, Steinberg G (2012) Myosin-5, kinesin-1 and myosin-17 cooperate in secretion of fungal chitin synthase. EMBO J 31:214–227
Seidel C, Zekert N, Fischer R (2012) The Aspergillus nidulans kinesin-3 tail is necessary and sufficient to recognize modified microtubules. PLoS One 7:e30976
Seiler S, Nargang FE, Steinberg G, Schliwa M (1997) Kinesin is essential for cell morphogenesis and polarized secretion in Neurospora crassa. EMBO J 16:3025–3034
Seiler S, Plamann M, Schliwa M (1999) Kinesin and dynein mutants provide novel insights into the roles of vesicle traffic during cell morphogenesis in Neurospora. Curr Biol 9:779–785
Shaw BD, Momany C, Momany M (2002) Aspergillus nidulans swoF encodes an N-myristoyl transferase. Eukaryot Cell 1:241–248
Shaw BD, Chung DW, Wang CL, Quintanilla LA, Upadhyay S (2011) A role for endocytic recycling in hyphal growth. Fungal Biol 115:541–546
Siegrist SE, Doe CQ (2007) Microtubule-induced cortical cell polarity. Genes Dev 21:483–496
Sinha I, Wang YM, Philp R, Li CR, Yap WH, Wang Y (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinases control septin phosphorylation in Candida albicans hyphal development. Dev Cell 13:421–432
Snaith HA, Sawin KE (2003) Fission yeast mod5p regulates polarized growth through anchoring of tea1p at cell tips. Nature 423:647–651
Steinberg G (2011) Motors in fungal morphogenesis: cooperation versus competition. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:660–667
Steinberg G (2014) Endocytosis and early endosome motility in filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol 20:10–18
Sudbery PE (2001) The germ tubes of Candida albicans hyphae and pseudohyphae show different patterns of septin ring localization. Mol Microbiol 41:19–31
Sudbery P (2011) Fluorescent proteins illuminate the structure and function of the hyphal tip apparatus. Fungal Genet Biol 48:849–857
Sutterlin C, Colanzi A (2010) The Golgi and the centrosome: building a functional partnership. J Cell Biol 188:621–628
Taheri-Talesh N, Horio T, Araujo-Bazan L, Dou X, Espeso EA, Penalva MA, Osmani SA, Oakley BR (2008) The tip growth apparatus of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 19:1439–1449
Taheri-Talesh N, Xiong Y, Oakley BR (2012) The functions of myosin II and myosin V homologs in tip growth and septation in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS One 7:e31218
Takeshita N (2016) Coordinated process of polarized growth in filamentous fungi. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80:1693–1699
Takeshita N (2018) Oscillatory fungal cell growth. Fungal Genet Biol 110:10–14
Takeshita N, Fischer R (2011) On the role of microtubules, cell end markers, and septal microtubule organizing centres on site selection for polar growth in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Biol 115:506–517
Takeshita N, Higashitsuji Y, Konzack S, Fischer R (2008) Apical sterol-rich membranes are essential for localizing cell end markers that determine growth directionality in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Biol Cell 19:339–351
Takeshita N, Mania D, Herrero de Vega S, Ishitsuka Y, Nienhaus GU, Podolski M, Howard J, Fischer R (2013) The cell end marker TeaA and the microtubule polymerase AlpA contribute to microtubule guidance at the hyphal tip cortex of Aspergillus nidulans for polarity maintenance. J Cell Sci 126:5400–5411
Takeshita N, Manck R, Grun N, de Vega SH, Fischer R (2014) Interdependence of the actin and the microtubule cytoskeleton during fungal growth. Curr Opin Microbiol 20:34–41
Takeshita N, Wernet V, Tsuizaki M, Grun N, Hoshi HO, Ohta A, Fischer R, Horiuchi H (2015) Transportation of Aspergillus nidulans class III and V chitin synthases to the hyphal tips depends on conventional kinesin. PLoS One 10:e0125937
Takeshita N, Evangelinos M, Zhou L, Serizawa T, Somera-Fajardo RA, Lu L, Takaya N, Nienhaus GU, Fischer R (2017) Pulses of Ca2+ coordinate actin assembly and exocytosis for stepwise cell extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(22):5701–5706
Tan K, Roberts AJ, Chonofsky M, Egan MJ, Reck-Peterson SL (2014) A microscopy-based screen employing multiplex genome sequencing identifies cargo-specific requirements for dynein velocity. Mol Biol Cell 25:669–678
Tatebe H, Nakano K, Maximo R, Shiozaki K (2008) Pom1 DYRK regulates localization of the Rga4 GAP to ensure bipolar activation of Cdc42 in fission yeast. Curr Biol 18:322–330
