Abstract
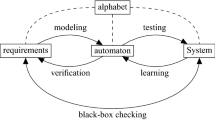
Behavioral interfaces describe the safe interactions with a component without exposing its internal variables and computation. As such, they can serve as documentation or formal contracts for black-box components in safety-critical systems. Learning-based generation of interaces relies on learning algorithms for inferring behavioral interfaces from observations, which are in turn checked for correctness by formal analysis techniques. Learning-based interface generation is therefore an interesting target when studying integration and combination of different formal analysis methods. In this paper, which accompanies an invited talk at the ISoLA 2018 track “A Broader View on Verification: From Static to Runtime and Back”, we introduce interpolation and symbolic search for validating inferred interfaces. We discuss briefly how interface validation may utilize information from runtime monitoring.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alur, R., Cerný, P., Madhusudan, P., Nam, W.: Synthesis of interface specifications for Java classes. In: ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages (POPL), pp. 98–109 (2005)
Angluin, D.: Learning regular sets from queries and counterexamples. Inf. Comput. 75(2), 87–106 (1987)
Armando, A., Mantovani, J., Platania, L.: Bounded model checking of software using SMT solvers instead of SAT solvers. In: Valmari, A. (ed.) SPIN 2006. LNCS, vol. 3925, pp. 146–162. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/11691617_9
Biere, A., Cimatti, A., Clarke, E., Zhu, Y.: Symbolic model checking without BDDs. In: Cleaveland, W.R. (ed.) TACAS 1999. LNCS, vol. 1579, pp. 193–207. Springer, Heidelberg (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49059-0_14
Burch, J.R., Clarke, E.M., McMillan, K.L., Dill, D.L., Hwang, L.-J.: Symbolic model checking: \(10^{20}\) states and beyond. Inf. Comput. 98(2), 142–170 (1992)
Caso, G.D., Braberman, V., Garbervetsky, D., Uchitel, S.: Enabledness-based program abstractions for behavior validation. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 22(3), 25:1–25:46 (2013)
Christ, J., Hoenicke, J., Nutz, A.: SMTInterpol: an interpolating SMT solver. In: Donaldson, A., Parker, D. (eds.) SPIN 2012. LNCS, vol. 7385, pp. 248–254. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31759-0_19
Clarke, E., Kroening, D., Lerda, F.: A tool for checking ANSI-C programs. In: Jensen, K., Podelski, A. (eds.) TACAS 2004. LNCS, vol. 2988, pp. 168–176. Springer, Heidelberg (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24730-2_15
Coudert, O., Berthet, C., Madre, J.C.: Verification of synchronous sequential machines based on symbolic execution. In: Sifakis, J. (ed.) CAV 1989. LNCS, vol. 407, pp. 365–373. Springer, Heidelberg (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-52148-8_30
Craig, W.: Three uses of Herbrand-Gentzen theorem in relating model theory and proof theory. J. Symb. Comput. 22, 269–285 (1955)
de Moura, L., Bjørner, N.: Z3: an efficient SMT solver. In: Ramakrishnan, C.R., Rehof, J. (eds.) TACAS 2008. LNCS, vol. 4963, pp. 337–340. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78800-3_24
Ge, Y., de Moura, L.: Complete instantiation for quantified formulas in satisfiabiliby modulo theories. In: Bouajjani, A., Maler, O. (eds.) CAV 2009. LNCS, vol. 5643, pp. 306–320. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02658-4_25
Giannakopoulou, D., Păsăreanu, C.S.: Interface generation and compositional verification in JavaPathfinder. In: Chechik, M., Wirsing, M. (eds.) FASE 2009. LNCS, vol. 5503, pp. 94–108. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00593-0_7
Giannakopoulou, D., Rakamarić, Z., Raman, V.: Symbolic learning of component interfaces. In: Miné, A., Schmidt, D. (eds.) SAS 2012. LNCS, vol. 7460, pp. 248–264. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33125-1_18
Godefroid, P., Klarlund, N., Sen, K.: Dart: directed automated random testing. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, PLDI 2005, pp. 213–223. ACM (2005)