Torralba S, Raudaskoski M, Pedregosa AM, Laborda F (1998) Effect of cytochalasin A on apical growth, actin cytoskeleton organization and enzyme secretion in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 144(Pt 1):45–53
Trinci AP (1974) A study of the kinetics of hyphal extension and branch initiation of fungal mycelia. J Gen Microbiol 81:225–236
Veith D, Scherr N, Efimov VP, Fischer R (2005) Role of the spindle-pole-body protein ApsB and the cortex protein ApsA in microtubule organization and nuclear migration in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Sci 118:3705–3716
Virag A, Lee MP, Si H, Harris SD (2007) Regulation of hyphal morphogenesis by cdc42 and rac1 homologues in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 66:1579–1596
Walther A, Wendland J (2004) Apical localization of actin patches and vacuolar dynamics in Ashbya gossypii depend on the WASP homolog Wal1p. J Cell Sci 117:4947–4958
Wang S, Cao J, Liu X, Hu H, Shi J, Zhang S, Keller NP, Lu L (2012) Putative calcium channels CchA and MidA play the important roles in conidiation, hyphal polarity and cell wall components in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS One 7:e46564
Warenda AJ, Konopka JB (2002) Septin function in Candida albicans morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 13:2732–2746
Wedlich-Soldner R, Bolker M, Kahmann R, Steinberg G (2000) A putative endosomal t-SNARE links exo- and endocytosis in the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. EMBO J 19:1974–1986
Wedlich-Soldner R, Altschuler S, Wu L, Li R (2003) Spontaneous cell polarization through actomyosin-based delivery of the Cdc42 GTPase. Science 299:1231–1235
Westfall PJ, Momany M (2002) Aspergillus nidulans septin AspB plays pre- and postmitotic roles in septum, branch, and conidiophore development. Mol Biol Cell 13:110–118
Win TZ, Gachet Y, Mulvihill DP, May KM, Hyams JS (2001) Two type V myosins with non-overlapping functions in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: Myo52 is concerned with growth polarity and cytokinesis, Myo51 is a cmponent of the cytokinetic actin ring. J Cell Sci 114:69–79
Wollman R, Meyer T (2012) Coordinated oscillations in cortical actin and Ca2+ correlate with cycles of vesicle secretion. Nat Cell Biol 14:1261–1269
Wu CF, Lew DJ (2013) Beyond symmetry-breaking: competition and negative feedback in GTPase regulation. Trends Cell Biol 23:476–483
Xiang X, Fischer R (2004) Nuclear migration and positioning in filamentous fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 41:411–419
Xiong Y, Oakley BR (2009) In vivo analysis of the functions of gamma-tubulin-complex proteins. J Cell Sci 122:4218–4227
Yamashita RA, May GS (1998) Constitutive activation of endocytosis by mutation of myoA, the myosin I gene of Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 273:14644–14648
Zander S, Baumann S, Weidtkamp-Peters S, Feldbrügge M (2016) Endosomal assembly and transport of heteromeric septin complexes promote septin cytoskeleton formation. J Cell Sci 129:2778–2792
Zekert N, Fischer R (2009) The Aspergillus nidulans kinesin-3 UncA motor moves vesicles along a subpopulation of microtubules. Mol Biol Cell 20:673–684
Zhang J, Tan K, Wu X, Chen G, Sun J, Reck-Peterson SL, Hammer JA 3rd, Xiang X (2011) Aspergillus myosin-V supports polarized growth in the absence of microtubule-based transport. PLoS One 6:e28575
Zhang Y, Gao X, Manck R, Schmid M, Osmani AH, Osmani SA, Takeshita N, Fischer R (2017) Microtubule-organizing centers of Aspergillus nidulans are anchored at septa by a disordered protein. Mol Microbiol 106:285–303
Zhou L, Evangelinos M, Wernet V, Eckert AF, Ishitsuka Y, Fischer R, Nienhaus GU, Takeshita N (2018) Superresolution and pulse-chase imaging reveal the role of vesicle transport in polar growth of fungal cells. Sci Adv 4:e1701798
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Takeshita, N., Fischer, R. (2019). The Cytoskeleton and Polarity Markers During Polarized Growth of Filamentous Fungi. In: Hoffmeister, D., Gressler, M. (eds) Biology of the Fungal Cell. The Mycota, vol 8. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05448-9_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05448-9_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-05446-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-05448-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)