Henzinger, T.A., Jhala, R., Majumdar, R.: Permissive interfaces. In: European Software Engineering Conference (ESEC) Held Jointly with ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE), pp. 31–40 (2005)
Howar, F., Giannakopoulou, D., Rakamaric, Z.: Hybrid learning: interface generation through static, dynamic, and symbolic analysis. In: ISSTA 2013, pp. 268–279 (2013)
Howar, F., Kahsai, T., Gurfinkel, A., Tinelli, C.: Trusting outsourced components in flight critical systems. In: AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace. AIAA (2015)
Howar, F., Steffen, B., Merten, M.: Automata learning with automated alphabet abstraction refinement. In: Jhala, R., Schmidt, D. (eds.) VMCAI 2011. LNCS, vol. 6538, pp. 263–277. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-18275-4_19
Isberner, M., Howar, F., Steffen, B.: The TTT algorithm: a redundancy-free approach to active automata learning. In: Bonakdarpour, B., Smolka, S.A. (eds.) RV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8734, pp. 307–322. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11164-3_26
Isberner, M., Howar, F., Steffen, B.: The open-source LearnLib - a framework for active automata learning. In: Kroening, D., Păsăreanu, C.S. (eds.) CAV 2015, Part I. LNCS, vol. 9206, pp. 487–495. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21690-4_32
Jaffar, J., Murali, V., Navas, J.A., Santosa, A.E.: TRACER: a symbolic execution tool for verification. In: Madhusudan, P., Seshia, S.A. (eds.) CAV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7358, pp. 758–766. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31424-7_61
Jaffar, J., Navas, J.A., Santosa, A.E.: Unbounded symbolic execution for program verification. In: Khurshid, S., Sen, K. (eds.) RV 2011. LNCS, vol. 7186, pp. 396–411. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-29860-8_32
Jaffar, J., Santosa, A.E., Voicu, R.: An interpolation method for CLP traversal. In: Gent, I.P. (ed.) CP 2009. LNCS, vol. 5732, pp. 454–469. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04244-7_37
Luckow, K., et al.: JDart: a dynamic symbolic analysis framework. In: Chechik, M., Raskin, J.-F. (eds.) TACAS 2016. LNCS, vol. 9636, pp. 442–459. Springer, Heidelberg (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49674-9_26
McMillan, K.L.: Applying SAT methods in unbounded symbolic model checking. In: Brinksma, E., Larsen, K.G. (eds.) CAV 2002. LNCS, vol. 2404, pp. 250–264. Springer, Heidelberg (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45657-0_19
McMillan, K.L.: Lazy annotation for program testing and verification. In: Touili, T., Cook, B., Jackson, P. (eds.) CAV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6174, pp. 104–118. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14295-6_10
Mues, M., Howar, F., Luckow, K.S., Kahsai, T., Rakamaric, Z.: Releasing the PSYCO: using symbolic search in interface generation for Java. ACM SIGSOFT Softw. Eng. Notes 41(6), 1–5 (2016)
Singh, R., Giannakopoulou, D., Păsăreanu, C.: Learning component interfaces with may and must abstractions. In: Touili, T., Cook, B., Jackson, P. (eds.) CAV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6174, pp. 527–542. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14295-6_45
Wintersteiger, C.M., Hamadi, Y., De Moura, L.: Efficiently solving quantified bit-vector formulas. Form. Methods Syst. Des. 42(1), 3–23 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Howar, F., Giannakopoulou, D., Mues, M., Navas, J.A. (2018). Generating Component Interfaces by Integrating Static and Symbolic Analysis, Learning, and Runtime Monitoring. In: Margaria, T., Steffen, B. (eds) Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, Verification and Validation. Verification. ISoLA 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11245. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03421-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03421-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-03420-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-03421-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)